Overview
iRISE UP (Intelligent, Resilient, and Integrated Systems for the Urban Population) is an intelligent and integrated early warning system that empowers the Local Government of Quezon City to address various hazards proactively, such as flooding and extreme weather events. By utilizing both the latest and traditional technologies, community engagement, and data-driven governance, iRISE UP has successfully enhanced the city’s disaster preparedness and response capabilities. Its impact includes improved risk assessment, streamlined communication channels, and establishing a resilient framework that prioritizes public safety and sustainable development.
Challenge
Before implementing the iRISE UP program, the Local Government of Quezon City was lacking on reliable, localized, and real-time data system that provided residents with timely and comprehensive hazard and disaster information. As a result, response time during disasters was delayed, the allocation of city resources was wasted, and the lives of its citizens were put on the line. With the city’s history of devastating disasters, including the traumatic impacts of the 2009 Tropical Storm Ondoy and the recurring threat of flooding, there is a critical need to enhance disaster preparedness and response mechanisms.
QCDRRMO Officer-in-Charge Ricardo Belmonte emphasized the need for a more precise method of gathering weather and flooding information, considering the extensive constituency comprising 142 barangays, covering approximately 35% of Metro Manila.
Solution
The iRISE UP program is established as a multi-hazard early warning system within the city’s Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Operations Center, enhancing the city’s capabilities to tackle the changing disaster risks and provide accurate information for informed decision-making and disaster preparedness. It employs a system-driven approach, converging multiple data and systems of the city government into a unified platform, thereby serving as a foundation for tailored interventions that build safer, more adaptive, and resilient communities. QCDRRMO Geographic Information System (GIS) Team Leader Jose Leo Martillano says that through iRISE UP’s GIS feature, they were able to allot essential resources such as rescue boats more effectively and efficiently.
Innovative features of the iRISE UP Program include:
- Backend System: The program incorporates an extensive sensor network and Geographic Information System (GIS) database, enabling dynamic analysis and data visualization. This allows for the continuous evolution of the program in response to changing disaster risks, facilitating informed decision-making and effective disaster preparedness.
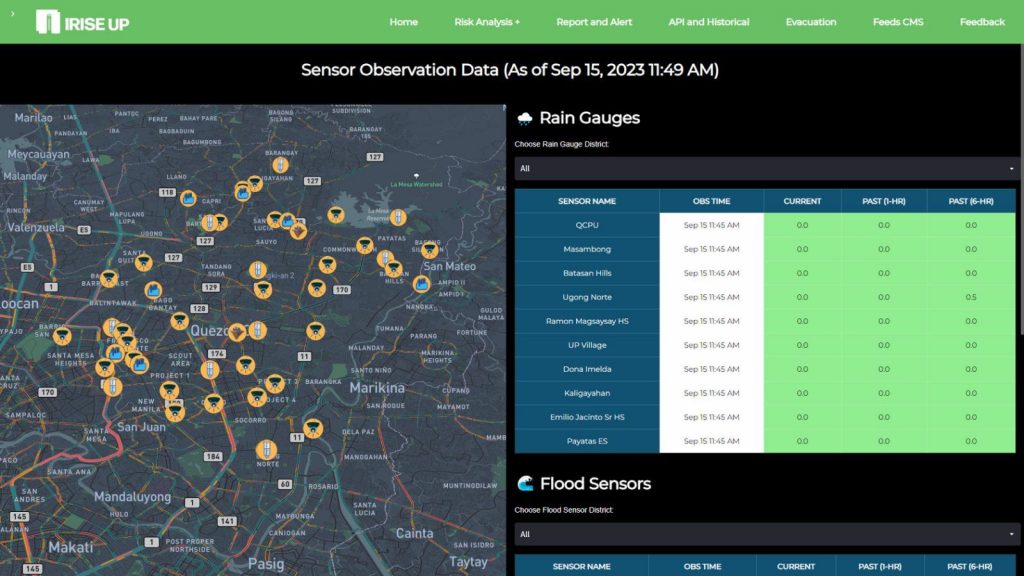
- Real-Time Monitoring: Utilizing remote sensors, field equipment, and data loggers, iRISE UP enables efficient data transmission, ensuring timely and accurate monitoring of various hazards. This real-time monitoring capability enhances the city’s ability to respond promptly to emerging risks and threats.
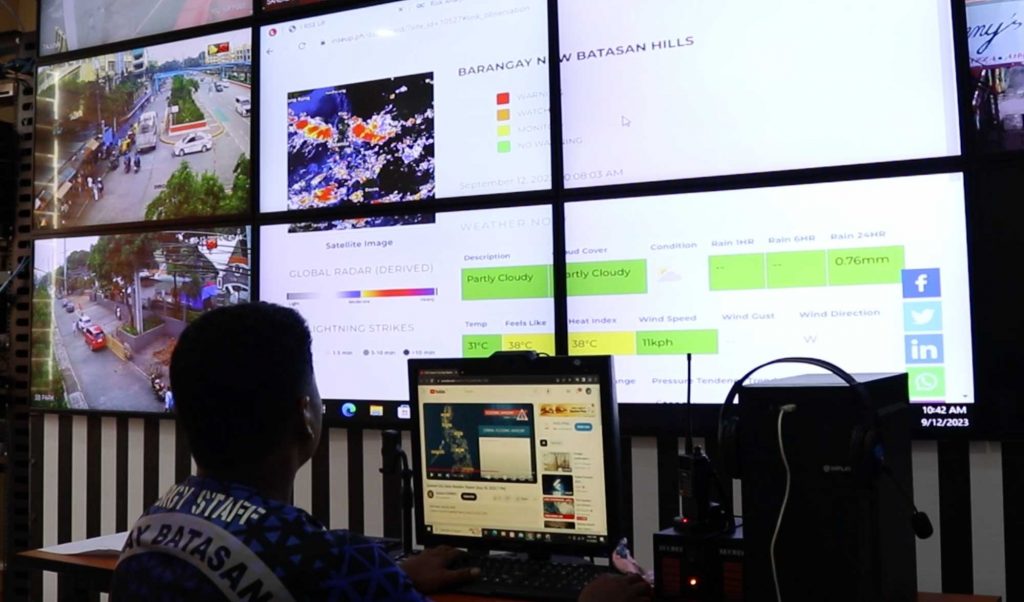

- Downloadable Historical and Live Data: iRISE UP provides accessible historical and live data, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions and implement targeted interventions based on past events and trends. This feature enhances overall disaster response capabilities and supports proactive risk management.
- Localized Hazard and Risk Maps: The program offers localized hazard and risk maps, providing accessible information for effective mitigation and response planning. This feature aids in identifying high-risk areas and supports the development of comprehensive strategies to address potential disasters.
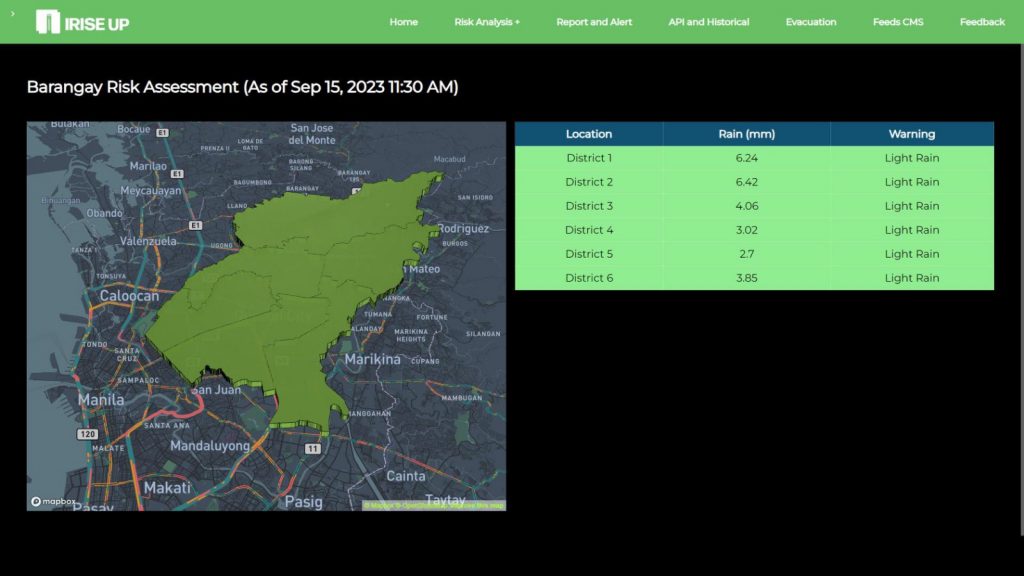
- Impact-Based Weather Forecasting: By focusing on impact-based weather forecasting, iRISE UP delivers actionable information for disaster preparedness, emphasizing the potential impacts of weather events rather than just the meteorological data. This approach informs anticipatory action helping communities and decision-makers make well-informed choices in their disaster response strategies.
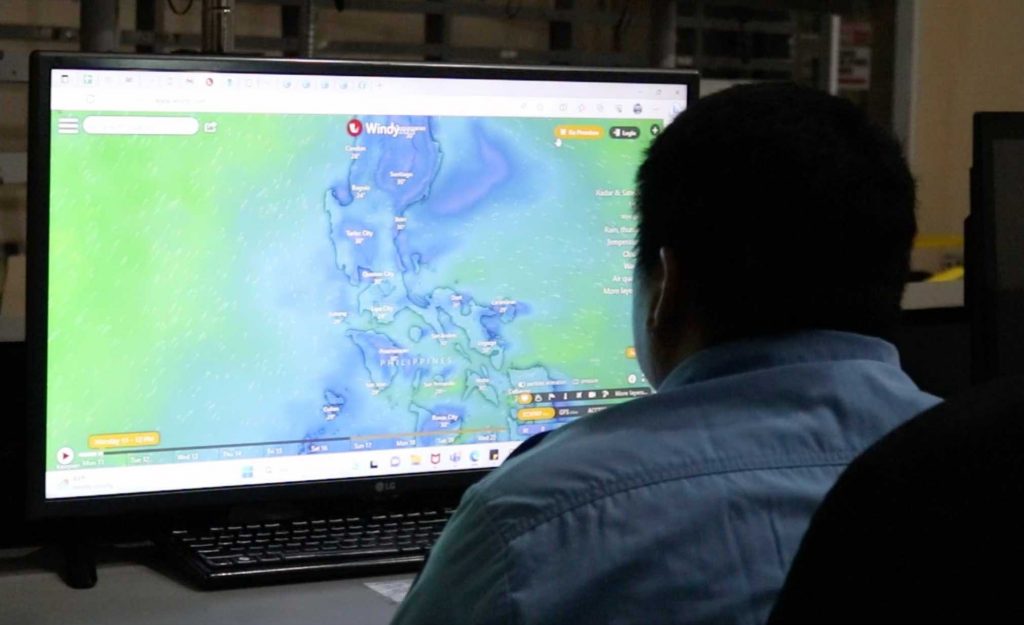

- End-to-End Approach: iRISE UP fosters community engagement and empowerment by promoting a comprehensive approach to risk assessment and management activities. An end-to-end approach, which is crucial in risk communication, ensures that the important messages reach the intended audience. This inclusive strategy also encourages community members to actively ensure their safety and well-being, thereby building more resilient communities.
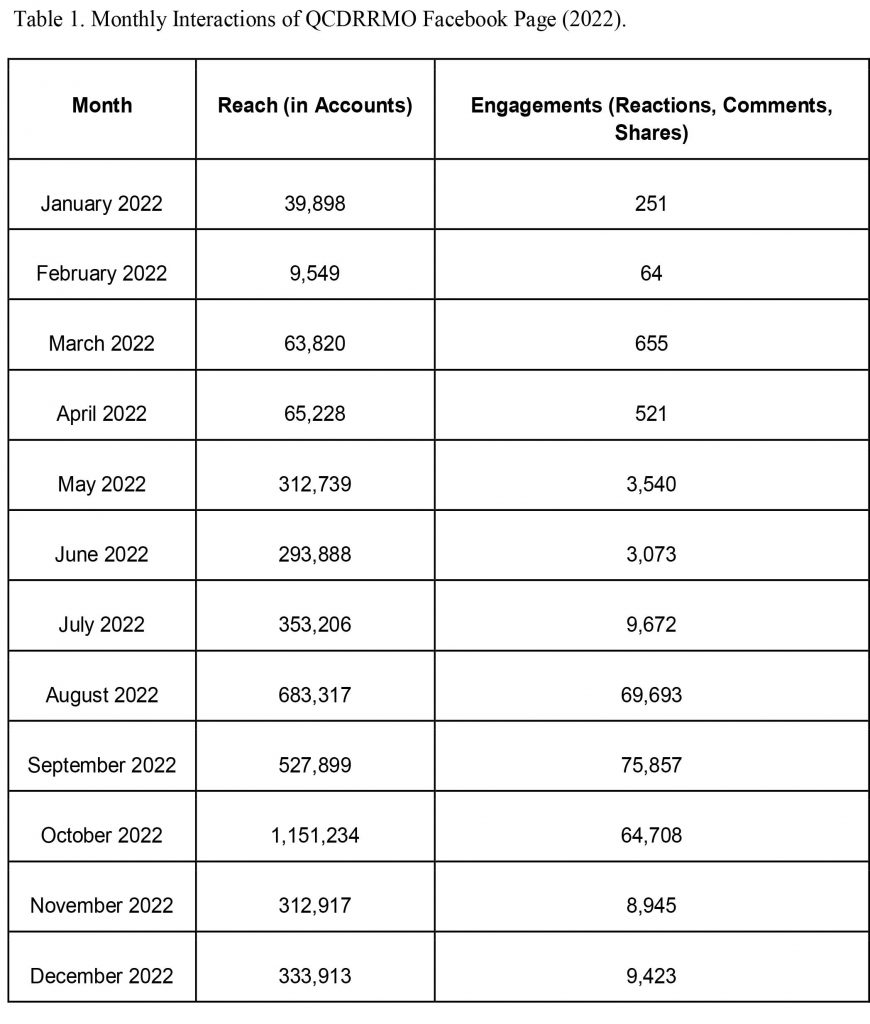
- Utilization of Digital and Traditional Instruments: The program integrates digital and traditional instruments, emphasizing the synergy between modern technology and community capabilities. This approach ensures that the benefits of technological advancements are combined with the practical knowledge and resources available within the community.
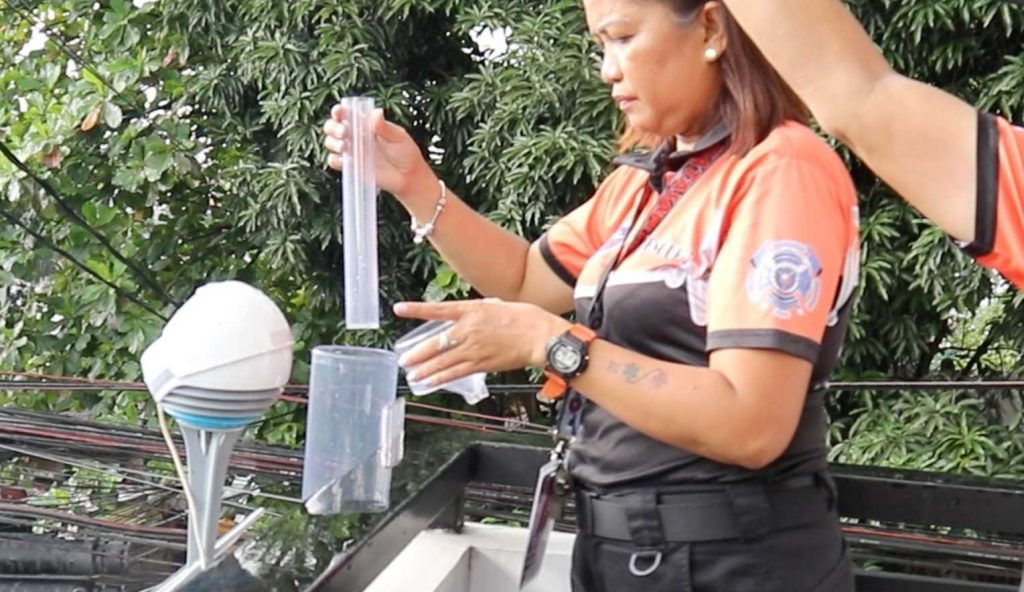

- System-Driven Whole-of-Government Approach: iRISE UP adopts a whole-of-government approach that converges data from various departments and offices within the city government. This unified approach facilitates effective disaster risk reduction and management, enabling a coordinated and comprehensive action plan for building resilient communities. This also helps in avoiding task duplication and reducing costs, promoting productivity.
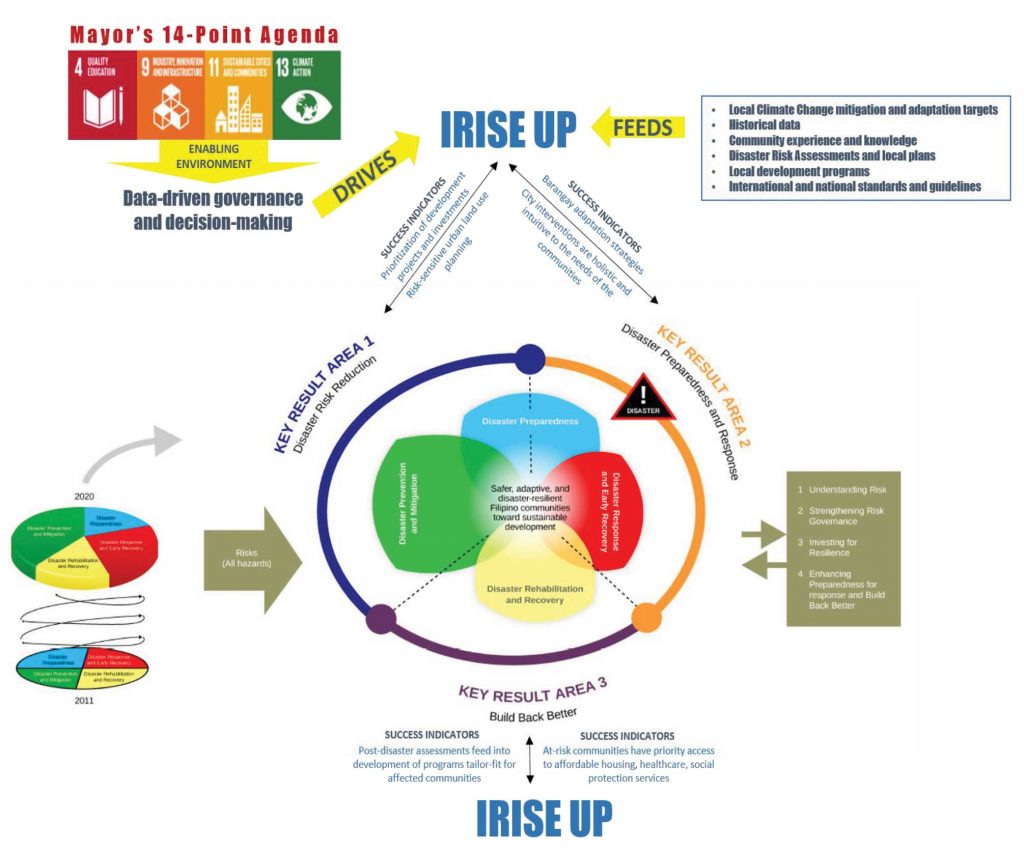
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
The integration of the iRISE UP program into the disaster risk management and response framework of Quezon City has yielded substantial and measurable productivity gains and outcomes, significantly enhancing the performance of the Local Government of Quezon City and the Quezon City Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Office (QCDRRMO).
Under the Disaster Risk Reduction key result area, iRISE UP has facilitated the generation of over 1,000 maps, enabling a comprehensive understanding of hazard-prone areas and informing preemptive actions such as localized evacuations. The program has also empowered Barangay DRRM Committees to implement preemptive and forced local evacuations, leading to a successful partnership with numerous grassroots organizations in executing DRRM programs. These initiatives have substantially reduced the number of casualties, with zero recorded casualties since the implementation of iRISE UP in 2020.
Regarding Disaster Preparedness and Response, the program has contributed to training more than 17,000 individuals as disaster response force multipliers, ensuring a more efficient and coordinated response during calamities. The identification of evacuation sites and camp managers using iRISE UP data has improved evacuation procedures’ management, guaranteeing evacuees’ safety and well-being. Moreover, providing hot and healthy meals and child-friendly spaces in evacuation sites has significantly enhanced the overall well-being of affected individuals and families. QCDRRMO Research and Planning Section Chief, EnP Ma. Bianca D. Perez, MPA, elaborated on these achievements in a key informant interview.
The Bounce Forward Together initiative has resulted in the design of stormwater harvesting detention basins and the identification of hazard-prone areas, paving the way for developing and implementing critical infrastructure projects. The identification and planned relocation of informal settler families living in hazardous zones reflect the city’s commitment to ensuring the safety and security of its citizens.
Lessons Learned and Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
A key lesson learned is the importance of redundancy for disaster resilience. The program has recognized that digital communication methods may falter during crises. The deployment of radio communication serves as a robust backup method, ensuring efficient information exchange among response teams and the community. This redundancy enhances disaster resilience by facilitating coordinated responses to emergencies. Integrating solar power and Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems in key buildings also ensures the availability of electricity during power outages, which is crucial for maintaining essential services and communication during disasters.
To further enhance the sustainability and effectiveness of iRISE UP, the institutionalization of the program is an ongoing process. Building the capacity of personnel, collaboration with various stakeholders, and budget allocation are essential elements of this institutionalization, ensuring the long-term viability of disaster risk management efforts in Quezon City. The end-to-end approach emphasizes community understanding of the information generated by iRISE UP and its subsequent actions provides valuable lessons in empowering and engaging communities. House-to-house education campaigns, the use of physical flood markers, traditional signages, and manual hand-crank sirens all contribute to ensuring that communities are well-prepared and proactive in their response to disaster-related information.
In terms of potential areas of improvement, ongoing community engagement and education are crucial to sustaining the program’s effectiveness. Continuous efforts to reinforce community understanding and action should be a priority. Additionally, regular maintenance and upgrading of technology, infrastructure, and communication equipment are essential to ensure their reliability during emergencies. Lastly, a review of the allocation of resources and budget to support the program’s long-term sustainability may identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Resources
Caliwan, C. L. (2023, October 13). Galing Pook winners urged to share best practices with other LGUs. Philippine News Agency. https://www.pna.gov.ph/articles/1211732
Gozum, I. (2023, November 1). Quezon City’s early warning system keeps residents prepared for weather events. Rappler. https://www.rappler.com/nation/metro-manila/quezon-city-early-warning-system-keep-residents-prepared-weather-events/
Mateo, J. (2023, October 16). Quezon City among Galing Pook Awardees for 2023. Philstar.com. https://www.philstar.com/nation/2023/10/17/2304339/quezon-city-among-galing-pook-awardees-2023
