Themes
Regulatory Reform: The ‘Good Regulatory Practice’ (GRP) initiative focuses on improving regulatory quality by reforming regulations to remove unnecessary obstacles, thereby promoting competition, innovation, and growth. It aims to ensure that regulations are efficient and serve important social objectives effectively.
e-Government: The use of information and communication technologies, such as the SMARTGPB System and Xpats Gateway, enhances the productivity and efficiency of public-sector delivery.
Overview
Through the Malaysia Productivity Corporation (MPC) strategy, digitalization initiatives were introduced to resolve regulatory burdens, and expedite approval process. These measures focus on public-private partnerships and workforce enhancement to enhance annual productivity by 3.7% from 2021 to 2025, which results in higher wages for citizens, increased profits for businesses and revenue for the government.
Challenge
Malaysia’s public sector faces inefficiencies that impede organizational productivity, which create bureaucratic barriers that complicate processes and stifle the business environment. This includes ineffective regulations contributing to delays, higher costs, and reduced competitiveness that hamper private sector growth and national development. Feedback from businesses and international competitiveness reports underscore these issues, highlighting the need for more streamlined regulations. The primary challenge lies in transforming these inefficiencies into an effective system that supports productivity and economic prosperity
Solution/s
Malaysia’s regulatory practices address administrative inefficiencies to enhance national productivity. Key solutions include modernizing regulations, streamlining processes, and fostering public-private partnerships through the following systems:
PEMUDAH: An acronym for “Pasukan Petugas Khas Pemudahcara Perniagaan” or Special Task Force to Facilitate Business, is a public-private partnership established in 2007 by the Malaysian government to drive business regulatory reforms. Its unique approach lies in its structured collaboration between high-level public officials and private sector leaders. The Chief Secretary to the Government serves as the chair, with a private sector leader as co-chair. This partnership focuses on addressing regulatory inefficiencies by assigning issues to specialized Focus Groups, each co-chaired by public and private sector representatives. These groups assess business regulatory challenges and make actionable recommendations.
Through monthly meetings of its Working Group on Efficiency Issues (WGEI) and technical working groups, PEMUDAH continuously refines policies to ensure they are not more burdensome than necessary. The creation of the MyMudah initiative, along with the Unified Public Consultation (UPC) Portal, enables businesses to voice concerns in real-time, ensuring dynamic regulatory responses. PEMUDAH’s ability to rapidly address challenges was evident during the COVID-19 pandemic when it quickly instituted meetings to resolve issues related to workforce disruptions, supply chains, and cash flow for businesses. By leveraging continuous public-private collaboration, PEMUDAH ensures that regulations remain practical, competitive, and responsive to the evolving business landscape.
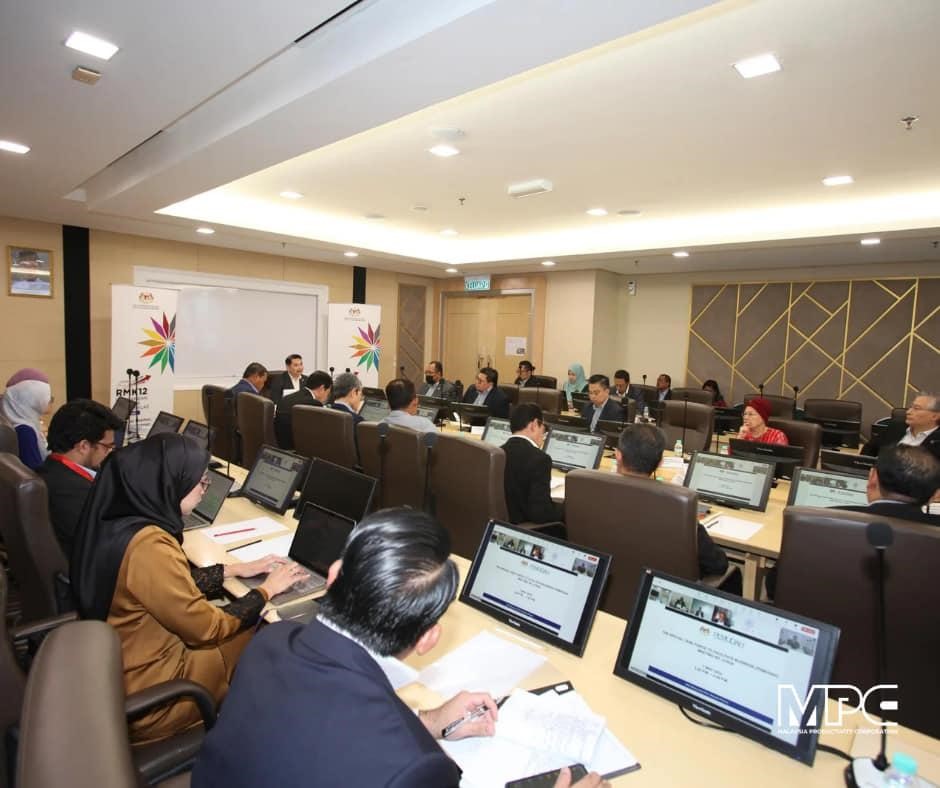

Image 1: PEMUDAH Meeting last 07 May 2024 held at Putrajaya, Malaysia
Productivity Nexus: An industry-led initiative that drives sector-specific productivity improvements across fourteen key subsectors, including Agro-Food, Chemicals and Chemical Products, Construction and Built Environment, Electrical and Electronics, Digital, Logistics, Machinery and Equipment, Professional Services, Retail and Food Beverages, Tourism, Private Healthcare, Automotive, Pharmaceuticals and Aerospace. Each sector is led by industry champions who act as role models for change, leveraging their deep connections and practical knowledge to drive impactful reforms. Its main focus is on empowering private sector entities—through associations and enterprise leaders—to take charge of productivity enhancements that are tailored to their unique sector needs. By capitalizing on their strong networks and acting as the collective voice of the sector, these industry leaders ensure that the reforms are not only relevant but also practical for real-world application.
Since its launch in 2017, it has successfully organized numerous programs, promoting public-private partnerships to advance the productivity agenda. Through WayUp.my, Malaysia’s official productivity portal, businesses and the public can access a single-window service that provides essential information and resources from the government, industry associations, research institutions, and NGOs. This strategic collaboration ensures that productivity-enhancing initiatives under the Malaysia Productivity Blueprint are accessible and impactful, fostering accountability and targeted improvements that are sector-specific, thus promoting long-term competitiveness and growth across industries.
Image 2: Screenshot of MPC’s Way-up Website, which houses the Productivity Nexus Program
SMARTGPB System: GPB stands for Gudang Pengilangan Berlesen, which translates to “Licensed Manufacturing Warehouse,” is a system developed by the Royal Malaysian Customs Department that transitions customs clearance from a manual three-day process to an online submission completed in one minute. Its innovation lies in leveraging digitalization and a risk-based approach to drastically reduce processing times and compliance costs, benefiting over 2,000 companies.
Image 3: Screenshot of the Royal Malaysian Customs Department Smart GPB Log-in Page
Xpats Gateway: This single-window platform integrates various systems to expedite expatriate work pass approvals from six months to five days. Its innovative nature stems from its comprehensive integration and streamlined process, which ensures the availability of skilled talent for high-growth sectors.

Image 4: Screenshot of the Xpats Gateway Single Window Platform Website
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
Improved customs clearance for LMW companies from a manual three-day process to the SMARTGPB System reduced the clearance time to just one minute. This digital innovation benefits 2,000 LMW companies and saves RM200 million annually in compliance costs. Expanding the SMARTGPB System across various regions and modules further enhances efficiency in customs processes.
Amending regulatory practices, such as allowing the construction of hospitals exceeding 12 floors, has increased productivity and investment, with each new hospital contributing RM411.6 million in value. This addresses land availability issues in major cities, leading to more efficient use of resources.
Malaysia Productivity Blueprint, launched in May 2017, aims to boost national productivity by 3.7% annually from 2021 to 2025. The strategy includes five strategic thrusts: workforce, digitalization, industry accountability, robust ecosystem, and strong implementation. Public-private partnerships, such as PEMUDAH, and the Productivity Nexus, which drives sector-specific reforms, are critical to these efforts. The measurable productivity gains from these regulatory improvements have led to higher wages for citizens, increased business profits, and more government revenue. These outcomes collectively enhance Malaysia’s competitiveness on the global stage, fostering a more prosperous and efficient economy.
Lessons Learned/Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
Effective collaboration between public and private sectors, as seen with PEMUDAH, has proven crucial for identifying and addressing regulatory bottlenecks. However, maintaining this collaboration requires continuous effort and transparent communication to ensure all parties remain committed and aligned.
While the SMARTGPB System and Xpats Gateway have significantly streamlined processes, the rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates regular updates and improvements to these systems to maintain their effectiveness and security. Additionally, integrating various regulatory processes into single platforms has shown the potential to reduce bureaucracy. Still, this integration must be continuously refined to address any emerging inefficiencies or challenges.
Challenges encountered include resistance to change within some regulatory bodies and the need for extensive training to ensure that all stakeholders can effectively utilize new systems. Addressing these challenges involves fostering a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability within government agencies.
Future improvements could focus on enhancing data analytics capabilities to better monitor and evaluate the impact of regulatory changes. This would enable more precise adjustments and ensure that productivity gains are sustained over the long term. Overall, the initiative underscores the critical role of regulatory efficiency in driving national productivity agenda and economic growth.
