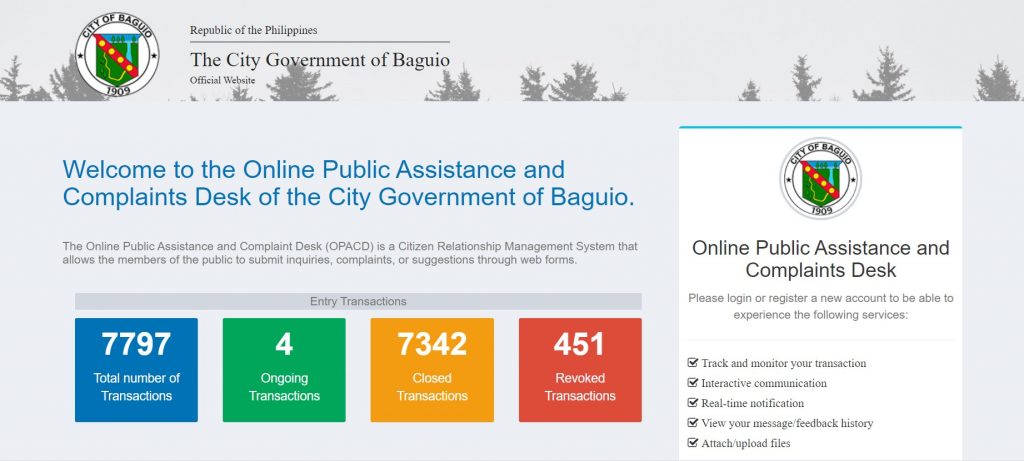
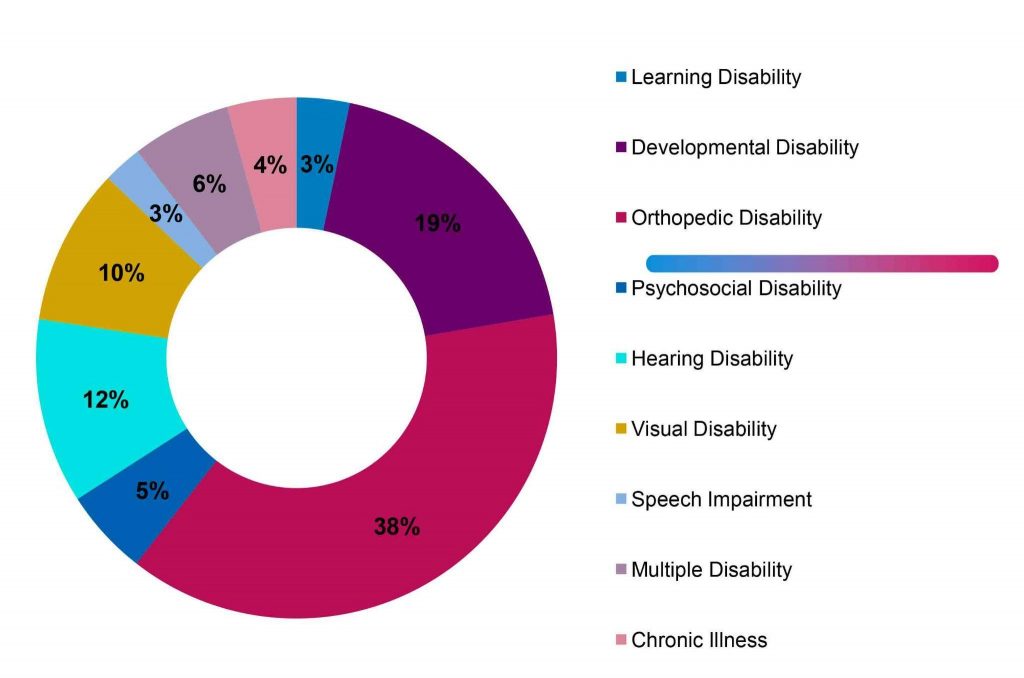
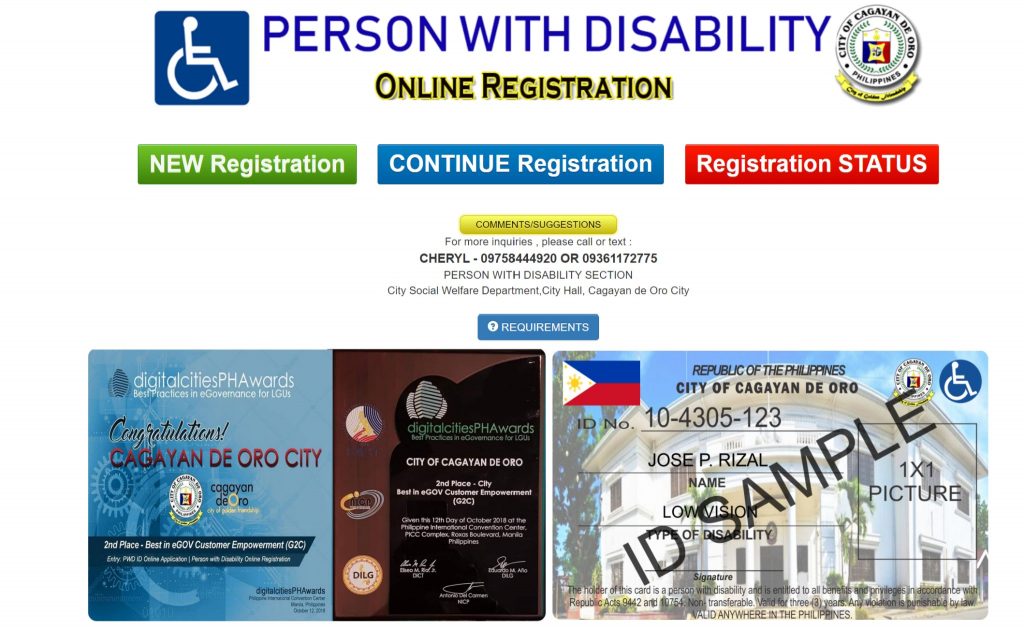
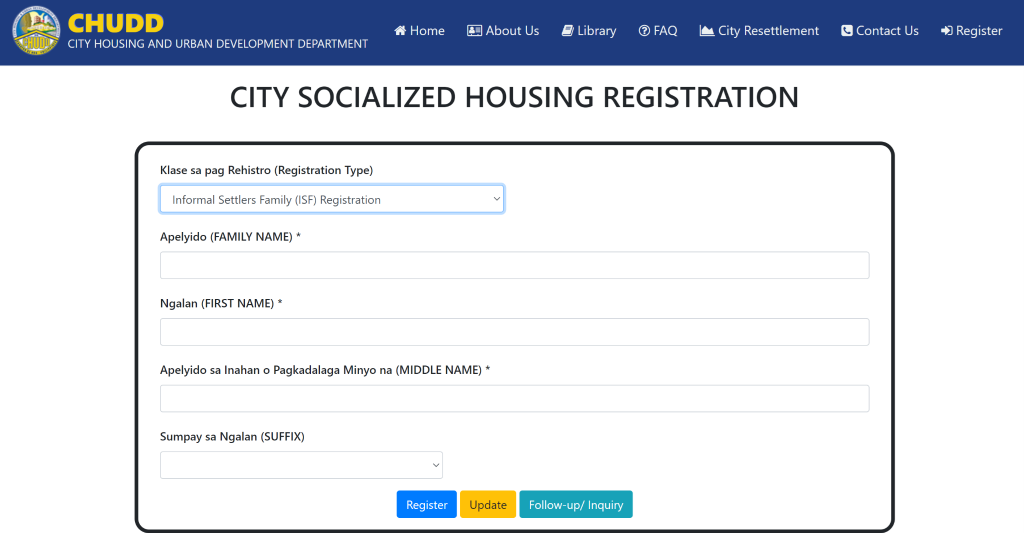
Overview
MyCareersFuture is a job search portal developed by Workforce Singapore, in partnership with the Government Technology Agency, which provides Singapore citizens and permanent residents with a fast and smart job search service. The portal matches jobseekers to relevant jobs based on their skills and competencies and highlights jobs eligible for government support through WSG’s Adapt and Grow Initiative. It provides career-related content through Seek Career Advice, including career insights and guidance to facilitate career planning. MyCareersFuture features the latest job-to-skills matching technology, which recommends adjacent jobs based on the jobseeker’s current skills and filters jobs eligible for government support. It is a comprehensive, technology-driven, and user-centric portal that serves the talent-related needs of job seekers and employers.
Challenge
The main productivity challenge MyCareersFuture addresses is the need to match job seekers with job opportunities curated by the National Jobs Council (NJC) in response to the COVID-19 outbreak in Singapore. The NJC has curated 92,000 new job opportunities, of which about half were significantly funded by the government, and private sector employers offered the other half. These job opportunities and the SGUnited Traineeships opportunities are hosted on MyCareersFuture.sg (MCF), which is an online job portal. The portal serves as a platform for job seekers to access these opportunities and apply for jobs in different industries.
The challenge lies in helping job seekers navigate the various available job opportunities, which may be unfamiliar or not what they are looking for. The government has therefore been ramping up efforts to implement SGUnited Traineeships, SGUnited Mid-Career Pathways, and SGUnited Skills training programs to upskill and prepare workers for economic recovery. In addition, Workforce Singapore (WSG) has been organizing events such as walk-in interviews and Career Workshops and deploying SGUnited Jobs and Skills Info Kiosks to promote and raise awareness of the various schemes under the SGUnited Jobs and Skills Package. The aim is to help job seekers better understand the opportunities available and how they can be accessed, thereby improving their chances of securing employment and contributing to the economy’s productivity.
Solution
Singapore MyCareersFuture (MCF) addresses the challenge of job search and career planning by providing a platform that matches job seekers’ skills with available job opportunities. The platform offers several innovative features that make it stand out:
- Use of machine learning. The skills displayed on MCF are identified using machine learning technology, which allows for a more accurate and personalized job match.
- Skills matching. The job fit scores are based on comparing the user’s skills and the skills required for the job role they are interested in. This gives job seekers a clear understanding of their fit for the job and areas where they need to improve their skills.
- List of jobs with high demand. The platform provides job seekers with a list of “job roles that need more applicants,” which helps job seekers target vacancies in high demand.
- Career guidance. MCF offers career guidance services such as resume writing, which further aids job seekers in their job search and career development process. This feature helps job seekers improve their chances of getting hired by providing expert guidance on presenting their skills and experience.
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
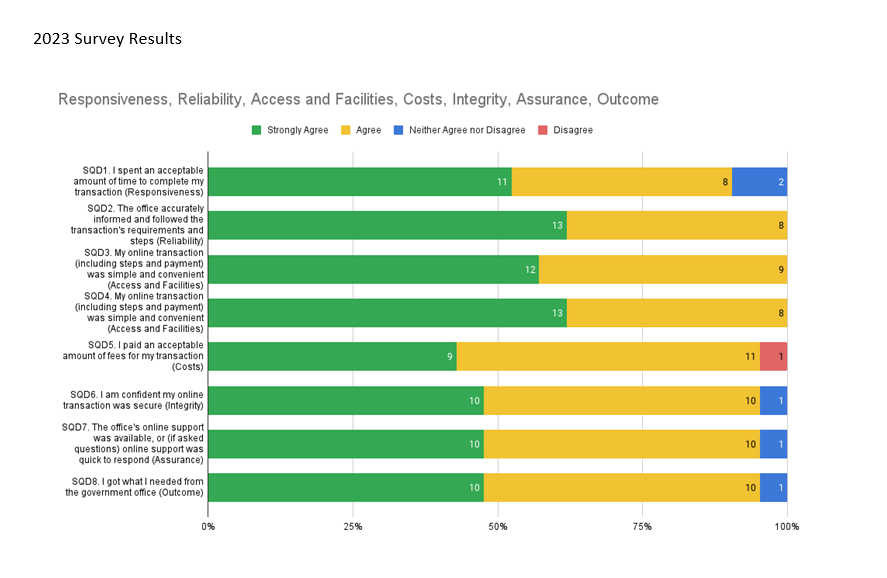
Singapore’s MyCareersFuture (MCF) has made significant strides in improving the productivity performance of Singaporeans by providing job seekers with the resources they need to secure their desired jobs. One of the notable initiatives is the SGUnited Jobs and Skills Info Kiosks, which reached over 5,700 individuals across five locations in July 2020. About 62% of visitors were 40 and above, indicating that the initiative is not limited to younger job seekers.
Based on feedback collected, around eight in 10 visitors better understood the SGUnited Jobs and Skills Package after visiting the information kiosk. More than 130 visitors interacted with WSG’s Career Ambassadors over live chat for bite-sized career advisory services. The provision of tailored career advice depending on their job situation has provided invaluable support for job seekers. In addition, less technically-savvy individuals were provided physical collaterals to take home.
Furthermore, MyCareersFuture’s Workipedia website has been an essential resource for job seekers, offering comprehensive guidance on securing the best job based on their requirements and expertise. The website provides tips and tricks to help job applicants choose the best role which suits their expertise, lifestyle, and expected salary, including insights from seasoned career advisors and documented relatable experiences from fresh graduates and long-serving experts.
In terms of measurable productivity gains and outcomes, MyCareersFuture has assisted over 2.7 million job seekers since its launch in 2018. As of March 2021, the website has over 200,000 active job listings from over 25,000 employers. In addition, MyCareersFuture has helped over 77,000 individuals find jobs as of August 2021.
The SGUnited Jobs and Skills Package has also been an effective intervention, with over 90,000 job seekers benefiting from the program as of June 2021. More than 43,000 persons have secured jobs or started on a traineeship. The program has also been successful in upskilling job seekers, with more than 26,000 individuals attending training courses and over 21,000 individuals completing courses as of June 2021.
Lessons Learned and Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
Singapore MyCareersFuture (MCF) has successfully improved the job search experience for Singaporeans. However, there are still areas for improvement. One of the potential areas of improvement is to increase the coverage of available jobs on the platform. While the platform has over 80,000 job listings, not all Singapore companies currently use MCF to advertise their job vacancies. To improve the platform’s coverage, MCF could consider partnering with more companies or incentivizing companies to use the platform.
Another potential area of improvement is to enhance the platform’s user experience. While MCF has made significant efforts to provide users with tailored career advice, the platform could benefit from further improvements to its search function and job recommendation algorithm. Improvements to these areas would enhance the platform’s usability and make it easier for job seekers to find relevant job listings.
In terms of challenges, the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the job market and created uncertainty for job seekers. The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of digital skills, which are increasingly necessary in the modern workforce. MCF could consider providing more resources and training programs to help job seekers acquire the digital skills they need to succeed in the job market.
Overall, MCF has successfully improved the job search experience for Singaporeans, but there is still room for improvement. By addressing these potential areas of improvement and responding to challenges posed by the pandemic, MCF can continue to support job seekers in Singapore.
Resources
Ang, J. (2020, August 12). Mom: National Jobs Council curated 92,000 new job opportunities as of end-July. Human Resources Online. Retrieved March 20, 2023, from https://www.humanresourcesonline.net/mom-national-jobs-council-curated-92-000-new-job-opportunities-as-at-end-july
6 hacks to land a great job via mycareersfuture.sg. Government Technology Agency. (2019, September 16). Retrieved March 20, 2023, from https://www.tech.gov.sg/media/technews/hacks-to-land-a-great-job-via-mycareersfuture