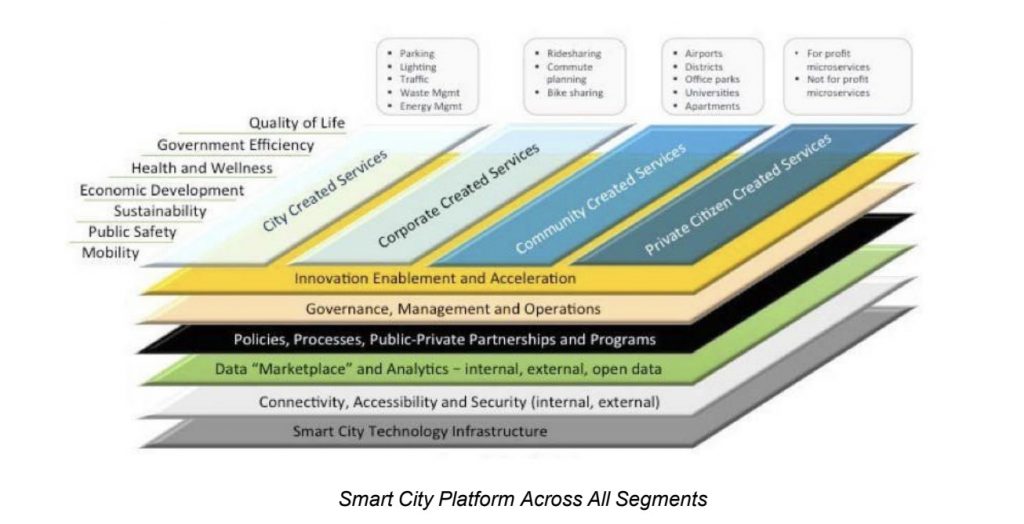
Overview
Through its innovative Smart City platforms, Baguio City leverages data analytics and artificial intelligence to enact good governance. This comprehensive initiative encompasses various aspects, including tourism management, public safety, traffic control, disaster risk reduction, environmental preservation, and citizen welfare. With the state-of-the-art Smart City Command Center at its core, Baguio City officials gain valuable insights from multiple data sources and cutting-edge technology such as AI-enabled cameras and environmental sensors. This streamlined approach ensures swift response times and efficient resource allocation.
Challenges
Before the implementation of the Smart City Project, the City Government of Baguio relied on a decentralized system to address pressing challenges within the city, such as traffic congestion, environmental degradation, and crimes. However, this outdated system posed additional obstacles, including extended resolution times, restricted operational collaboration, and communication issues among various offices and departments. Consequently, the delivery of public services suffered from delays and inefficiencies.
Solutions
In September 2018, Baguio City took a significant step towards enhancing the services provided to residents and tourists by inaugurating the groundbreaking Smart City Command Center. As the first of its kind in the country, this cutting-edge hub offers a comprehensive and unified view of the entire city, accessible to all government agencies, including the City Mayor. The primary aim of this pioneering project is to centralize and streamline all city operations, enabling swift and informed decision-making and responses to various situations. By consolidating critical data and resources in one location, the Smart City Command Center empowers the city authorities to proactively address the community’s needs and ensure efficient service delivery.
Since its inception, the Smart City Command Center has emerged as the central hub for data analysis and decision-making in Baguio, effectively serving as the city’s eyes and ears. With its advanced capabilities, the Command Center can swiftly identify anomalies and promptly alert the relevant authorities for resolution, often within minutes. This includes round-the-clock monitoring of traffic conditions, public well-being, and environmental factors. The traditional process of generating department-specific reports for the City Mayor, coordinating with other government entities for cohesive action, and navigating various obstacles has replaced the Command Center’s ability to gather, process, and analyze data in real-time. Consequently, it can produce comprehensive reports within minutes, leading to timely resolutions and swift responses to emerging challenges.
Baguio City has significantly upgraded its infrastructure, including mainframe computers, AI-enabled CCTVs, environmental monitors, GPS devices for public transport, high-resolution panoramic surveillance cameras, and a team of skilled staff with hardware and software development expertise.
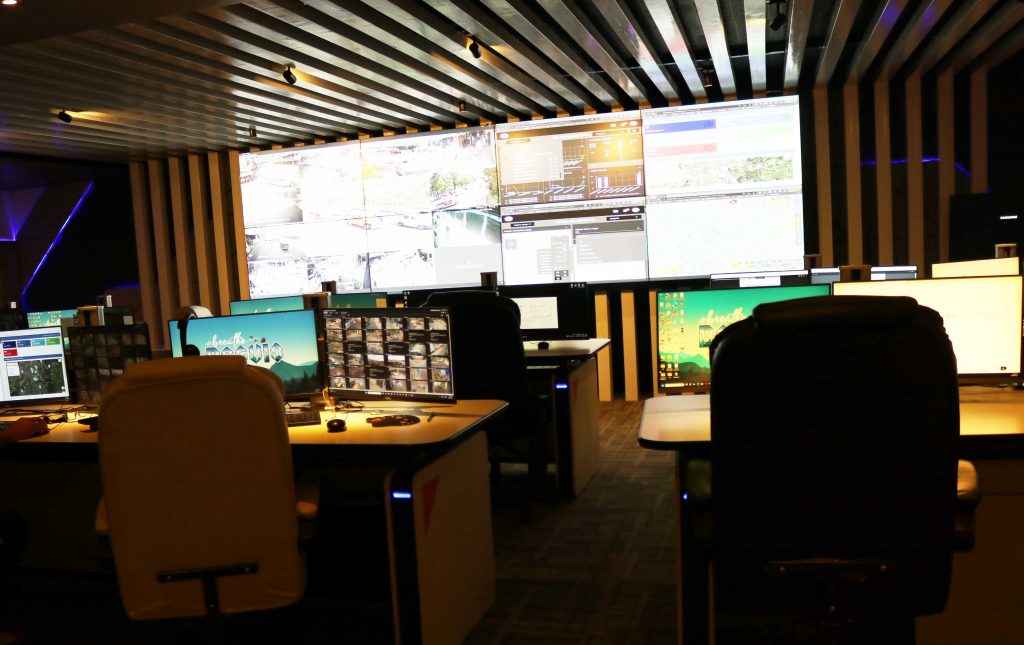

safety and security, lighting, waste management, and other services.
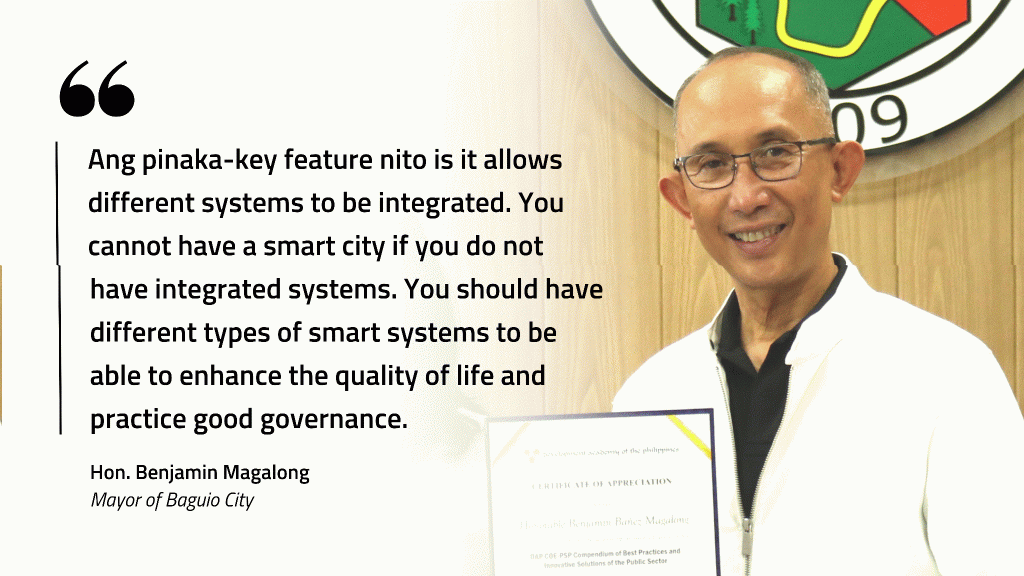
Baguio City Mayor Benjamin Magalong underscored that addressing the safety and security of the city is just one component of the Smart City Project.
The Baguio Smart City key features include:
- Smart Security System: AI-powered surveillance cameras enable real-time monitoring, facial recognition, object detection, and traffic congestion analysis. Immediate deployment of resources and personnel is facilitated once an issue is identified.
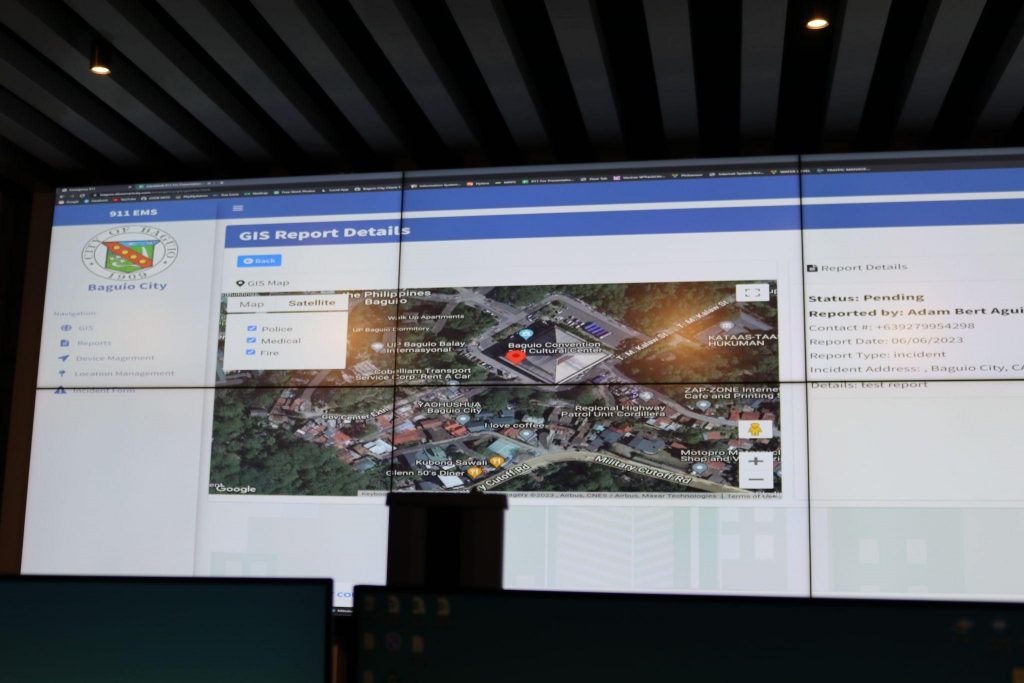
- Smart Emergency Response System: Utilizing Baguio In My Pocket (BIMP) and Baguio 911, distress calls can be promptly located and addressed within the city’s geofence area.
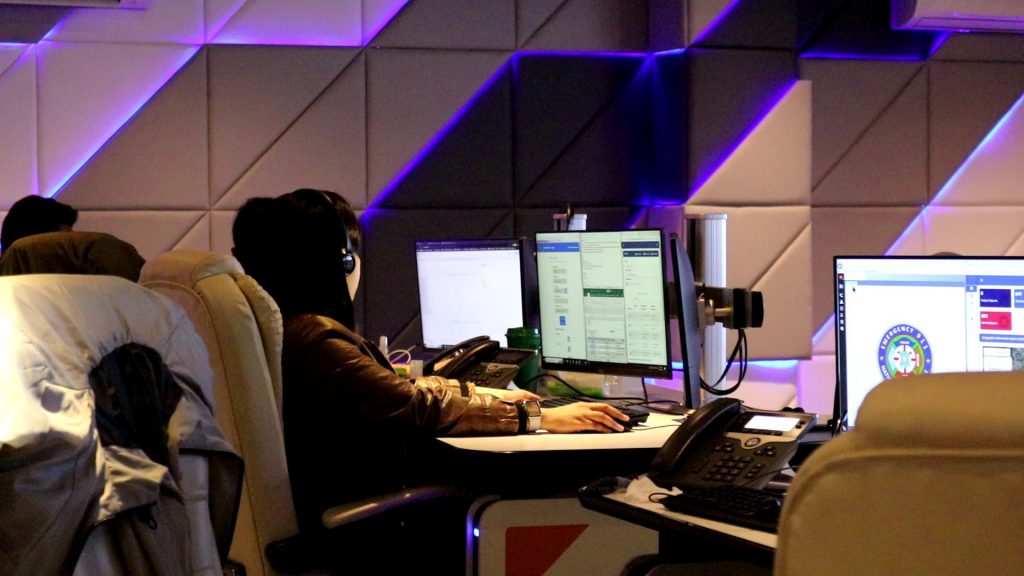

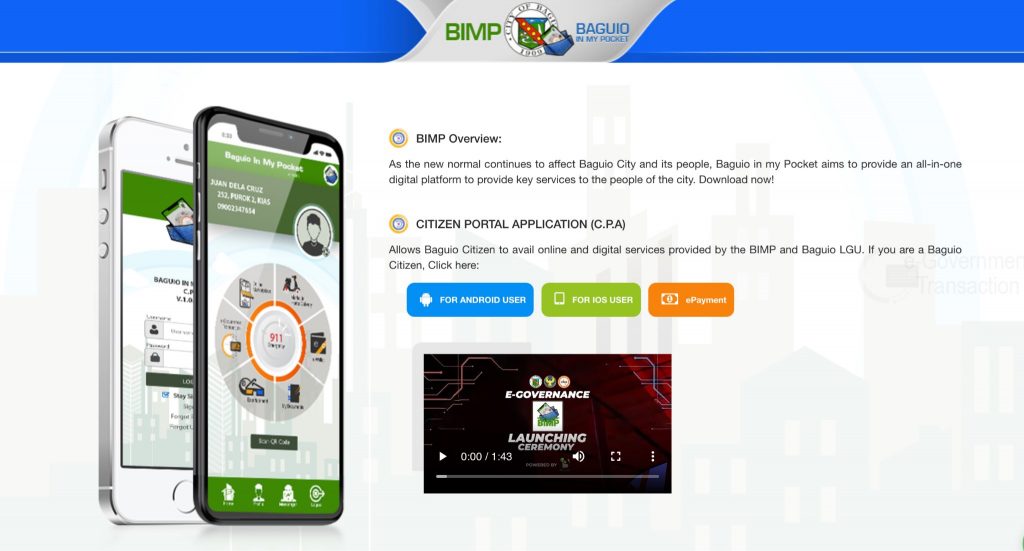
- E-Government System and E-Business Infrastructure: The BIMP app enables real-time property tax assessment, settlement, and online business payments to the city hall.
- Smart Tourism: Baguio VISITA (Visitor Information and Travel Assistance) is a dedicated tourist app that provides information on city navigation, rules, and regulations. It proved especially valuable during the easing of lockdown restrictions, ensuring safe and compliant tourism practices.
- Environment Management: Monitoring devices at high-traffic locations regularly update air and water pollution levels.
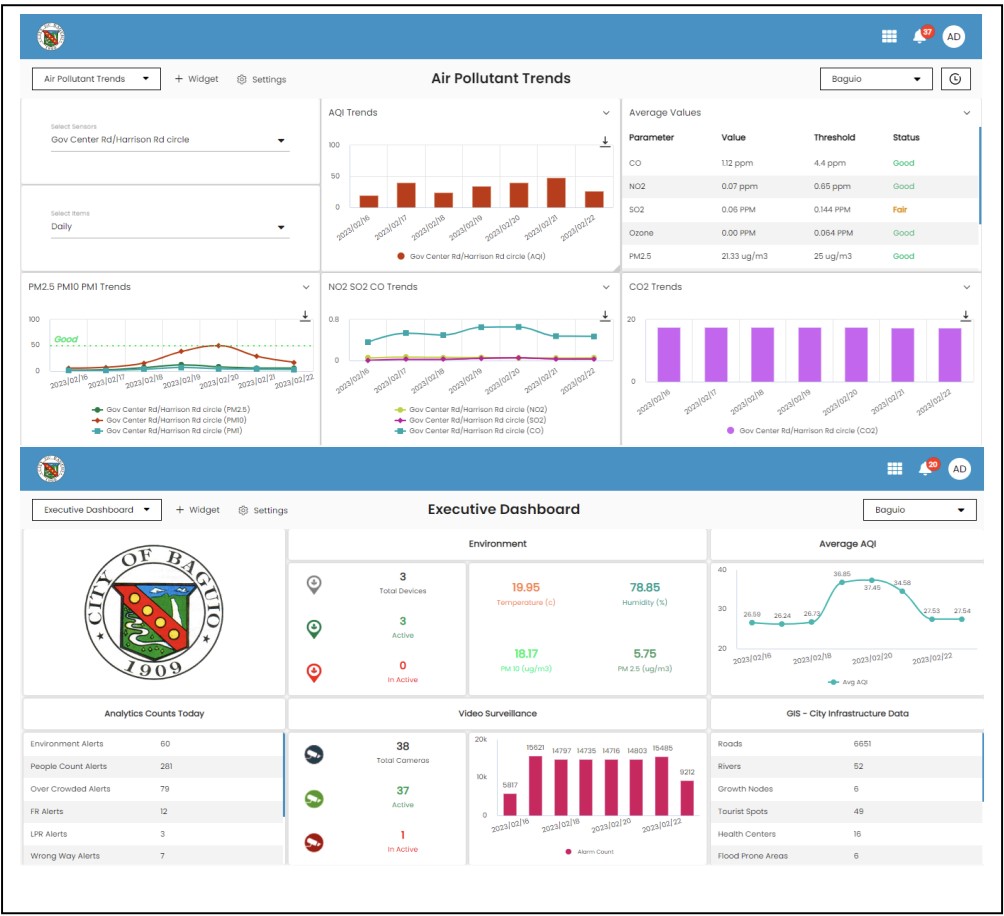
- Smart Transportation: GPS monitors installed in public transport vehicles enable real-time speed monitoring, allowing instant communication with drivers. This system also assists with lost items, accidents, and other transportation-related issues.
- Smart Healthcare Monitoring System: Collaborating with healthcare providers, the Smart City Command Center creates disease heat maps to respond to outbreaks such as Dengue and COVID-19. The system also helps identify nearby healthcare centers for emergency response.
- External Projects: Besides funding from the Executive branch, the development of Baguio’s Smart City was made possible through project engagements and grants from various international actors. These external projects placed Baguio on the map for environmental innovations and significantly enhanced its resources. Two notable initiatives that contributed to the city’s growth are MINERVA and the Flood Early Warning System projects.
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, Impact
Through the Smart City Command Center, Baguio City has implemented data-driven policies, leading to tangible outcomes and improved governance.
According to Mayor Magalong, they can generate real-time data from the Smart City platform within a few hours and utilize this relevant data in crafting strategic responses to various issues in the city. For instance, analysis of pollution levels and traffic patterns facilitated the decision to replace taxis with mass transport options, addressing air pollution and congestion issues. During the pandemic, the strategic mapping of COVID-19 cases enabled targeted lockdowns and minimized disruptions.
Adam Bert Lacay, Supervisor of the Smart City Command Center, emphasized the impact of the command center in helping City Officials make better decisions for the welfare of Baguio citizens.

The Command Center’s continuous monitoring of CCTVs has expedited responses to traffic violations and lost items. As of 9 June 2023, the Smart City Command Center has catered to 665 CCTV video playback requests and 120 CCTV video extractions. The latter two are most important in achieving lower crime rates and infractions.
As of 9 June 2023, Baguio 911 has been most helpful in Ambulance Assistance, garnering 760 calls, with police assistance at 290 calls, vehicular accident distress calls at 94, a public nuisance at 84 calls, and disturbance and petty infractions at 34 calls.
Lessons Learned And Challenges In Implementing The Intervention
Baguio’s transition to a Smart City model has brought about a modernized governance that can be incomparably reachable to its people. However, their challenges during the implementation are internet speed, consistency issues, resistance to technology adaption among constituents, and coordination difficulties among departments. The deployment of facial recognition and personal data plotting awaits the release of Implementing Rules and Regulations by the National Privacy Commission.
Despite these hurdles, Baguio Smart City remains operational 24/7 through failsafe mechanisms and backup connectivity plans, ensuring the city’s commitment to data-driven good governance.
The Command Center is poised to expand in the next few years, moving to a higher and more strategic location to take advantage of Baguio’s terrain for a 360-degree view, digitally and in reality. Beyond this, the Command Center is pushing to automate other services for future generations– from waste management to crime prevention.
Mayor Magalong emphasizes the crucial role of youth in this endeavor, recognizing them as the actual beneficiaries and innovators who will carry this project forward. While his generation may serve as catalysts, the mayor envisions the youth as the driving force behind the continued success and advancement of the Command Center. To Mayor Magalong, the Command Center is not just a project; it represents a lasting legacy that he hopes will position Baguio City as an advanced, smart city, potentially surpassing international smart city models in terms of technological prowess and progress.
Sources
- Baguio City Mayor’s Office. (ND). Smart City Vision for Baguio City. PDF.
- Baguio City Mayor’s Office. (ND). Smart City Project. PDF.
- Baguio Visita. (n.d.). https://visita.baguio.gov.ph/
- BIMP User Manual. Baguio In My Pocket. (n.d.). https://baguioinmypocket.ph/
- N.A. (ND). Pioneering the Development of a Cutting-Edge Smart City in the Philippines. PDF.
- N.A. (ND). Executive Summary for Smart City Command Center. PDF.
