Overview
The Cagayan de Oro City Government, through the City Housing and Urban Development Department (CHUDD), is spearheading innovative initiatives in providing groundbreaking programs as they roll out the City Housing and Urban Development Department CHUDD Information System (CHUDDIS). CHUDDIS is a comprehensive system designed to assess the qualification of socialized housing applicants and beneficiaries, while also tracking the health vulnerability of household heads, spouses, and dependents.
In addition to adopting a paperless system, CHUDDIS strives to enhance the convenience and efficiency of housing applications, benefiting both applicants and beneficiaries. This innovative system expedites the qualification and background verification of beneficiaries, thereby saving valuable time, resources, and effort. Prior to its implementation, Cagayan de Oro City relied on manual processes and basic databases, leading to a backlog of applications, outdated information, and extended processing durations.
The main challenge faced was ensuring the specific needs of vulnerable populations were identified and addressed in a timely manner. The solution was the implementation of CHUDDIS, which tracks and provides appropriate support and special accommodations to those in need. By doing so, CHUDDIS improves the safety and well-being of beneficiaries, ensuring that socialized housing initiatives cater to the unique requirements of individuals, including persons with disabilities and other vulnerable populations.
Challenge
The manual assessment and qualification process for socialized housing applicants and beneficiaries takes time and has a high risk for human errors. CHUDDIS is an attempt to address this while boosting the department’s productivity.
Prior to the implementation of CHUDDIS, the department faced numerous administrative hurdles and time-consuming procedures in evaluating and determining the eligibility of individuals for socialized housing programs. This manual process often led to delays, errors, and inconsistencies, hindering the overall productivity of the department and impacting the timely delivery of housing services to those in need.
However, with the introduction of CHUDDIS, the department has been able to streamline and automate the application and assessment process. The system gathers and organizes all necessary data and information, allowing for a more efficient and accurate evaluation of applicants’ qualifications. This digital solution minimizes paperwork, reduces redundant tasks, and enhances the overall productivity of the department. Additionally, CHUDDIS provides real-time tracking of the health vulnerability of household heads and their dependents, enabling the department to address the specific needs of vulnerable populations promptly.
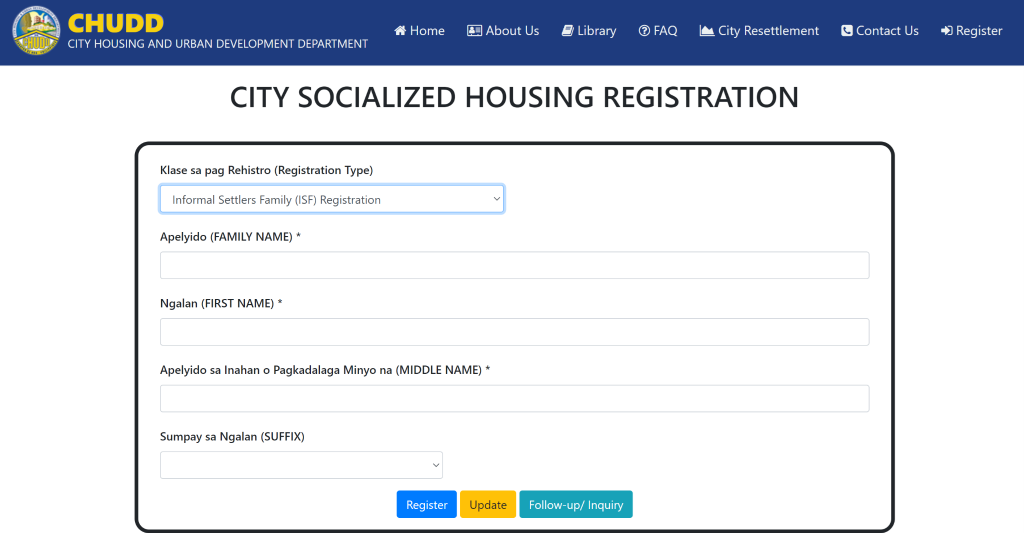
By addressing these productivity challenges, CHUDDIS enables the City Housing and Urban Development Department to effectively manage and allocate resources, improve service delivery, and ensure that socialized housing programs reach their intended beneficiaries in a timely manner.
Solution
CHUDDIS addresses the challenge of efficient assessment and qualification of socialized housing applicants and beneficiaries through the following solutions and innovative features:
- Centralized Digital Platform: CHUDDIS provides a centralized digital platform for applicants to submit their information and required documents, eliminating the need for physical paperwork and streamlining the application process.
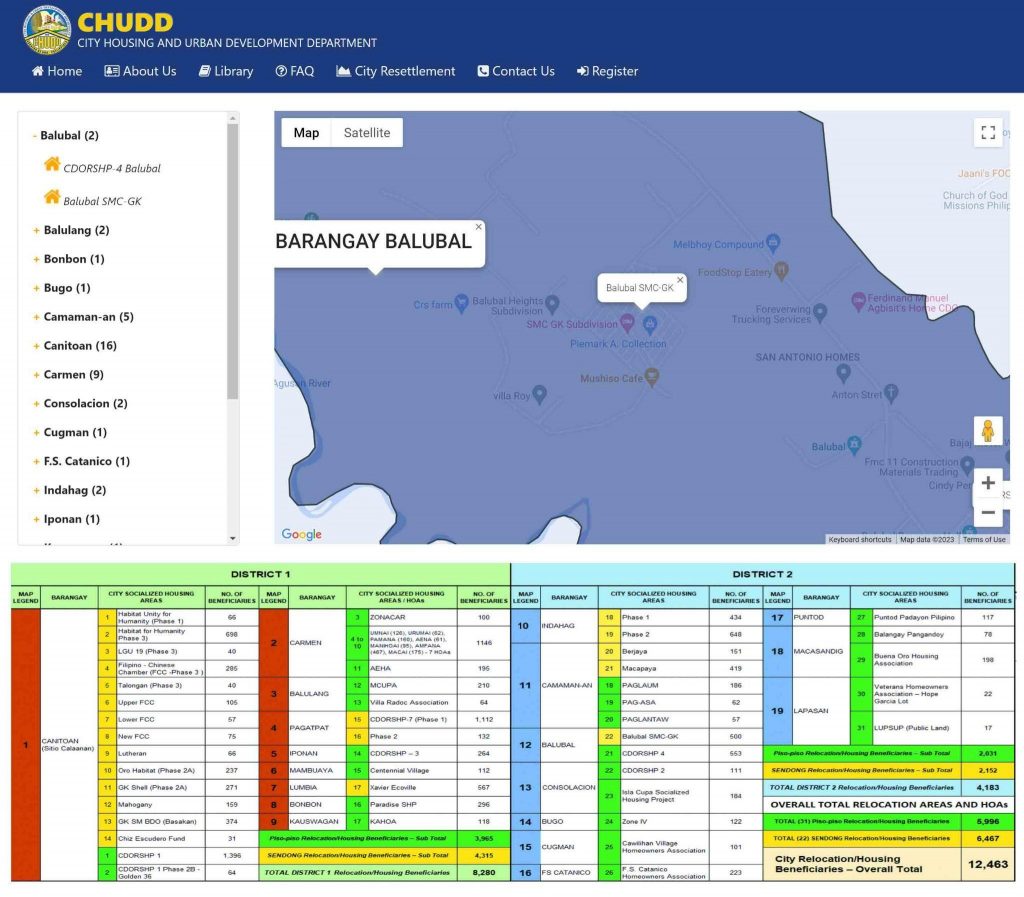
- Spatial Analysis and Visualization: The Geographic Information System (GIS) technology allows the housing department to spatially analyze and visualize data related to informal settlements and ISFs. By mapping the locations of informal settlements, the department can gain insights into the distribution and density of these settlements, helping prioritize areas for intervention and resource allocation. GIS maps can provide a clear visual representation of the extent and concentration of informal settlements, aiding in decision-making processes. By leveraging GIS technology, the housing department can enhance its understanding of informal settlements, improve decision-making processes, and implement targeted interventions to address the housing needs of ISFs more effectively.
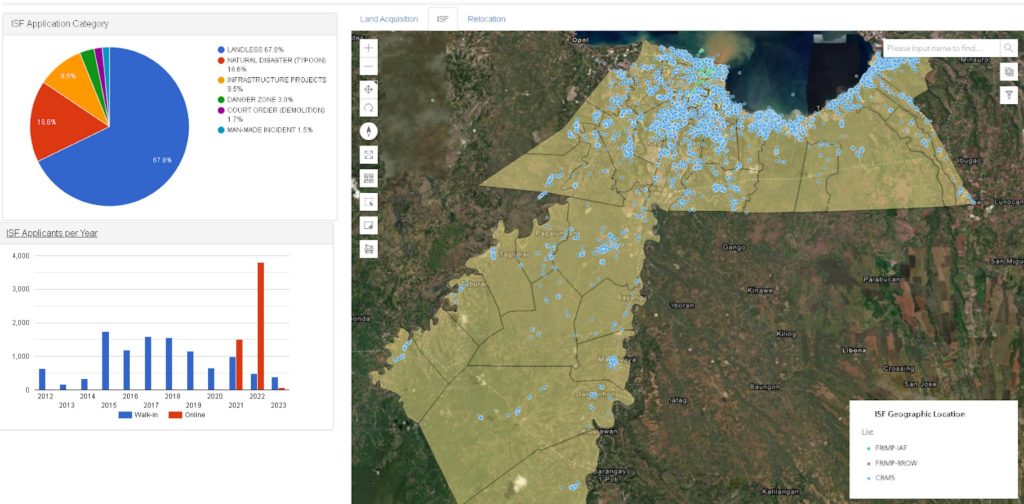
- Advanced Data Analytics: CHUDDIS utilizes advanced data analytics capabilities to assess the eligibility of applicants more accurately and efficiently. This feature minimizes human error and ensures a fair and consistent evaluation process. GIS enables the integration of diverse datasets, such as demographic information, socioeconomic data, infrastructure data, and environmental data. By overlaying this information with the spatial data of informal settlements, the housing department can perform comprehensive analyses. This integrated analysis helps in understanding the social, economic, and environmental factors influencing informal settlements, facilitating informed decision-making and targeted interventions. The department may use GIS to identify the location of informal settler families in the disaster-prone area. By using GIS, the housing department can target disaster preparedness and response efforts in areas where informal settler families are located. The housing department can target affordable housing development to areas where informal settler families are located for “on-site relocationâ€.
- Health Vulnerability Tracking: CHUDDIS tracks the health vulnerability of household heads, spouses, and dependents. This innovative feature goes beyond the primary purpose of the system, enabling timely identification and support for vulnerable populations.
- User-Friendly Interface: CHUDDIS incorporates a user-friendly interface that simplifies the application and evaluation processes. It provides clear instructions, guides applicants through the required steps, and allows them to track their application status, enhancing transparency and user experience.
- Streamlined Resource Allocation: CHUDDIS helps the department manage and allocate resources more effectively by providing comprehensive reports and data analysis, ensuring resources are directed to those in genuine need.
- Timely Service Delivery: By automating tasks and reducing administrative burden, CHUDDIS enables timely service delivery, ensuring that qualified applicants receive housing assistance promptly.
What sets these features apart as innovative is their incorporation of technology, which streamlines processes, enhances accuracy, promotes transparency, and provides personalized support. CHUDDIS harnesses the power of data analytics and automation to overcome the challenges associated with manual paperwork, human errors, and time-consuming evaluation procedures. Its emphasis on health vulnerability tracking demonstrates a proactive approach in addressing the specific requirements of vulnerable populations. Moreover, the user-friendly interface enhances the overall user experience, simplifying the system navigation for applicants. By combining these elements, CHUDDIS revolutionizes the productivity and efficiency of the City Housing and Urban Development Department, ultimately elevating the delivery of socialized housing programs to the community.
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
The implementation of the City Housing and Urban Development Department Information System (CHUDDIS) has resulted in significant measurable productivity gains and positive outcomes for both the department and its intended beneficiaries.
One of the key productivity gains is the reduction in processing time for housing applications. Previously, the manual assessment and qualification process was time-consuming and often faced delays. The initial registration typically required 10 to 30 minutes. Pre-evaluation, which involved processing an estimated 200 applicants, took around 5 days. Once these steps were completed, the post-evaluation process took approximately 3 to 5 minutes to verify document validity. The selection and prioritization of 200 applicants for household profiles would take 1 to 2 weeks, after which they were endorsed for approval within 1 to 2 days. Every household received an approval notification via text thereafter.
However, with the automation and streamlining of processes through CHUDDIS, the department has experienced faster application processing times. The online system allows for registration and document uploading within just 5 to 10 minutes through automatic cross-matching. Pre-evaluation now takes approximately 3 to 5 minutes, with an additional 5 minutes for uploading any supplementary documents. Post-evaluation is also completed within 3 to 5 minutes. Generating prioritized household profiles now requires only 5 minutes or less, and applicants are promptly endorsed for approval. Following these streamlined steps, every household receives an approval notification within 5 minutes or less.
The online system has greatly enhanced the overall productivity of the City Housing and Urban Development Department by enabling staff to handle a larger volume of applications within shorter time frames–from the average of waiting time of at 2 weeks for application processing, it is now reduced to just around 40 minutes.
Kent Ryan C. Silao, representing the City Housing and Development Department (CHUDD), emphasized the importance of CHUDDIS implementation, citing its ability to address the issues surrounding prolonged application processing times and outdated systems. Additionally, it alleviates the burdensome task of preparing the required documentation for housing applications.
“CHUDDIS was created as a tool to support the digitalization of the socio-economic form. So medyo marami siyang data. Its purpose is to provide the necessary data and information to help assess the qualification of the socialized housing project.†he mentioned.

Additionally, CHUDDIS has enhanced the accuracy and consistency of evaluations. By utilizing advanced data analytics capabilities, the City Government is able to make informed decisions. For example, CHUDD can now easily track the availability of land, the cost of land, and the demand for housing in different areas.
CHUDDIS has also been helpful in planning and development. Land acquisition is crucial for initiating housing development projects and potential sites for new housing development. By tracking land acquisition, the housing department can identify suitable parcels of land for development and allocate resources accordingly. It allows them to plan and strategize the expansion of housing infrastructure to meet the growing demands of the population. GIS can support the housing department in identifying suitable locations for housing projects or relocation sites for informal settler families (ISFs). By considering factors such as proximity to job opportunities, transportation networks, social services, and infrastructure availability, GIS can assist in selecting sites that meet the specific needs and preferences of ISFs. This approach enhances the chances of successful housing interventions and improves the integration of ISFs into existing urban development.
The positive impact on intended beneficiaries is evident through improved service delivery. With the faster processing times and accurate evaluations enabled by CHUDDIS, eligible applicants receive timely assistance and access to socialized housing programs. This not only improves their quality of life but also provides them with the necessary support to secure safe and affordable housing. By effectively addressing the needs of the beneficiaries, CHUDDIS contributes to their overall well-being and contributes to poverty reduction efforts.
Furthermore, the tracking of vulnerability in CHUDDIS has helped the City Government in responding to the specific needs of vulnerable populations. This feature enables the department to provide targeted support and special accommodations, such as accessibility features for persons with disabilities or health services for individuals with specific medical conditions. The declaration of vulnerabilities of the intended beneficiaries has also helped CHUDD in providing housing options and tailored support services.
In summary, the productivity gains and outcomes of CHUDDIS include reduced processing time, improved accuracy and consistency, enhanced service delivery, and targeted support for vulnerable populations. These gains not only improve the productivity performance of CHUDD but also positively impact the lives of the intended beneficiaries.
Lessons Learned and Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
The implementation of CHUDDIS has provided valuable lessons and highlighted potential areas for improvement.
One of the key lessons learned is the importance of stakeholder engagement and training. During the implementation process, it became apparent that comprehensive training programs for department staff and beneficiaries are essential to maximize the system’s benefits. Adequate training ensures that users understand how to navigate CHUDDIS effectively and utilize its features to their full potential. Additionally, involving stakeholders early on in the system’s development and seeking their feedback helps to address any concerns and tailor the system to their specific needs.
Another lesson learned is the need for continuous system maintenance and upgrades. As technology evolves, it is crucial to keep CHUDDIS up to date with the latest security measures, software updates, and hardware compatibility. Regular maintenance and upgrades ensure the system’s reliability and usability, minimizing downtime and potential disruptions in service delivery.
The challenges encountered during the implementation of CHUDDIS include the initial transition from manual processes to a digital system. Resistance to change and limited digital literacy among staff and beneficiaries can pose obstacles. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive change management strategies, including clear communication, training, and ongoing support.
Additionally, data security and privacy are critical considerations. The system must have robust security measures in place to protect sensitive applicant and beneficiary information. This includes implementing encryption protocols, access controls, and regular data backups.
Furthermore, the scalability of CHUDDIS is an important area for improvement. As the number of applicants and beneficiaries increases, the system should be capable of handling a larger volume of data and users without compromising its performance. Regular system performance evaluations and capacity planning are necessary to ensure CHUDDIS can accommodate future growth.
In conclusion, the lessons learned from the implementation of CHUDDIS underscore the importance of stakeholder engagement, training, system maintenance, and addressing challenges such as resistance to change and data security. By continually improving and addressing these areas, the City Housing and Urban Development Department can enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of CHUDDIS, resulting in improved service delivery and better support for housing initiatives.
Resources
Cagayan de Oro City Housing. City Housing CdeO. (n.d.). https://chudd.cagayandeoro.gov.ph/
MGSD. (2023, February 22). Oro Dad Backs Inventory on housing projects. Mindanao Gold Star Daily. https://mindanaogoldstardaily.com/archives/136152
Mindanao Daily. (2018, May 14). https://issuu.com/sudaria_publications/docs/mdn_may_14
