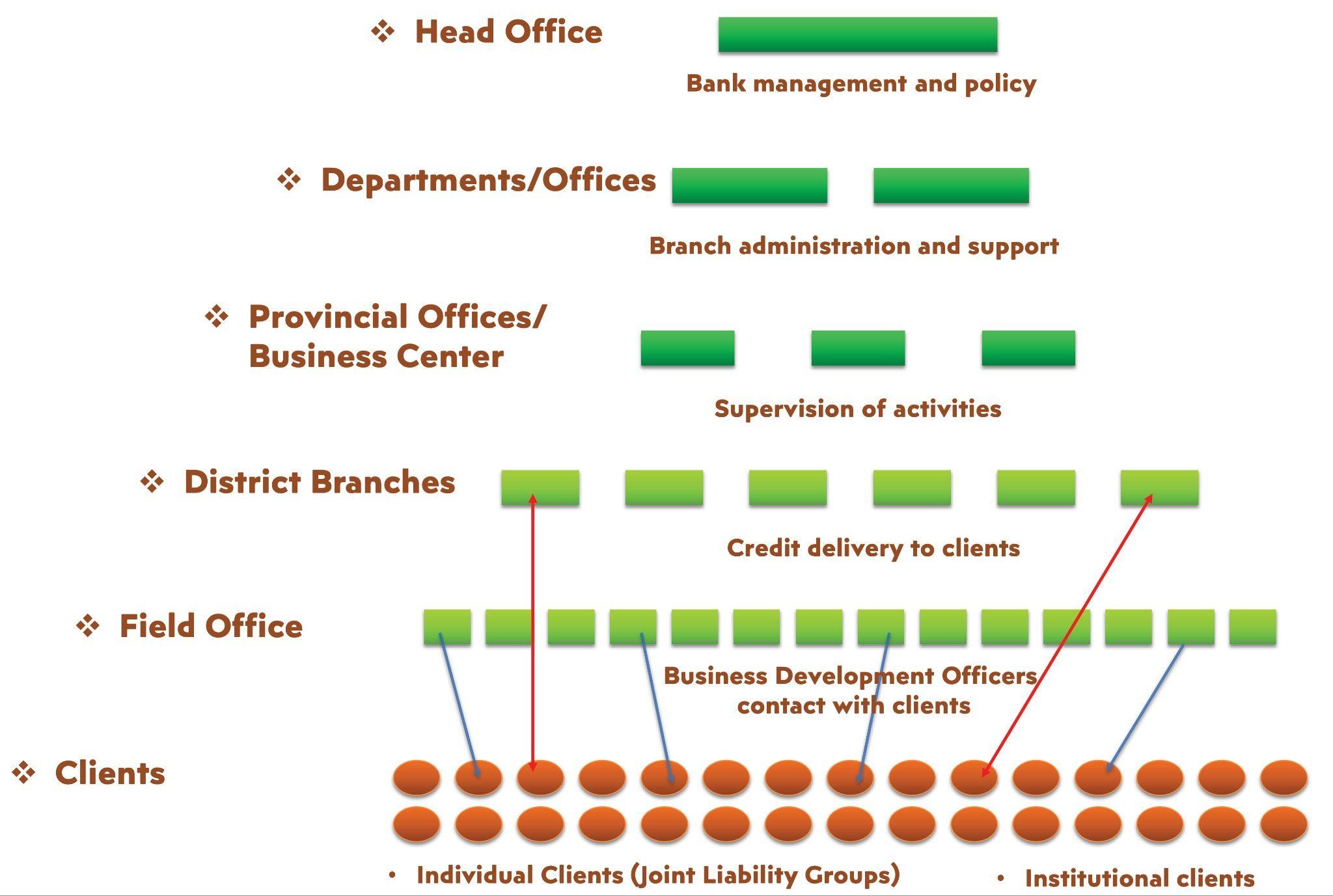
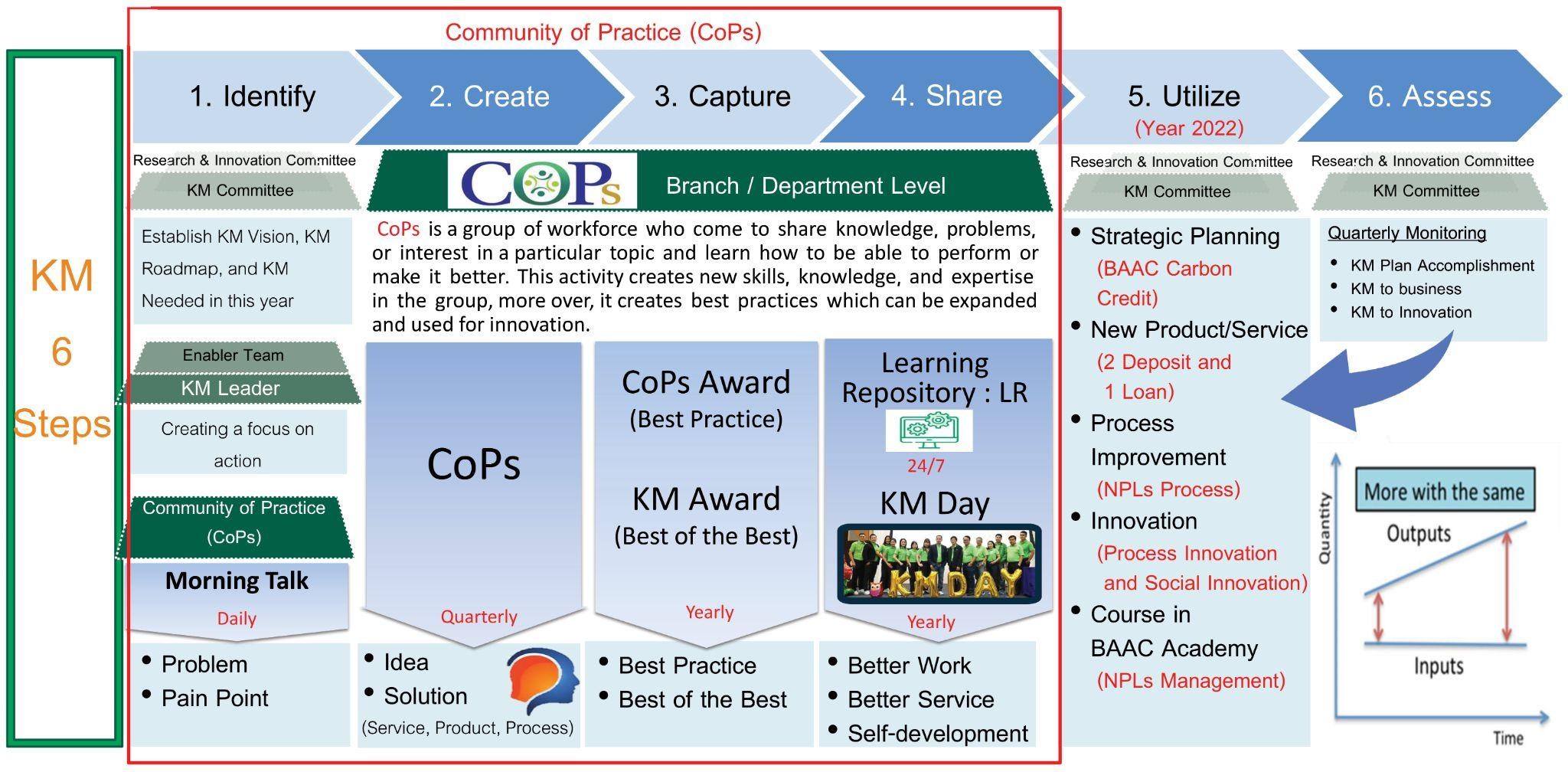
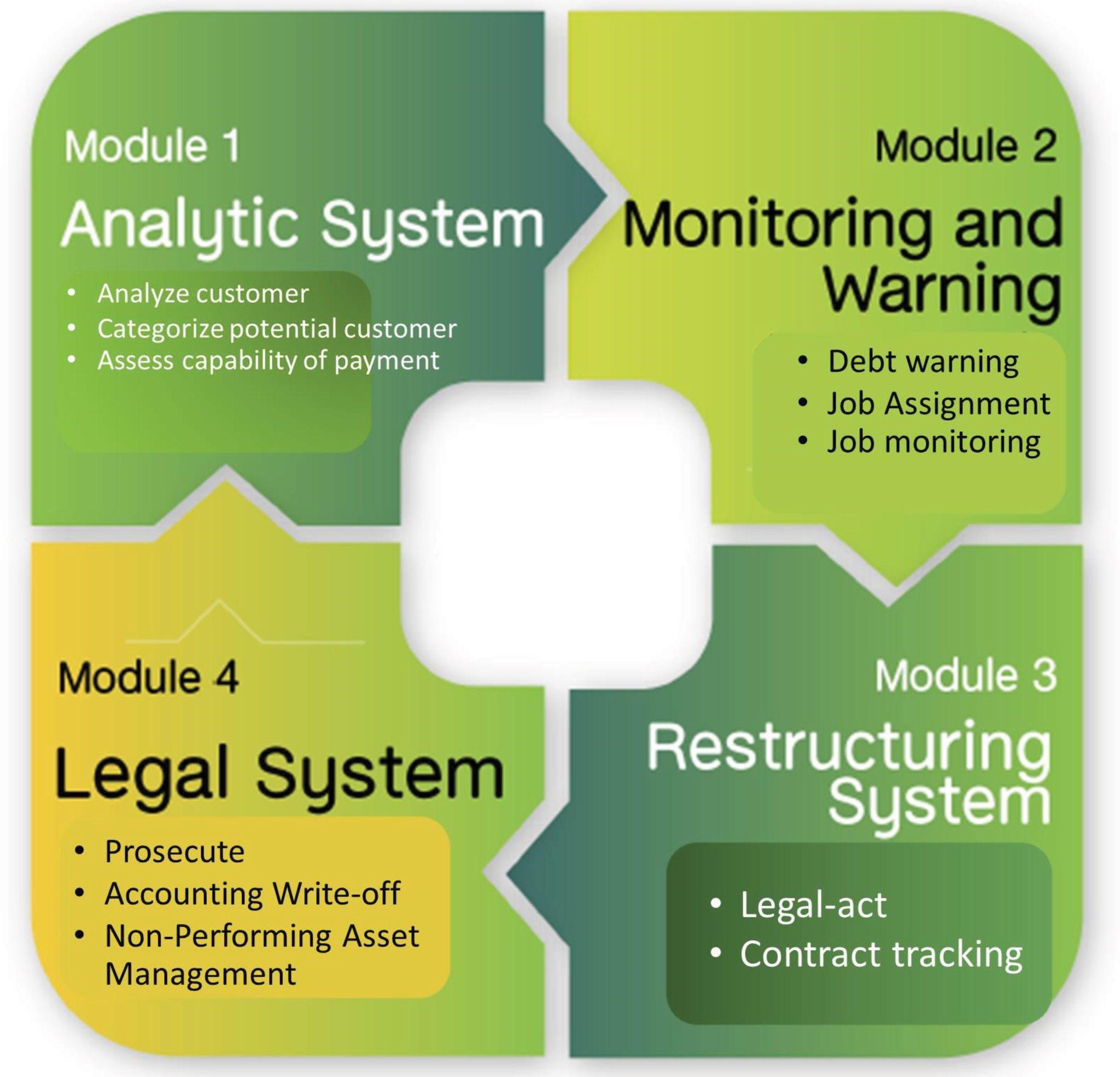
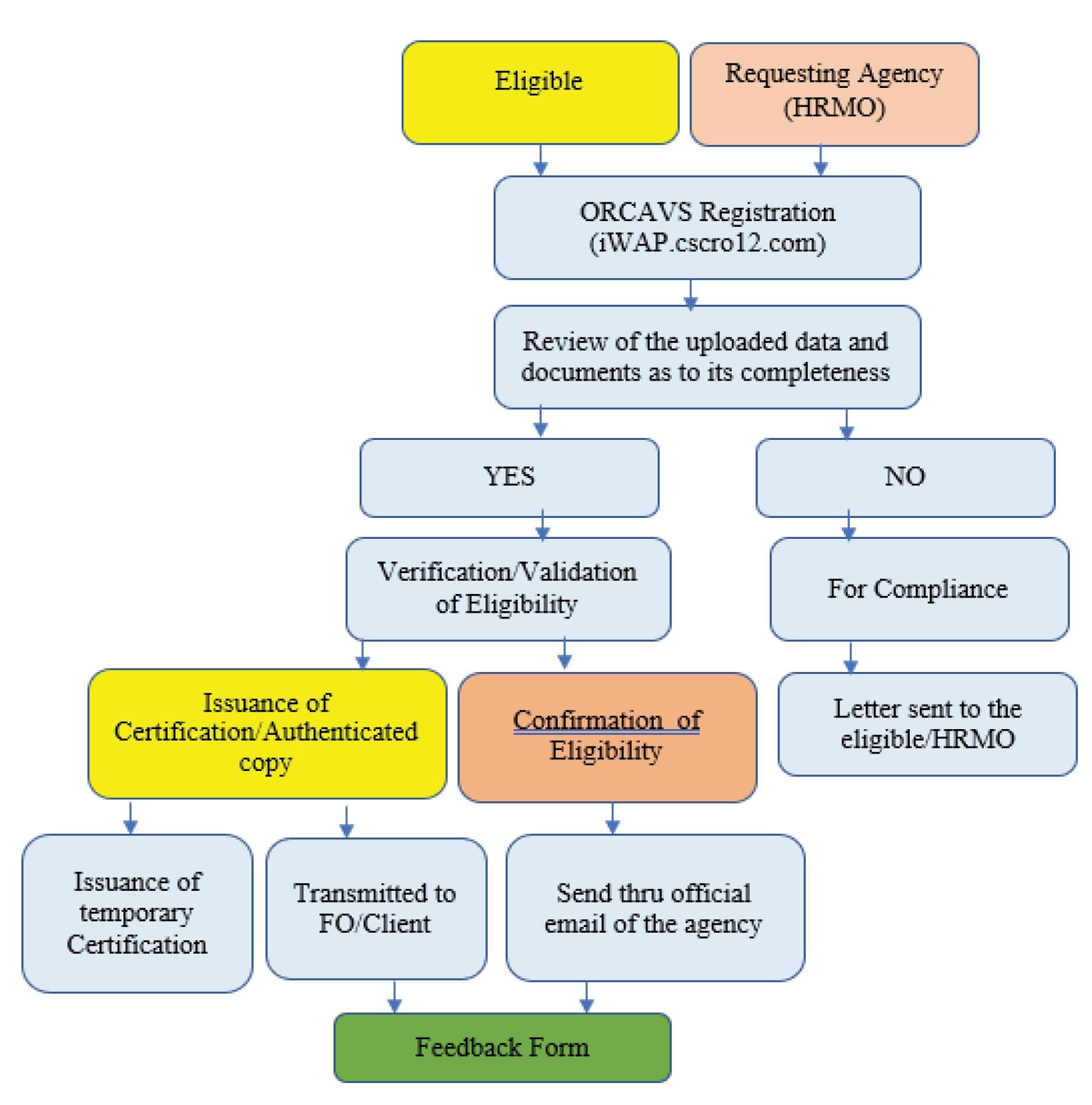
Themes
Citizen-Centered Service: The initiative emphasizes stakeholder collaboration, ensuring that health services are responsive to the needs and expectations of communities and empowering citizens through co-creation and engagement.
Innovation Leadership: SIHI leads the way in fostering social innovations in health, creating effective and inclusive solutions that improve public health outcomes.
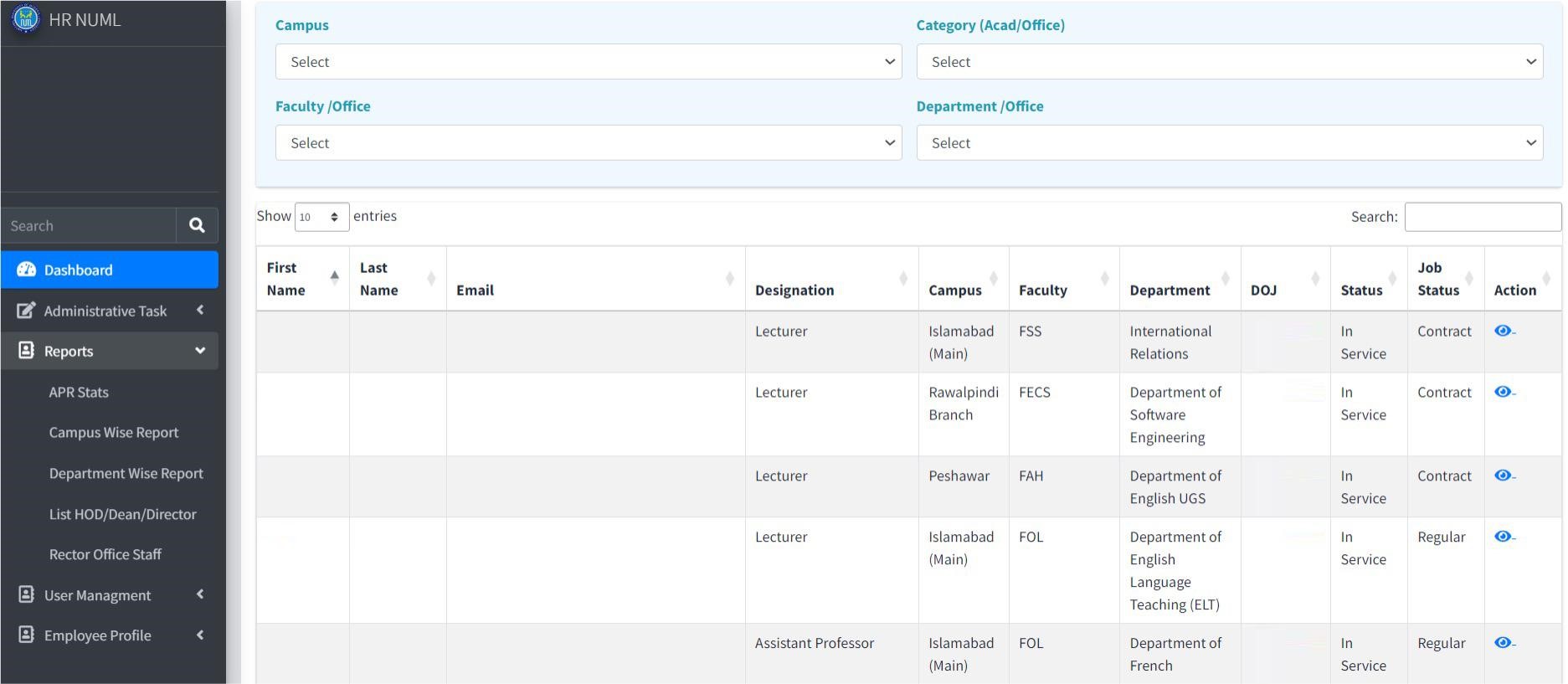
Overview
The UP Manila National Institutes of Health (NIH) Program on Social Innovation and Entrepreneurship in Health (PSIEH) focuses on addressing systemic health challenges in the Philippines through creative, community-driven solutions. One notable example of a social innovation in health is the One Boat Project. This innovative project addressed a significant challenge in healthcare accessibility in remote areas through an inter-island referral system connecting remote health centers to main birthing facilities. The PSIEH’s main strategies to advance social innovations in health include facilitating multi-stakeholder collaboration, capacity strengthening, and research to mainstream innovations in the broader health systems through initiatives like the Gelia Castillo Award on Research in Social Innovation in Health (GCARSIH), the PSIEH partners with social innovators to empower local solutions to improve health outcomes nationwide.
Challenge
The challenge lies in inefficient healthcare service delivery and difficulties in accessing healthcare services, particularly for marginalized populations in geographically isolated and disadvantaged areas. These inefficiencies contribute to inequitable access to essential healthcare, insufficient service quality, and overuse of already scarce public resources. Systemic issues such as poorly managed programs, fragmented health systems, corruption, and the failure to actively involve communities as partners in healthcare decision-making further exacerbate the problem and limit the potential for sustainable improvements. Services often do not align with the actual needs of these communities, which leads to inappropriate or ineffective care. The result is ineffective use of public funds, stagnant service delivery, and non-prioritization of the needs of underserved populations.
Solution/s
With these prevailing health challenges in the country, the Social Innovation in Health Initiative (SIHI) Philippines Hub was established in 2017 under the leadership of the late Dr. Noel Juban, with the aim of becoming a leading institutional partner for strengthening the country’s health system through social innovation. Seven years later, the Hub has been institutionalized as PSIEH and is hosted at the Institute of Clinical Epidemiology of the UP Manila National Institutes of Health (NIH) with Dr. Meredith del Pilar-Labarda as the lead. The program serves as the home of SIHI Philippines and the SIHI Secretariat. The SIHI Philippines Hub is part of a broader SIHI Global Network which consists of thirteen hubs across Africa, Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), and Europe. This network fosters international collaboration and knowledge sharing, creating a collective movement that empowers local actors to develop innovative health solutions tailored to their contexts.
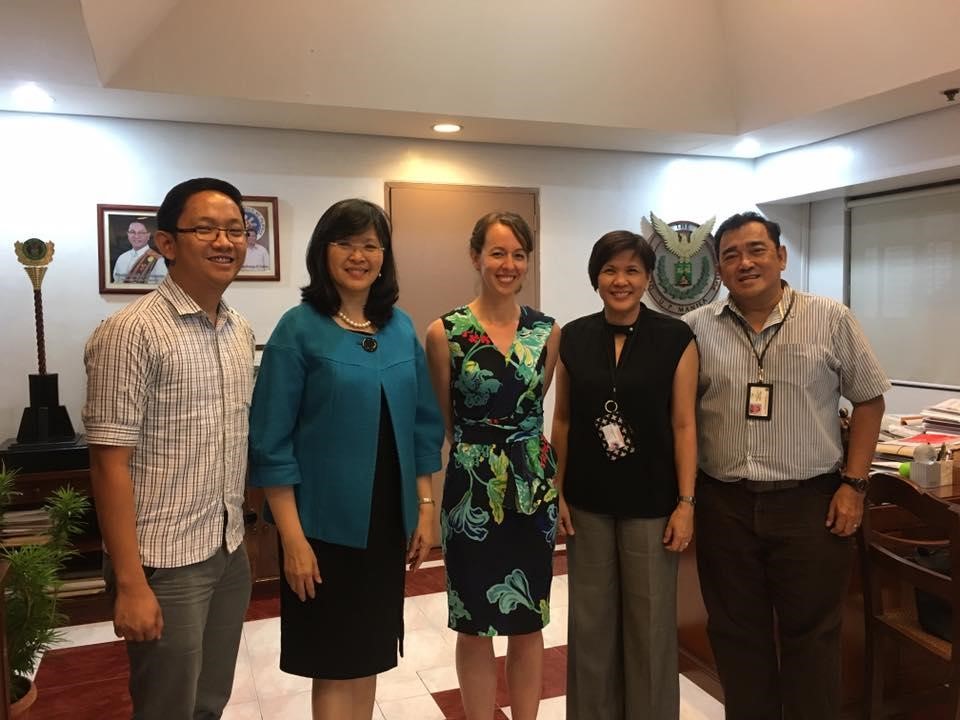

Image 1: UP Manila officials launched the SIHI program in 2017.
PSIEH focuses on social innovations as a catalyst to transform health systems by 2030. This program seeks to support community-engaged research and entrepreneurial initiatives through various activities, including capacity strengthening, knowledge brokering, and ecosystem development. By promoting social entrepreneurship in health, it aims to enhance the overall health landscape, improve health equity, and ensure that health solutions are accessible to all. It comes from the concept of social innovation in health, which refers to the development and implementation of creative and inclusive solutions that address systemic health challenges through multi-stakeholder collaboration. As defined by van Niekerk et al. (2017), it encompasses a variety of processes, products, and practices that profoundly challenge existing health systems, making healthcare more inclusive, effective, and affordable. Key characteristics of social innovation in health include:
- Stimulus: Addressing social problems faced by individuals and communities.
- Actors: Involvement of diverse social actors, organizations, and institutions.
- Sectors: Interplay across technical, social, economic, and political dimensions.
- Process: Emphasis on inclusive participation, collaboration, and coordination in decision-making.
- Qualities: Solutions that are more effective, efficient, sustainable, and just compared to existing approaches.
- Outputs: Introduction of new initiatives, services, and programs that enhance health delivery.
- Outcomes: Promotion of institutional or systemic changes and empowerment of communities.
- Impact: Improvement of quality of life and overall societal well-being.
SIHI emphasizes the importance of stakeholder collaboration across its four main focus areas:
Identification and Research: The initiative conducts rigorous research to identify and analyze local social innovations in health. Programs like GCARSIH recognize and support initiatives that address persistent health challenges in the Philippines. Guided by the principles of the late Dr. Gelia Castillo, a revered Filipino national scientist, the award emphasizes that “science must serve a human purpose” by extending research benefits equitably to all Filipinos.
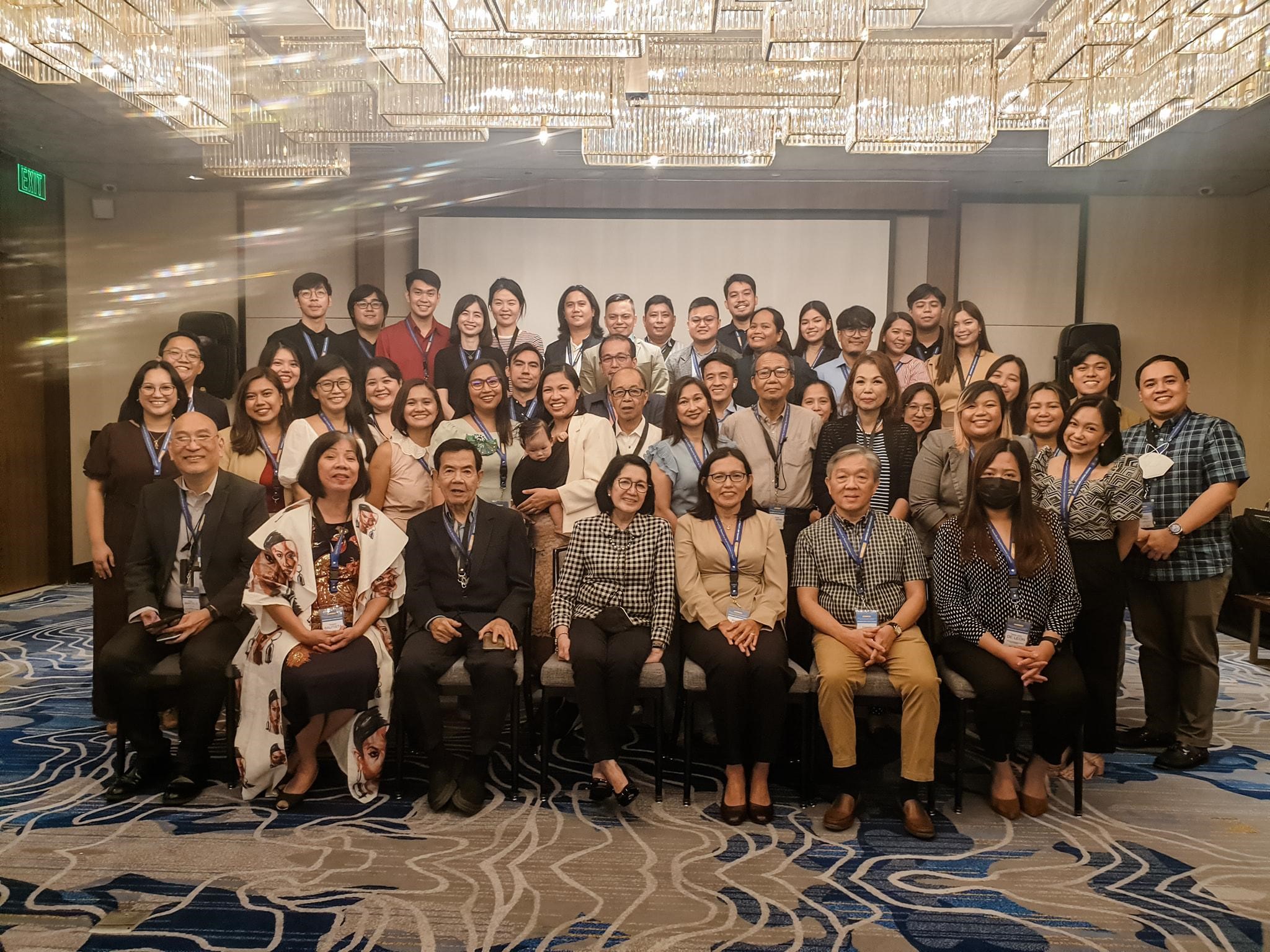

Image 2: Winners and finalists of the 2023 Gelia Castillo Award for Research on Social Innovations in Health.
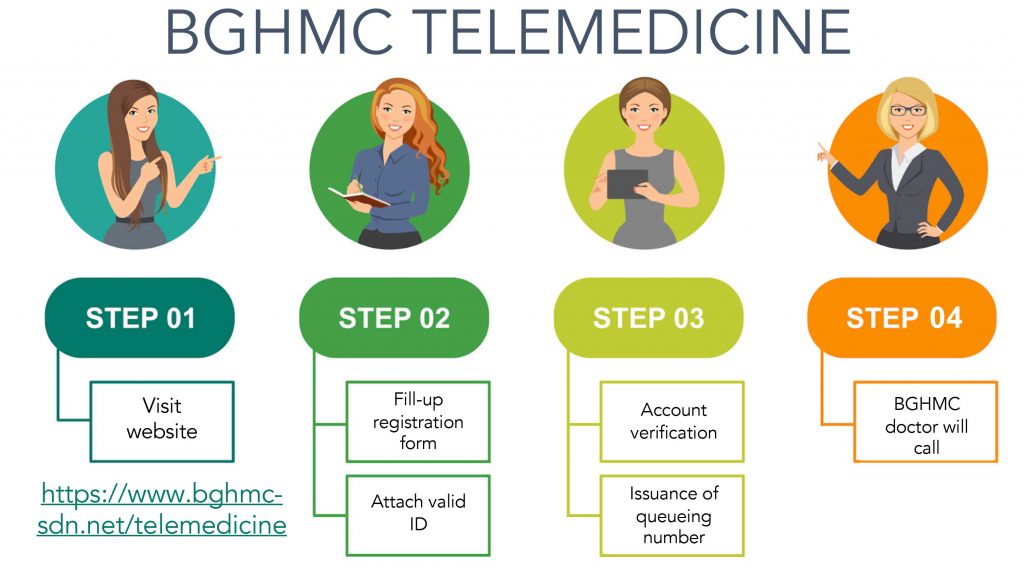
Capacity Strengthening: SIHI offers capacity strengthening activities and educational tools for stakeholders in the health sector. Utilizing human-centered design (HCD) approaches, it develops innovative models for delivering essential health services, training community health workers, and implementing telemedicine systems.
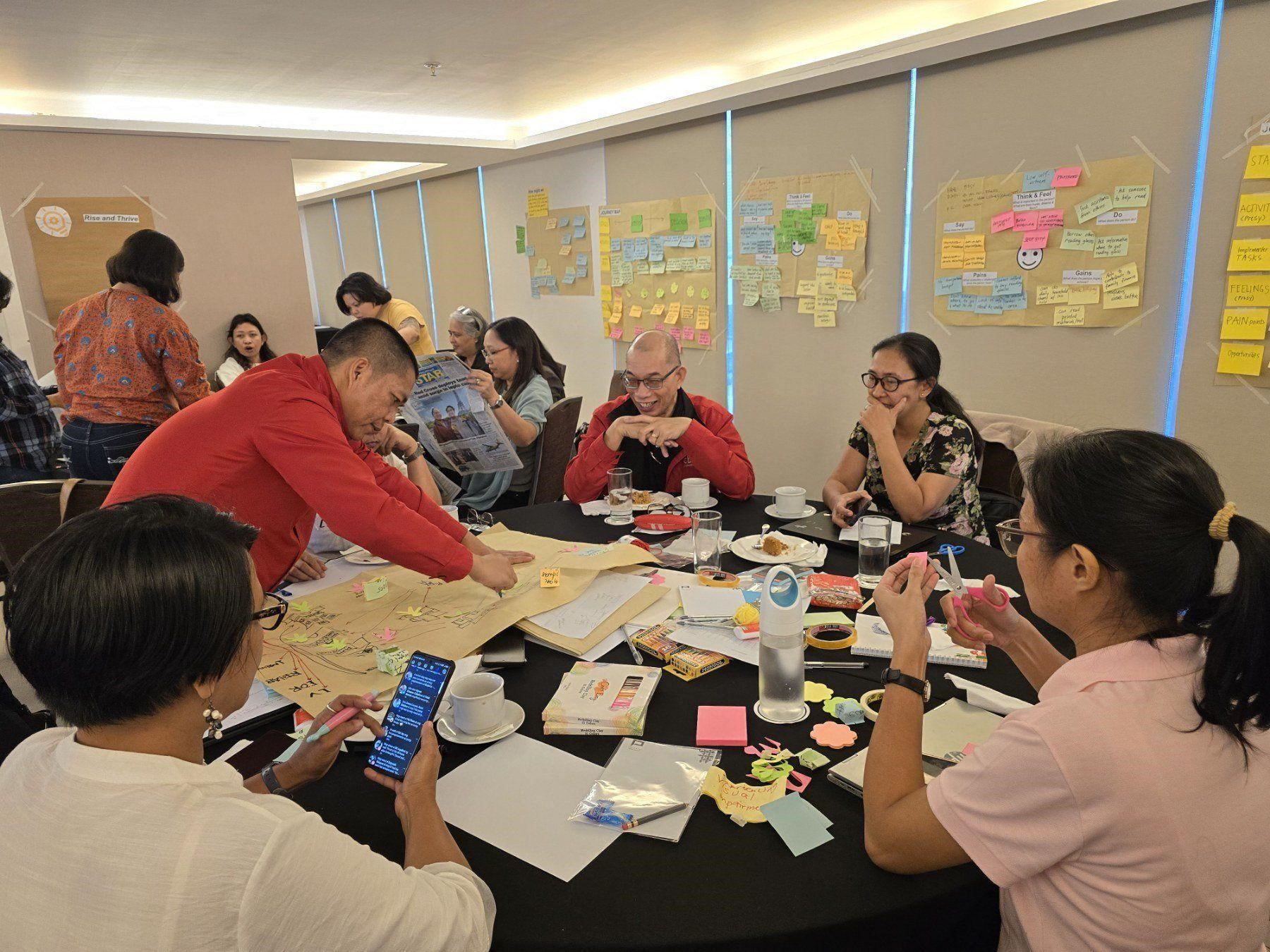

Image 3: Human-centered design (HCD) workshop for social innovations last September 2024 at Pasig City
Connecting and Convening: SIHI actively connects innovators, partners, and resources through initiatives such as the SIH Exchange (InnovEx) Platform and regular community engagement events. This fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and mutual support within the health innovation ecosystem. InnovEx serves as a hub for exchanging best practices, tools, and strategies for developing and scaling social innovations in health. It encourages participatory engagement by offering resources such as case studies, training modules, research articles, and opportunities for networking among like-minded individuals and organizations. The platform’s main goal is to break down silos, enabling the cross-pollination of ideas and fostering partnerships that can lead to impactful health innovations.
Image 4: Screenshot of the InnovEx website, which connects stakeholders to collaborate and address pressing health challenges through innovative approaches.
Knowledge Translation and Uptake: To facilitate the uptake of social innovations, SIHI employs advocacy strategies and support for innovators and other stakeholders in upscaling and institutionalization of the innovation into the health system. One of their examples is assisting the LGU of Del Carmen, Siargao in translating the Community Engagement Self-Monitoring (CE-SM) Strategy for social innovations in health into a municipal ordinance. CE-SM is a strategy for monitoring and evaluation that aims to empower communities by actively involving them in monitoring the progress and effectiveness of interventions. This innovative approach recognizes the importance of community participation as a cornerstone of successful health solutions, particularly in addressing systemic challenges and improving health outcomes at the local level. In the Philippine pilot of CE-SM, the strategy was tested and refined by drawing from the deep involvement of local communities in the identification, development, and assessment of social innovations before institutionalization as a municipal ordinance in Del Carmen, Siargao.
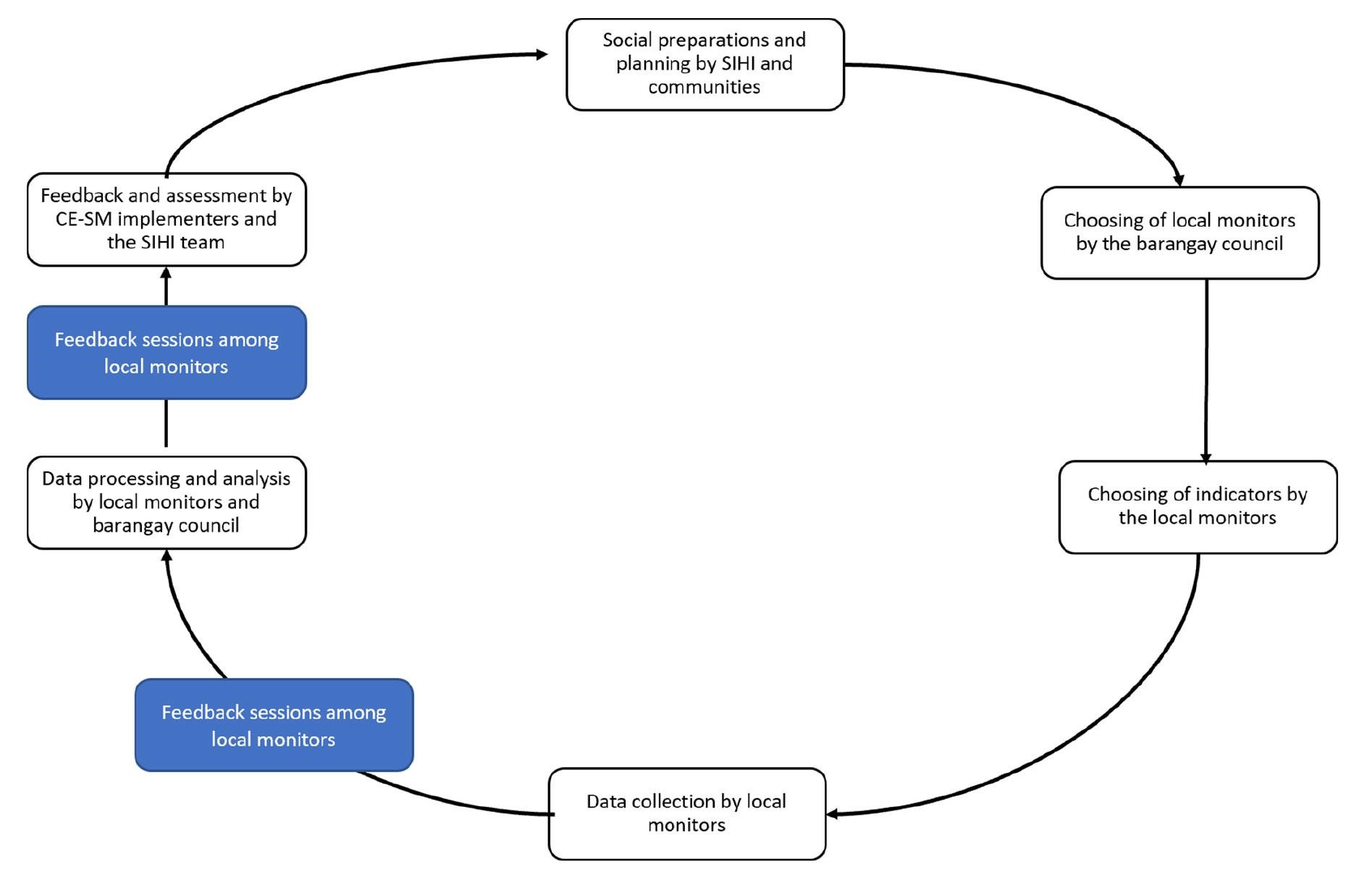
Image 5: Steps in the implementation of the CE-SM strategy. CE-SM, community engagement self-monitoring
By mainstreaming stakeholder collaboration, the Social Innovation in Health Initiative aims to build a robust ecosystem that empowers communities and enhances health service delivery across the Philippines.
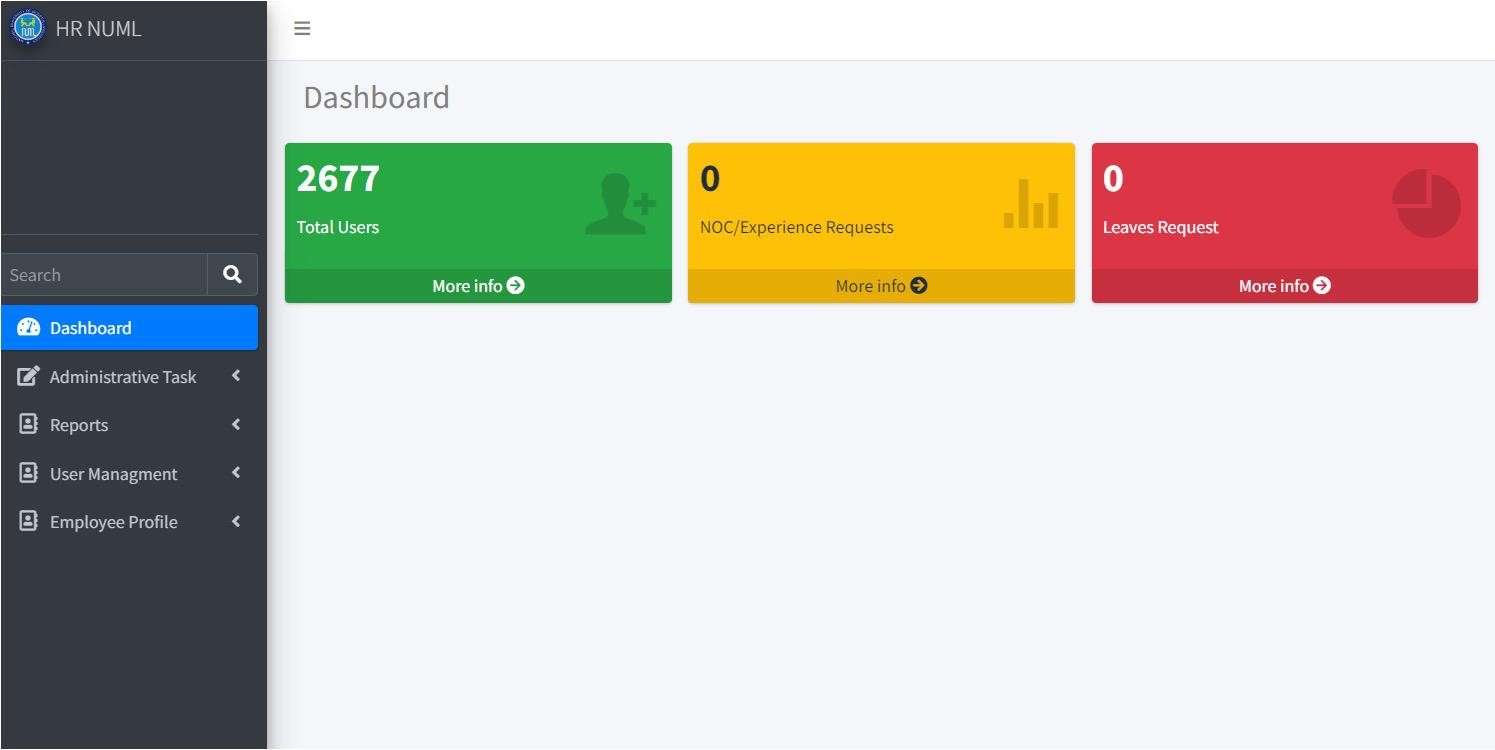
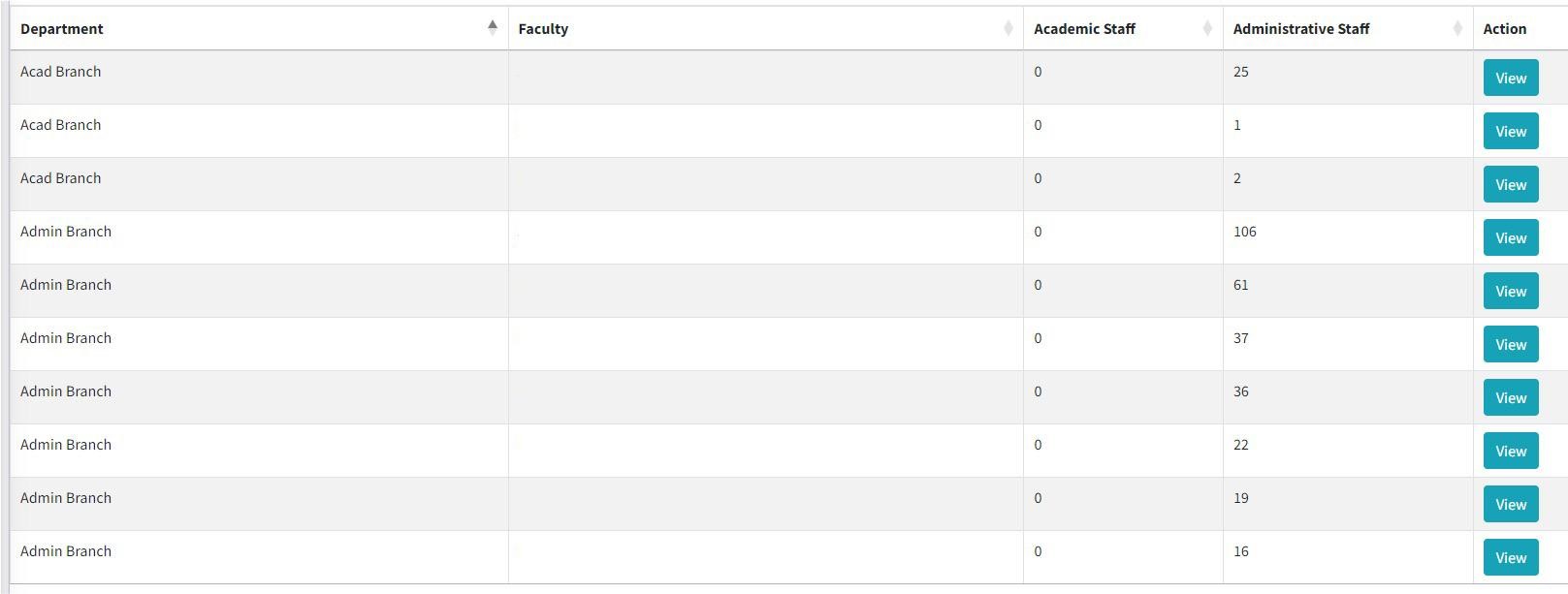
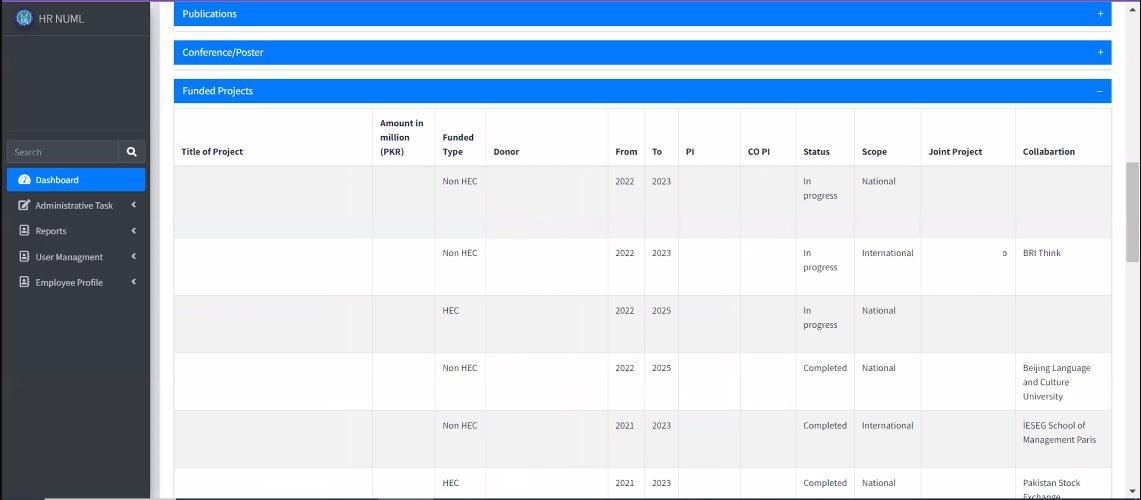
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
Since its inception in 2020, GCARSIH has recognized six winners and fourteen finalists over two cycles of the award. Each winner and finalist put forth innovative solutions that improve health outcomes and address systemic health challenges in their communities and has been support through the award. GCARSIH was established in collaboration with the Department of Science and Technology-Philippine Council for Health Research and Development (DOST-PCHRD). For instance, initiatives like the Holistic Water Systems for Pumping Water Uphill, Telepsychiatry, and the COVID-19 Risk Assessment, Monitoring, and Management Systems exemplify the diversity and effectiveness of social innovations nurtured by SIHI.
By fostering collaboration among government, academia, NGOs, and the private sector, these initiatives help fulfill UP Manila NIH’s mandate of creating scalable models that can be integrated into existing health systems. The support for these innovative projects not only elevates the profile of social innovations in health but also ensures that effective solutions are disseminated widely, ultimately improving health service delivery and equity for underserved communities. The impact of SIHI enhances productivity in health research and translates those gains into tangible benefits for Filipino communities, ensuring that innovative health solutions are accessible and sustainable.
Lessons Learned/Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
A key challenge was maintaining effective stakeholder collaboration, given the diversity of actors involved across sectors, with their own priorities. Establishing consistent communication and coordination mechanisms among these stakeholders can be difficult, as has ensuring inclusive participation, particularly from marginalized communities. Moreover, the sustainability of the initiatives has posed a challenge, as some projects have struggled to maintain momentum and funding once initial support waned.
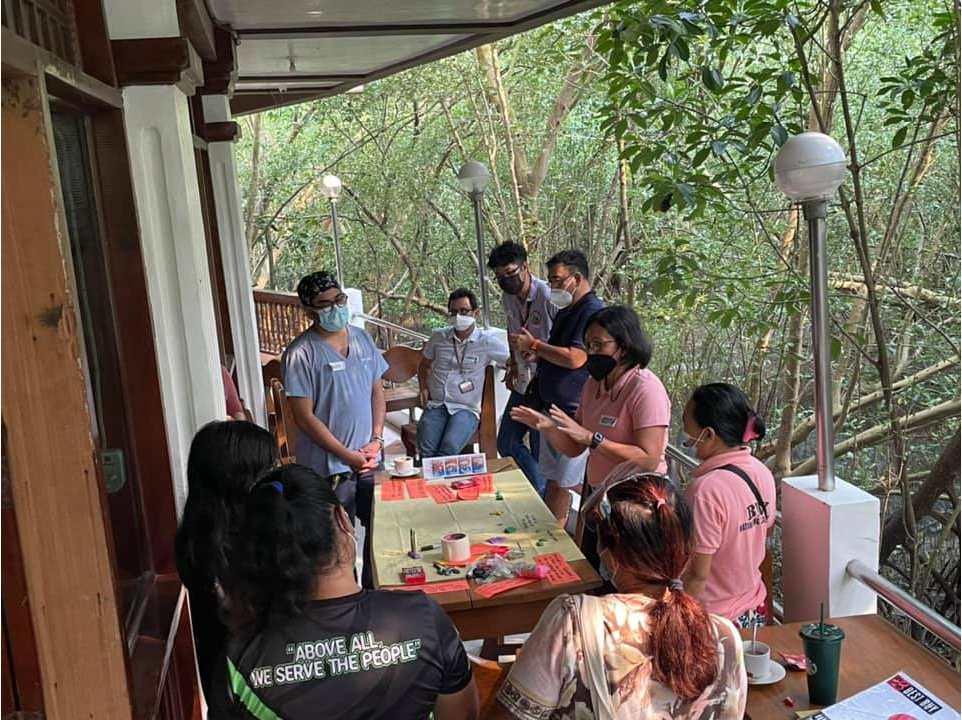

Image 6: SIHI and community members use human-centered design (HCD) to co-create solutions in three rural Philippine communities amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lessons learned from these challenges highlight the importance of embedding strong governance structures and accountability mechanisms early in the design phase to ensure project continuity. Additionally, there is a need for more robust monitoring and evaluation frameworks to measure the long-term impact of social innovations. Strengthening capacity-building efforts, particularly in research and implementation skills, will also be crucial for future success. Moving forward, PSIEH could benefit from focusing on improving resource mobilization and social entrepreneurship strategies, fostering deeper community engagement, and enhancing knowledge dissemination to ensure a broader uptake of successful innovations in the health sector.