Overview
The Marinduque Veterinary Field Hospital (MVFH) is a provincial government initiative to address the challenge of providing timely and relevant veterinary services. The key points of this project include the need for more access to veterinary healthcare in rural areas, limited resources and infrastructure, and low productivity due to the absence of specialized veterinary services. To tackle these issues, the field hospital was established, providing mobile veterinary clinics, veterinary training programs, and improved infrastructure. By decentralizing veterinary services, increasing accessibility, and enhancing the skills of local veterinarians, the project aims to boost public sector productivity by ensuring efficient and effective delivery of veterinary care, promoting animal health, and supporting the agricultural sector in Marinduque.
Challenge
The main challenge addressed by MVFH is the inadequate access to quality veterinary healthcare services in rural areas. Marinduque, a province in the Philippines, faces significant geographical challenges with scattered and remote communities, making it difficult for residents to access essential veterinary care for their livestock and animals. Barangay Kagawad Davis Troy Alvarico of Maniwaya, Santa Cruz, shares his insights on managing an island community located northeast of the main island of Marinduque.

This challenge also hampers agricultural productivity, which plays a vital role in the province’s economy. Livestock, such as cattle, swine, and goats, are crucial for agricultural livelihoods and food production. However, with proper veterinary services, the health and productivity of these animals can improve, leading to increased agricultural output and income for farmers. Marinduque Governor Presbitero Jose Velasco Jr. also echoes the sentiments of his constituents in the province.

The limited resources and infrastructure available for veterinary services also exacerbate the challenge. The absence of specialized veterinary care and training opportunities in Marinduque limits the capacity of local veterinarians to address complex animal health issues effectively.
The establishment of MVFH helped in addressing these challenges head-on. The field hospital provides mobile veterinary clinics that can reach remote communities, improving access to veterinary care. It also offers training programs to enhance the skills of local veterinarians, enabling them to provide more comprehensive and specialized services. These efforts directly contribute to boosting productivity by promoting animal health, enhancing diesease precention and control, and ultimately improving the economic well-being of Marinduque. Marinduque Provincial Veterinarian Dr. Josue M. Victoria shares the importance of citizen-centered design in providing public services.

Solution
The concept started way back in 2004 with continuous upgrading and innovation to meet the ever-changing needs of the time. MVFH addresses the challenge of limited access to quality veterinary healthcare services in rural areas through several innovative features:
- Veterinary Field Hospital: The field hospital operates mobile clinics that can reach remote communities in Marinduque. By bringing veterinary services directly to these areas, the hospital ensures farmers and pet owners have convenient access to essential healthcare for their animals. This mobile approach is innovative as it overcomes geographical barriers and improves the outreach of veterinary services.
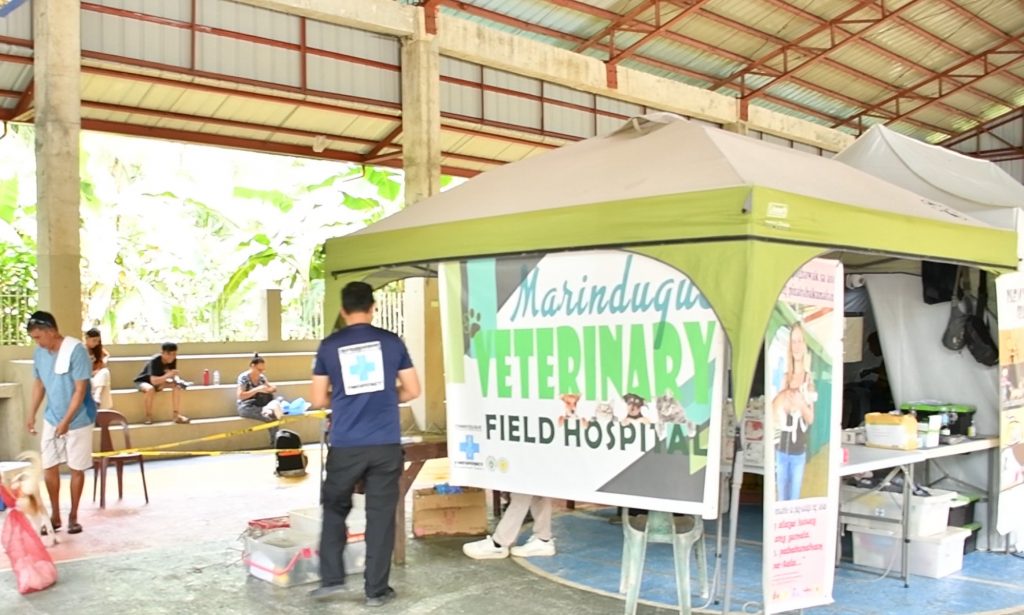

- Capability-building and Information Campaigns: The hospital implements capacity-building initiatives such as training programs and workshops for local veterinary professionals and animal owners. By sharing knowledge and providing education, the field hospital contributes to the development of science-based animal husbandry within the community. This knowledge transfer empowers individuals, enhances long-term agricultural productivity, and promotes responsible pet ownership.
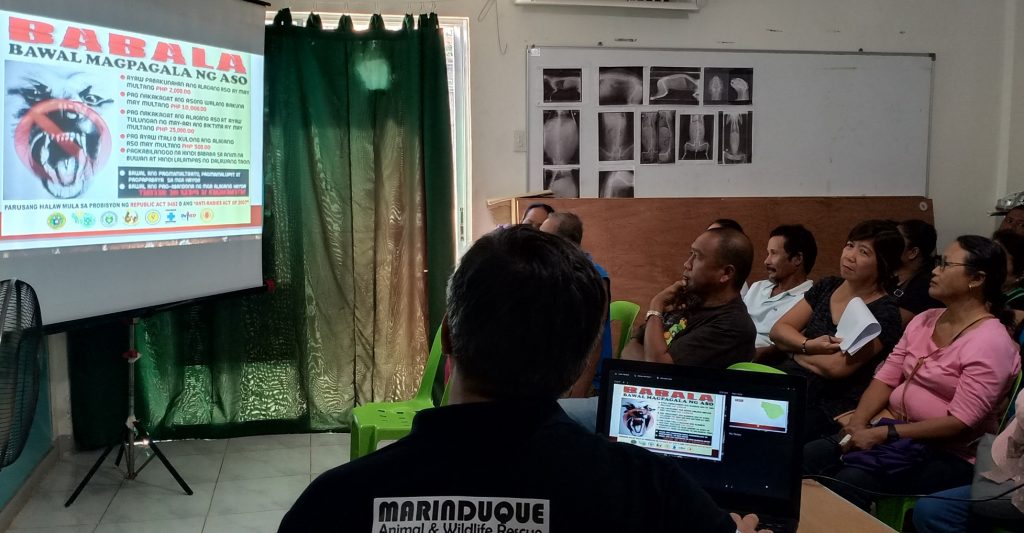

- Specialized Services: The field hospital offers specialized veterinary services to cater to specific animal health needs. This includes diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures for various pet and livestock diseases. By providing specialized care, the hospital ensures that pet owners and farmers have access to comprehensive veterinary care that addresses specific challenges faced by their animals. This focus on specialization is innovative as it tailors services to the unique needs of the agricultural sector in Marinduque. The following flowcharts describe the workflow for both pet and livestock animals undergoing consultation and treatment in the field hospital.
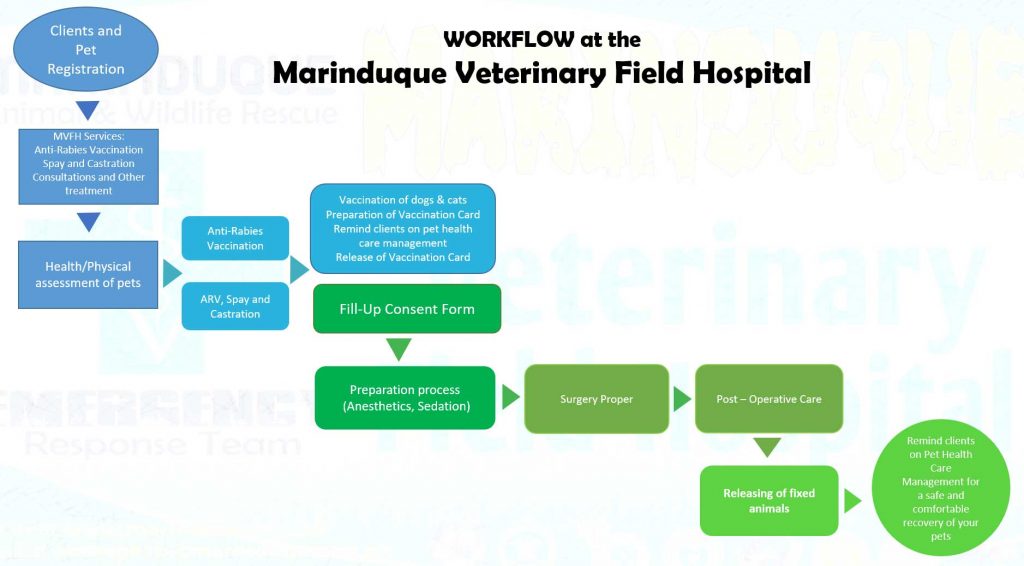
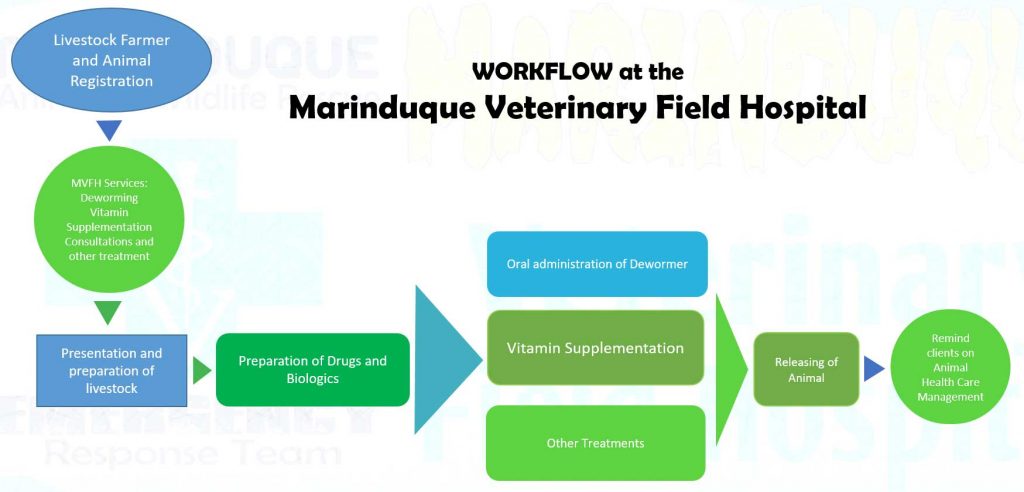
- Collaboration and Partnerships: MVFH collaborates with local government units, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders to maximize its impact. By fostering partnerships, the hospital leverages resources and expertise, creating a network of support for veterinary healthcare in the region. The MIMAROPA Initiative, also known as “Sa MIMAROPA ang Pagsugpo sa Rabies Sama-Sama, Hindi Kanya-Kanya,” is a program derived from the successful Marinduque Rabies Eradication Program. Its main objective is to make the entire MIMAROPA region the first rabies-free region in the Philippines. The initiative focuses on collaborative efforts among the provinces of MIMAROPA to create a perimeter defense around Marinduque and implement measures such as mass vaccination of dogs, spaying and neutering, culling of stray dogs, and restricting the movement of unvaccinated dogs. International foundations such as the Japan International Cooperative Agency (JICA) and Humane Society International (HSI) provided support to alleviate the measures by providing technology transfer and equipping the Provincial Veterinary Office through modern spay and neuter programs. The program’s main activity is the surgical removal of the reproductive organs of dogs and cats to prevent the birth of unwanted litters contributing to the overpopulation of unwanted animals that increases the transmission of rabies.

Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
MVFH has implemented various programs and services focused on animal health, disease prevention and control, animal welfare, animal production and development, regulatory services, and wildlife rescue.
Before the program was implemented, human deaths due to rabies reached 12 in the late ‘90s. In 2001, six people died due to rabies. The radical approach of MVFH finally resulted in zero human deaths from 2006 up to the present. The province was then officially declared rabies-free in 2012 by the Department of Agriculture, Department of Health, and National Rabies Prevention and Control Committee.
Barangay Ipil Health Worker and Pet Owner Nina Pereda Rocamora and Marinduque Agricultural Technologist Glenn Deligero shared their insights on the importance of the Veterinary Field Hospital in her community.


These initiatives aim to protect the province from the incursion of emerging and existing animal diseases with economic and public health importance while also providing immediate control and management of any possible occurrence of animal diseases or livestock infections. The following measurable productivity gains were recorded:
- From only 473 dogs and cats vaccinated against rabies in 2007, it increased to 2,885 in 2022, benefiting 2,082 pet owners.
- From only 150 dogs and cats spayed and castrated in 2012, it has increased to 1,627 in 2022.
- From 927 livestock animals provided vitamin supplementation in 2003, it has increased to 1,569 in 2022, further enhancing resistance to infection and preventing disease outbreaks, benefiting 898 livestock farmers.
- From 2,694 livestock animals receiving prophylactic medication in 2003, it doubled to 4,988 in 2022 to further control and eradicate parasitic infestations among susceptible animals, benefiting 2,087 farmers.
- In 2022, 3,083 livestock farmers were served, and 5,072 different species of animals with various health conditions were treated and prescribed with appropriate veterinary medicine.
- Intensive serological surveillance was conducted in every barangay and stockyard to expedite sentineling and repopulation of hogs.
- Awareness campaigns and orientations on rabies prevention were conducted, with 234 posters distributed and 63 orientations held.
- The veterinary field hospital conducted a pet blessing event, where 184 dogs and cats received check-ups, deworming, and vitamin supplementation.
- Artificial insemination was performed on 273 sows and gilts, improving swine productivity and efficiency.
- Animal dispersal programs distributed 4,255 animals, including cattle, carabao, goats, horses, native pigs, and native chickens, benefiting marginalized farm families.
These programs and services have contributed to improving animal health, disease prevention and control, animal welfare, and livestock development in Marinduque province. They have also enhanced the protection of public health and economic stability by ensuring the biosecurity and well-being of animals.
Lessons Learned and Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
Throughout its implementation, several lessons were learned, and potential areas of improvement were identified. One significant lesson learned was the importance of comprehensive disaster preparedness planning. The field hospital faced challenges in terms of logistics and resources during its establishment. It became evident that having a robust contingency plan, including prepositioned supplies and trained personnel, is crucial to ensure efficient response during emergencies. Additionally, the experience highlighted the need for effective coordination and collaboration among relevant stakeholders, such as government agencies, local communities, and veterinary organizations. Strengthening partnerships and establishing clear lines of communication can enhance the overall effectiveness of the field hospital. Provincial Public Employment Officer and Pet Owner Alma Timtiman shared the importance of the hospital’s partnerships with other Provinces in the MIMAROPA Region.

Another lesson learned was the significance of community engagement and education. The field hospital faced challenges in reaching remote communities and raising awareness about the services it provided. To overcome this, it was important to involve local leaders and community members in the planning process and design outreach strategies that consider the unique needs and cultural context of the region. By investing in community engagement and education, the field hospital can foster a greater understanding of the importance of animal welfare and create a network of support during emergencies. Marinduque Provincial Agricultural Technician Verona Laylay shares the importance of community engagement and education.

In terms of potential areas of improvement, MVFH could benefit from ongoing training and capacity building for its staff. By staying updated on the latest veterinary practices and techniques for disaster response, the hospital can enhance its ability to provide high-quality care to animals. Additionally, the field hospital could explore the use of technology and data management systems to streamline its operations and improve the efficiency of data collection, analysis, and reporting. This can help in monitoring the impact of the hospital’s services and identifying areas for improvement.
Furthermore, the field hospital could consider establishing partnerships with local veterinary clinics and organizations to expand its reach and capacity. By leveraging existing resources and expertise, the hospital can extend its services beyond emergency response and contribute to long-term animal healthcare in the region. Finally, the field hospital should continue to evaluate its performance and collect feedback from stakeholders to ensure continuous improvement and address any emerging challenges.
Overall, the implementation of MVFH has provided valuable insights into the importance of preparedness planning, community engagement, and ongoing capacity building. By incorporating these lessons and focusing on potential areas of improvement, the field hospital can enhance its effectiveness and significantly impact animal welfare during emergencies.
Resources
Benosa, D. J. A. (2016, September 30). 2 island municipalities of Romblon declared as rabies-free, Marinduque among Best Rabies Program implementer. Department of Agriculture MIMAROPA. https://mimaropa.da.gov.ph/media-resources/news-and-events/2-island-municipalities-of-romblon-declared-as-rabies-free-marinduque-among-best-rabies-program-implementer
Stranded na sunfish sa Marinduque Sinaklolohan ng mga mangingisda. ABS-CBN News. (2021, July 21). https://news.abs-cbn.com/news/07/21/21/stranded-na-sunfish-sa-marinduque-sinaklolohan-ng-mga-mangingisda?fbclid=IwAR08AafqBfcb2g0iWnPqBn0Vc-6MIBV55hCqpGoUQPskhJPkaUW56qBrRLU
