Themes
e-Government: The Fortified OMGS is an app that leverages information and communication technologies to enhance the productivity and efficiency of public sector operations. By automating data collection, reporting, and analysis for operations and maintenance (O&M) inspections, the app significantly improves overall productivity and streamlines processes that were previously time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Innovation Leadership: The app introduces a more efficient and effective approach to O&M inspections, influencing public sector organizations to adopt new technologies and methodologies to accomplish public tasks more efficiently.
Overview
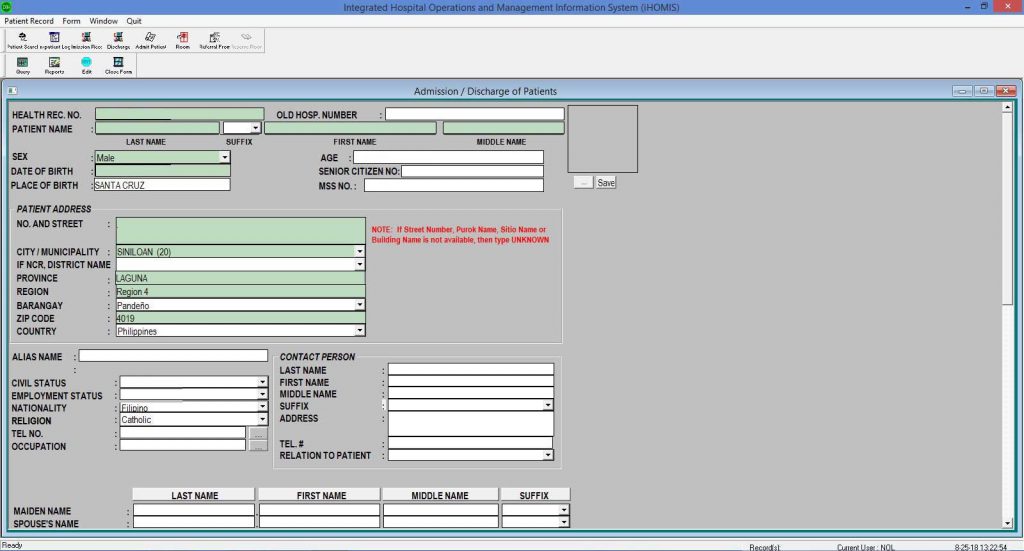
Using traditional operations and management (O&M) inspection processes, it faces lengthy data collection, reporting delays, and inefficient monitoring. The solution, the Fortified OMGS mobile application, utilizes geotagging technology to streamline inspections, enabling real-time data collection, reporting, and monitoring. This innovation significantly reduces processing times, improves data quality, enhances accessibility and transparency, and fosters cost-effective operations. The project benefits multiple stakeholders, including the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH), Toll Regulatory Board, and private concessionaires, ensuring improved infrastructure quality and public safety. Public-Private Partnership Service (PPPS) Director Pelita V. Galvez shares her thoughts on the use of technology in improving the delivery of public services.
Challenge
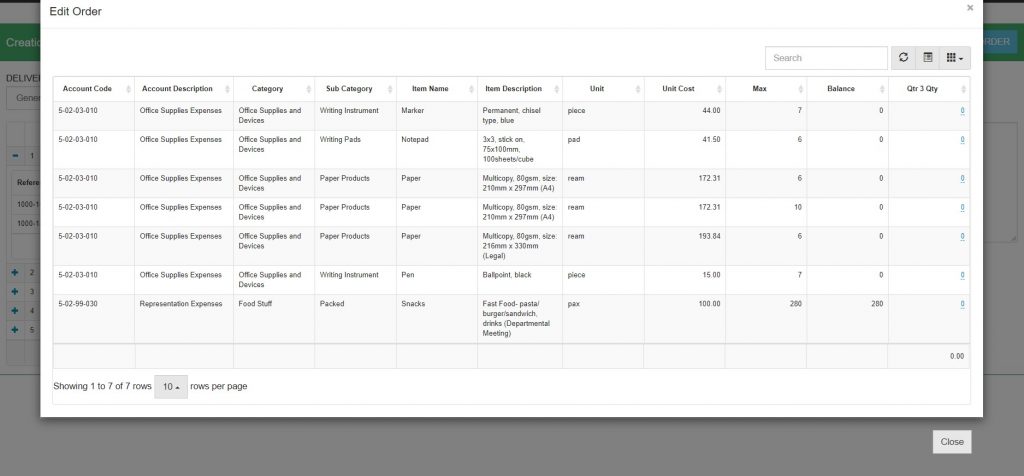
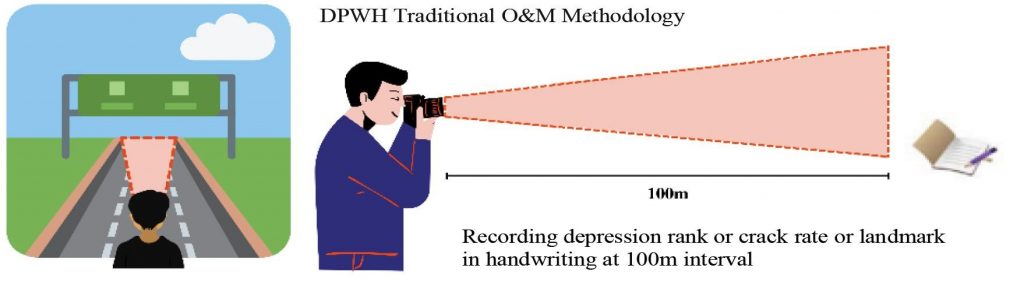
O&M inspectors are faced with the inefficient and time-consuming nature of traditional site visits for completed infrastructure projects, particularly national roads and expressways. The previous inspection process involves intensive manual methods such as visual inspections, handwriting recordings, and physical consolidations, leading to significant delays and gaps in data quality and usability. This cumbersome approach hampers timely rectification of road defects, causes delays in reporting and responding to issues, and leads to fragmentation among stakeholders. Consequently, there is a pressing need for a more efficient, accurate, and real-time system to enhance the overall productivity and effectiveness of the O&M inspection process.
Solution
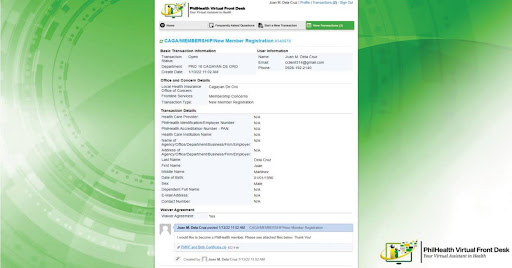
The Fortified Operations and Maintenance Geotagging System (OMGS) is an innovative mobile application designed to streamline and enhance the road inspection process for the DPWH and related stakeholders. This systematically gathered and analyzed data to identify shared challenges in the traditional O&M inspection process, which informed the development of the Fortified OMGS. The key features of the Fortified OMGS include:
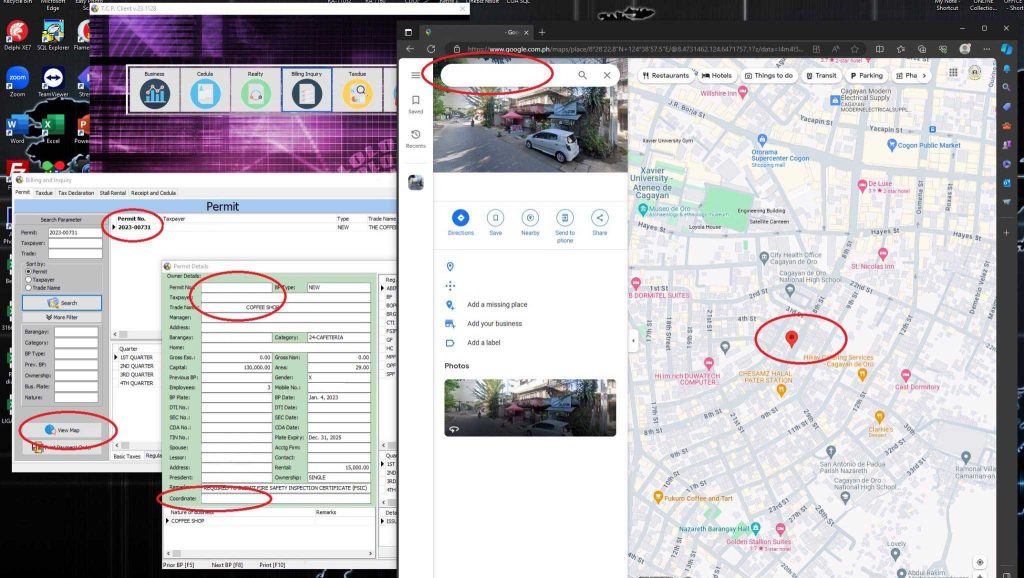
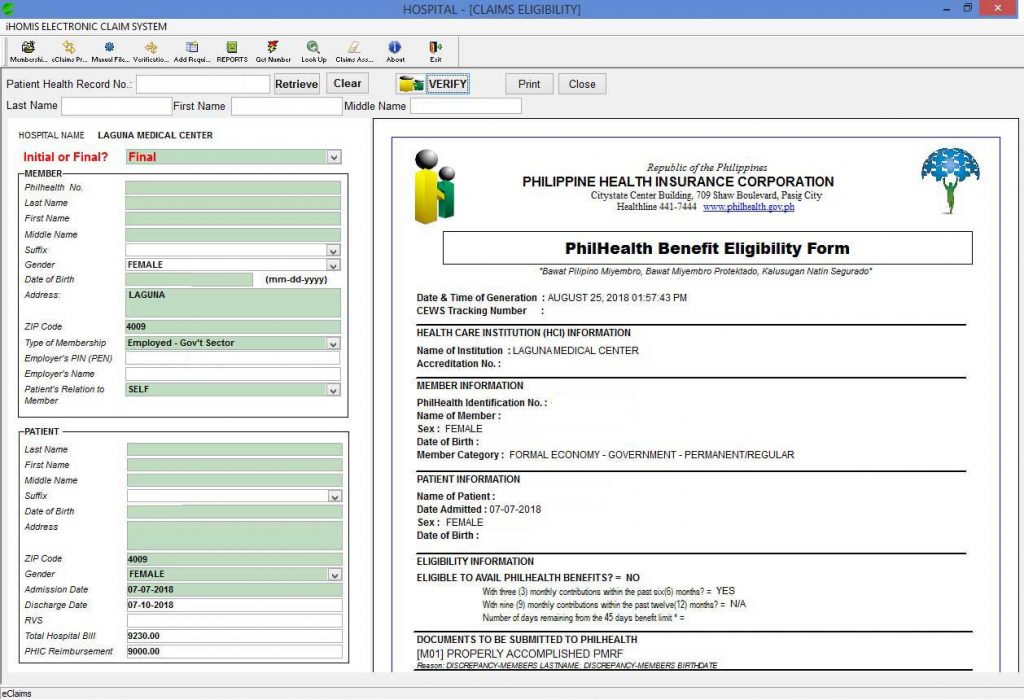
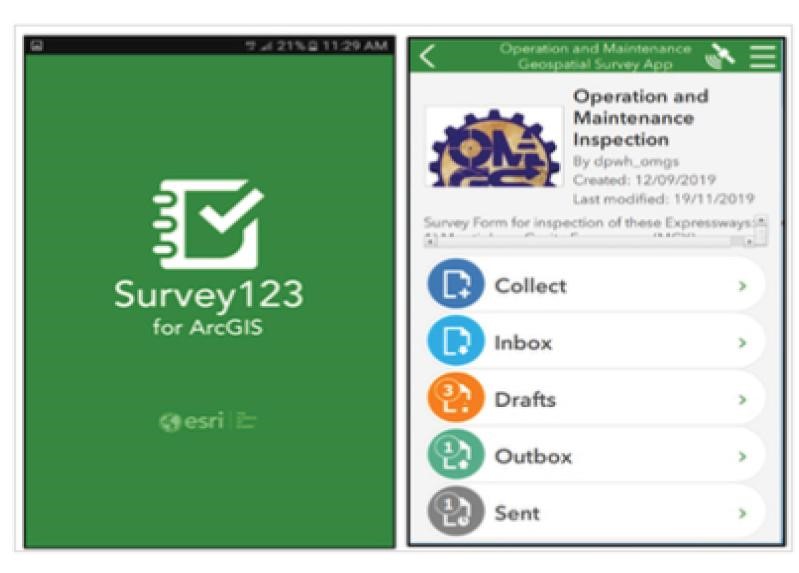
Geotagging and Photo Elicitation: Enables inspectors to geotag defects and upload photos, allowing for precise location tracking and visual documentation of road conditions.
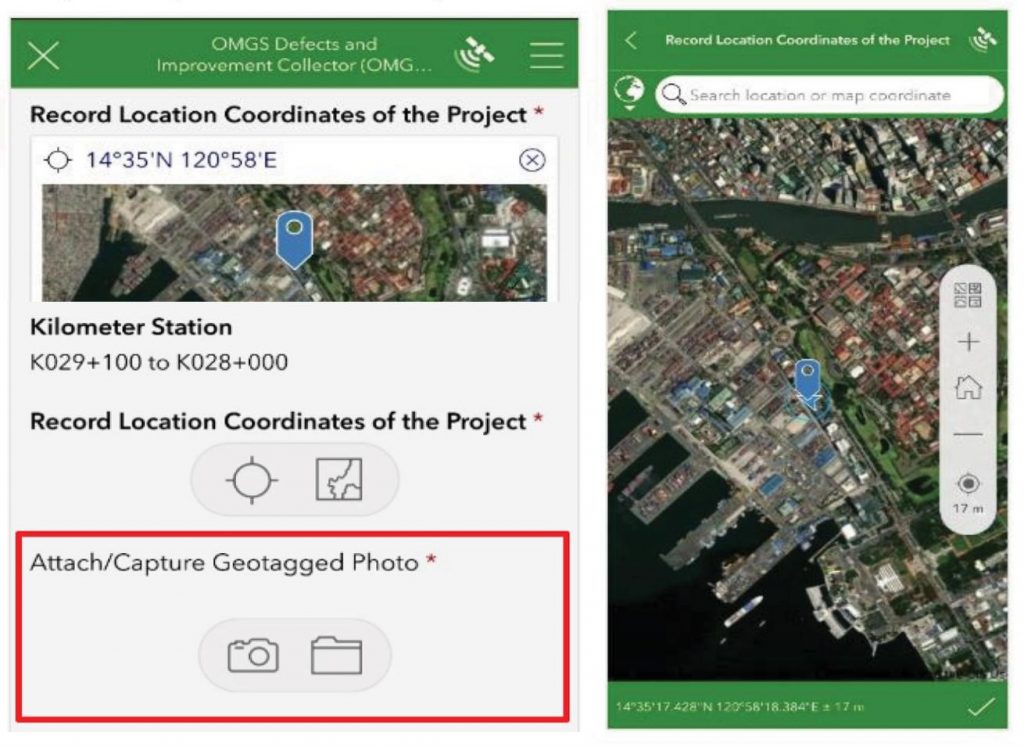
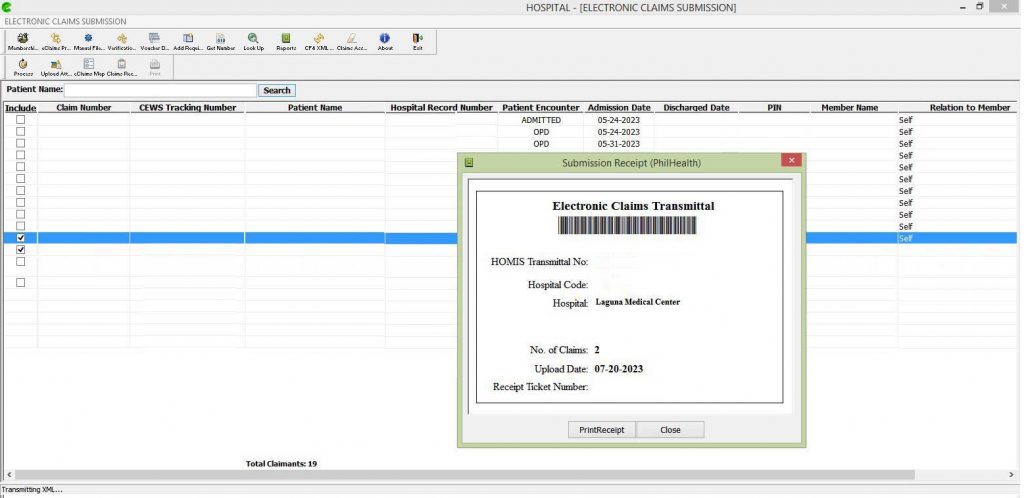
Real-time Data Submission and Notifications: Facilitates immediate reporting and notifications of identified road defects, enhancing communication between inspectors and concessionaires.
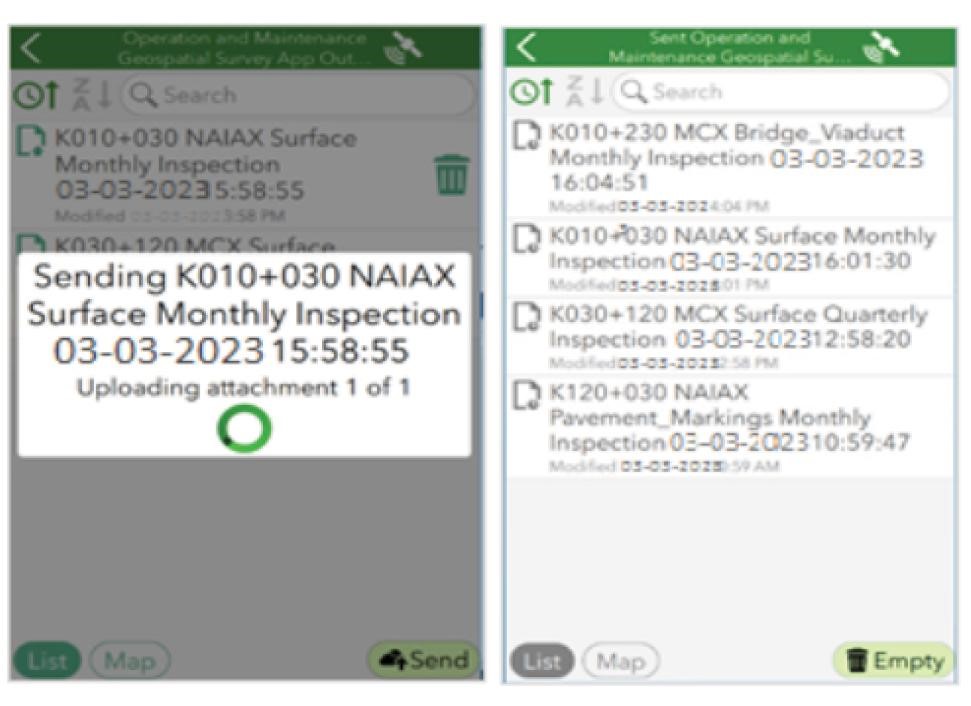
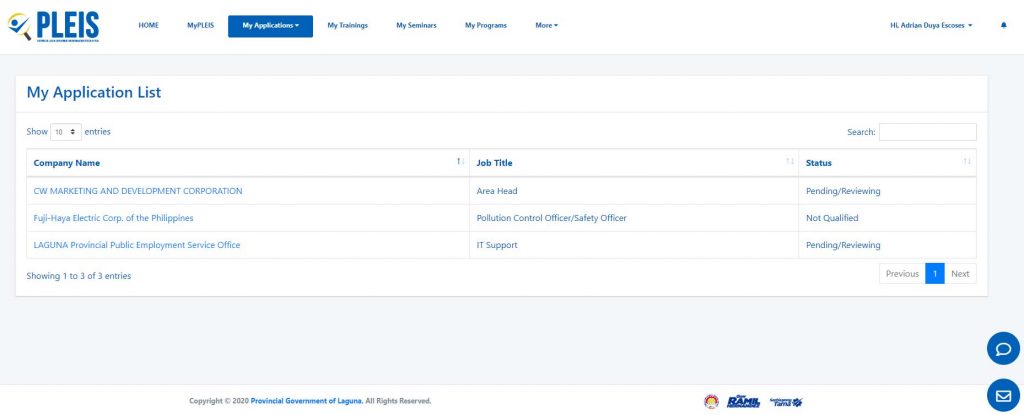
Defect Monitoring Dashboard: Provides a centralized platform for tracking the status of reported defects and ongoing repairs.
Automated Reporting: Streamlines the preparation of inspection reports, reducing time and effort in documentation.
User-friendly Interface: Simplifies data input and retrieval processes for inspectors, making the application accessible and easy to use.
The application was developed through a rigorous process involving qualitative data collection from interviews and focus groups, and quantitative data from surveys and field tests. This mixed-methods approach ensured that the Fortified OMGS was tailored to address practical issues identified by O&M inspectors, ultimately enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and transparency of the road inspection process. The implementation plan includes continuous refinement and updates, ensuring that the system evolves to meet emerging needs and technological advancements.
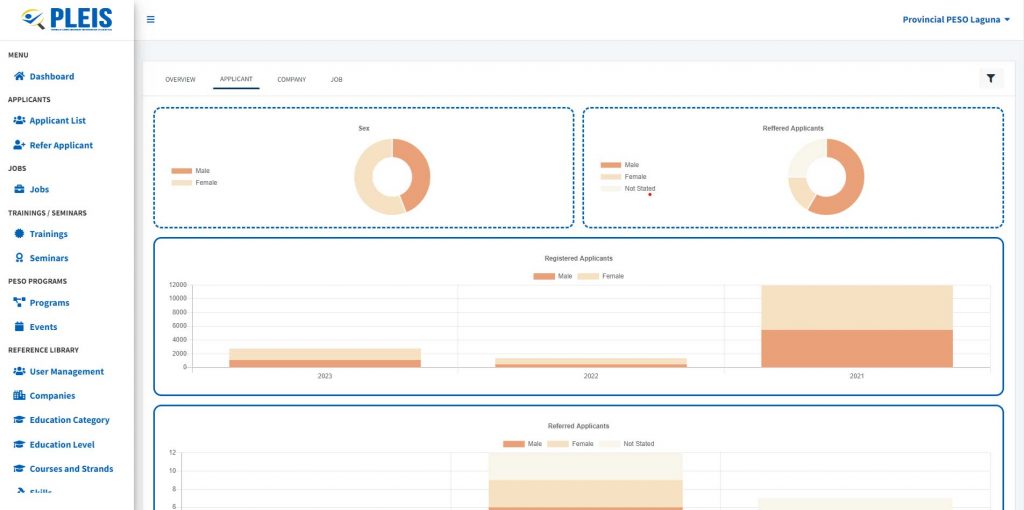
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
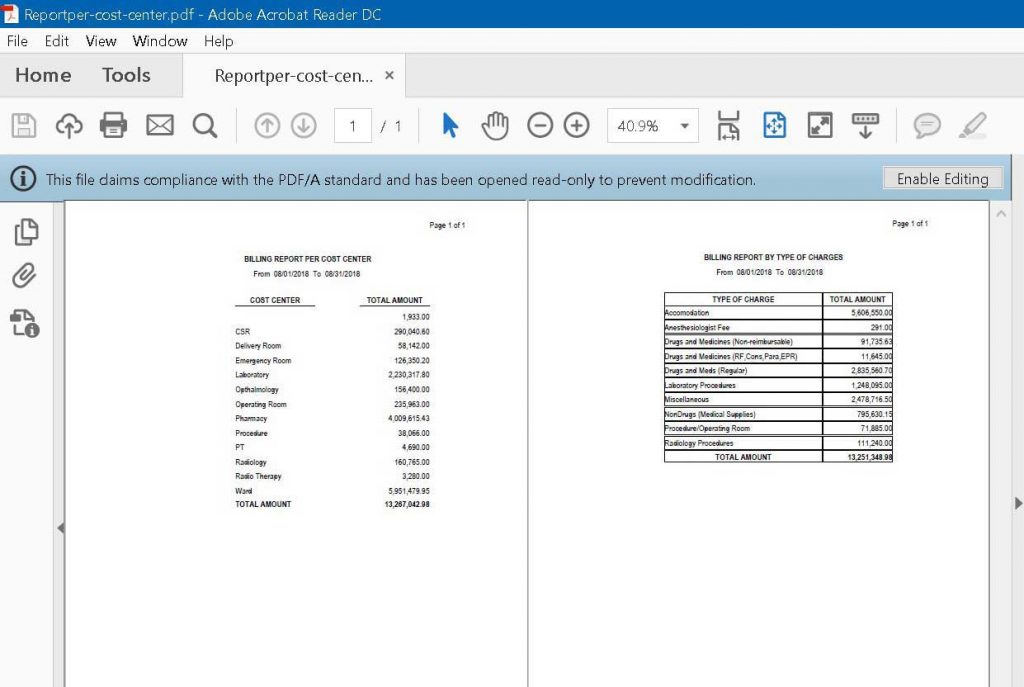
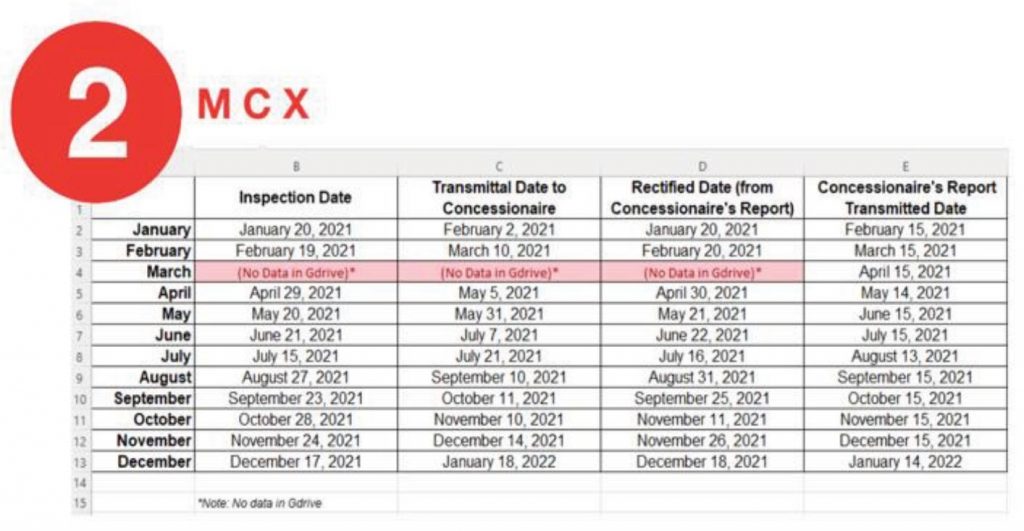
The Fortified OMGS mobile app has significantly reduced processing and reporting time. Traditional manual processing took an average of three working days. With Fortified OMGS, this is reduced to real-time processing, achieving a 240.43% rate of increase in efficiency from the first to the sixth trial. This translates to a reduction in reporting time from three weeks to hours.
On-site inspection periods were reduced from five days to one day. Trials showed a decrease in the time required for recording and reporting: from 2 minutes and 40 seconds initially to just 47 seconds by the sixth trial. The Fortified OMGS scored consistently high on accuracy and transparency, with a 5 out of 5 rating in each trial. This ensures that the inspection data collected and reported is reliable and transparent, addressing gaps in the traditional methodology.
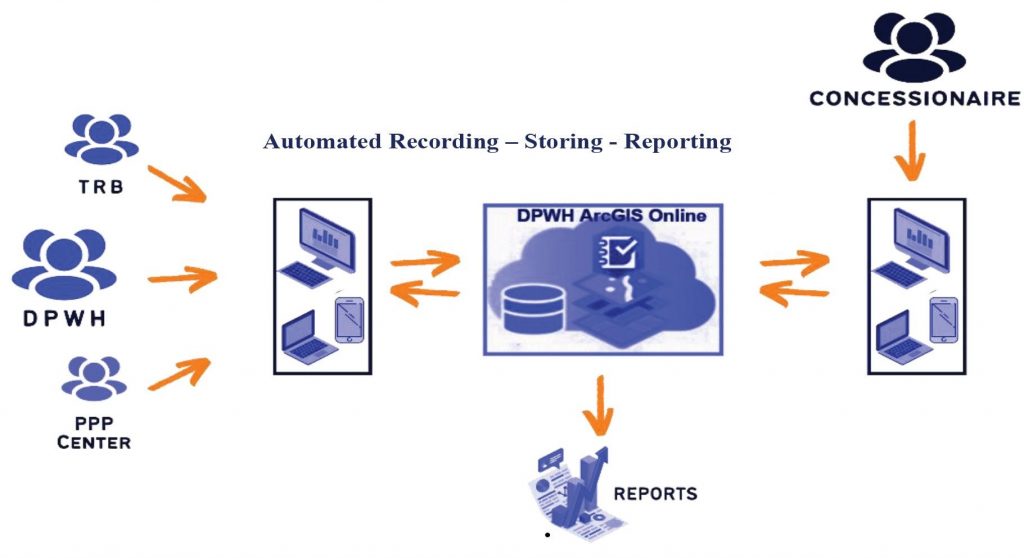
The app also fostered better collaboration among the DPWH, Toll Regulatory Board, and concessionaires, enhancing communication and cooperation through streamlined processes and real-time data sharing. Qualitative feedback from the inspectorate teams highlighted the app’s efficiency and convenience. Users praised the app for automating tasks that previously took weeks and providing immediate insights into road conditions.
The app ensures compliance with existing regulations and improves data management, making it easier to store, retrieve, and analyze inspection data digitally. The implementation of Fortified OMGS has streamlined the O&M inspection process, significantly reducing time and effort, and improving overall productivity and service delivery in DPWH. Engr. Ferdinand Caesar P. Lulu from the Operations and Maintenance Department of San Miguel Corporation Infrastructure – NAIAX shares the improvements through the use of the mobile app.
Lessons Learned/Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
The implementation of the Fortified OMGS mobile app offered several lessons and revealed potential areas for improvement. One key lesson learned was the importance of stakeholder engagement and training. Active participation from all relevant parties, including the DPWH IMS and inspectorate teams, was crucial for the successful adoption and functionality of the app. Additionally, the process underscored the need for continuous feedback loops to ensure the app meets user needs effectively.
Challenges encountered included limited stakeholder representation during initial orientation sessions, necessitating stronger engagement efforts. Expertise in quantitative data analysis was another hurdle, addressed by involving a statistician from the DPWH. Furthermore, minor issues in the e-technology framework required reorganization, which emphasized the need for flexible and adaptive design processes.
Potential areas of improvement include enhancing training programs to ensure all users are proficient with the app, refining the e-technology framework for better integration, and ensuring continuous updates and refinements based on user feedback. Establishing a robust support system for ongoing technical issues and considering financial sustainability strategies, such as budget allocation for future updates, will be vital for long-term success. Overall, these improvements could further streamline operations and maximize the app’s impact on O&M inspections.