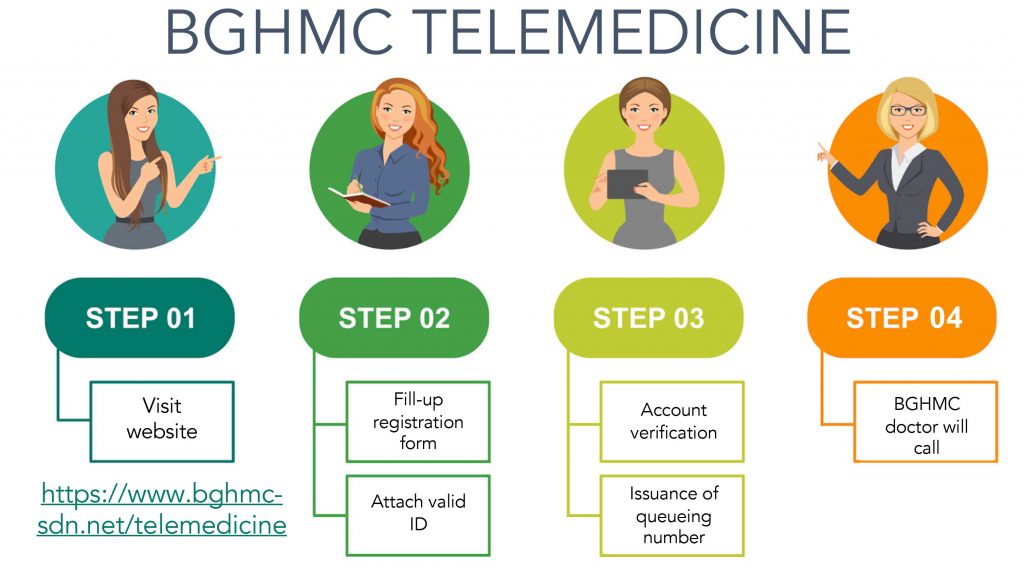
Themes
Service Quality – MWSS-CO emphasizes continuous improvements in service delivery, using tools such as the Customer Contact Hub (CCH), Citizen’s Charter, and Quality Management System to achieve service excellence. The organization’s commitment to understanding and addressing stakeholder needs ensures efficient and high-quality service for the public.
Citizen-Centered Service – MWSS-CO prioritizes understanding citizens’ expectations through feedback mechanisms, ensuring transparency, accountability, and timely resolution of complaints. The focus on empathetic, personal engagement, especially through the CCH, highlights its dedication to placing citizens at the heart of its operations.
Overview
The Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System (MWSS) in the Philippines is committed to enhancing service quality delivery in response to the growing demands on water supply and sanitation across Metro Manila and parts of Cavite, Rizal, and Bulacan and operates through two distinct entities: the MWSS-Corporate Office (MWSS-CO) and the MWSS-Regulatory Office (MWSS-RO). As the Philippine Government’s chief agency on water and sewerage services, MWSS-CO is responsible for ensuring the continuous and adequate supply and distribution of potable water, as well as the proper operation and maintenance of sewerage systems. MWSS-CO also acts as the asset owner and steward of water resources and related infrastructure. Meanwhile, the MWSS-RO is mandated to monitor the Concession Agreement, focusing on reviewing, monitoring, and enforcing rates and service standards, arranging and reporting regular independent audits of concessionaire performance. Amid growing challenges such as rising water demand, MWSS-CO implemented customer-centered service hubs and evidence-based satisfaction measures. Its approach includes innovative infrastructure projects, regulatory reforms, and advanced communication systems, such as the Customer Contact Hub, to improve service interactions with the public. Through strategic partnerships and citizen-centered reforms, MWSS-CO aims to strengthen trust and resilience in the public sector.
Challenge
The MWSS-CO, through its Concessionaires Manila Water Company, Inc. and Maynilad Water Services, Inc., is faced with compounding customer concerns such as billing disputes, inadequate water pressure, service interruptions, and delays in resolving complaints. These issues, if left unresolved or mishandled, significantly undermine public trust and confidence in the agency’s ability to deliver reliable and efficient water services. Additionally, MWSS-CO aims to uphold transparency, ensure regulatory standards, and meet the rising expectations of citizens, creating an intricate operational environment. These highlight the agency’s resolve to maintain organizational productivity while ensuring equitable and timely water service delivery.
Solution/s
MWSS-CO has undertaken multiple solutions to address citizen and concessionaire concerns. Each solution integrates digital transformation to address service quality gaps innovatively.
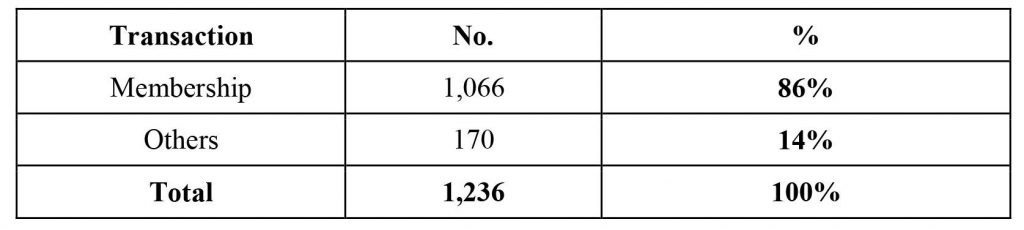
Customer Contact Hub (CCH) is a centralized platform designed to streamline customer interactions, resolve grievances efficiently, and strengthen accountability in water service delivery. It operates as a 24/7 service, allowing stakeholders—including the general public, Concessionaires, and government agencies—to raise complaints, make requests, and seek assistance regarding water-related issues. The CCH serves as a critical nexus between MWSS, its Concessionaires, and the Regulatory Office, ensuring that all concerns are directed to the appropriate delivery unit or agency for resolution. Key features of the CCH include its multi-channel accessibility, such as mobile hotlines, email, chatbots, and walk-in services, catering to a wide range of users. It also incorporates robust tracking and reporting mechanisms, ensuring that clients are informed of their case progress and resolution status. Additionally, the hub gathers valuable primary data on recurring customer issues, such as billing disputes or service interruptions, which informs MWSS’ management decisions and long-term planning. This citizen-centered system exemplifies MWSS’ commitment to responsive, transparent, and efficient public service, positioning the CCH as a model for handling public sector productivity challenges

Image 1: Social media art card promoting the MWSS-CO Customer Contact Hub hotline and digital platforms.
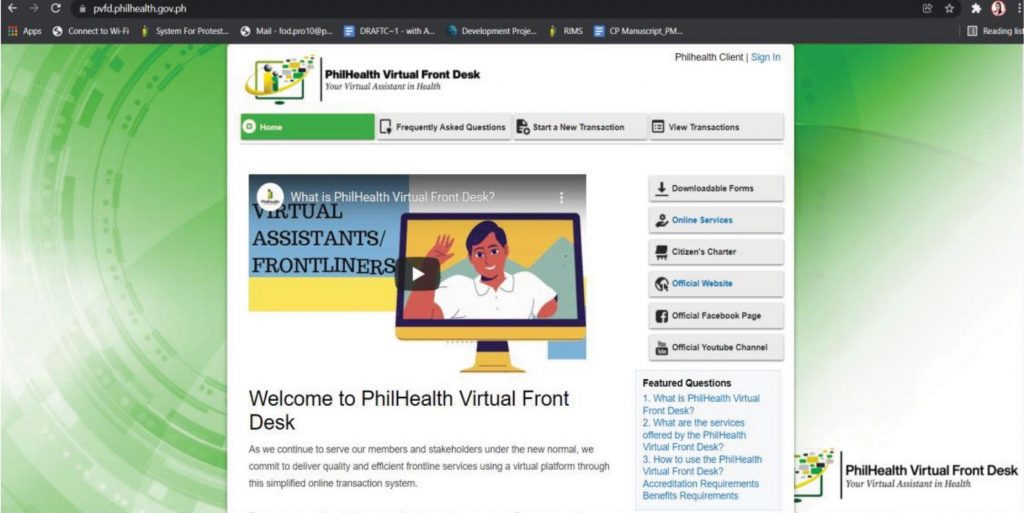
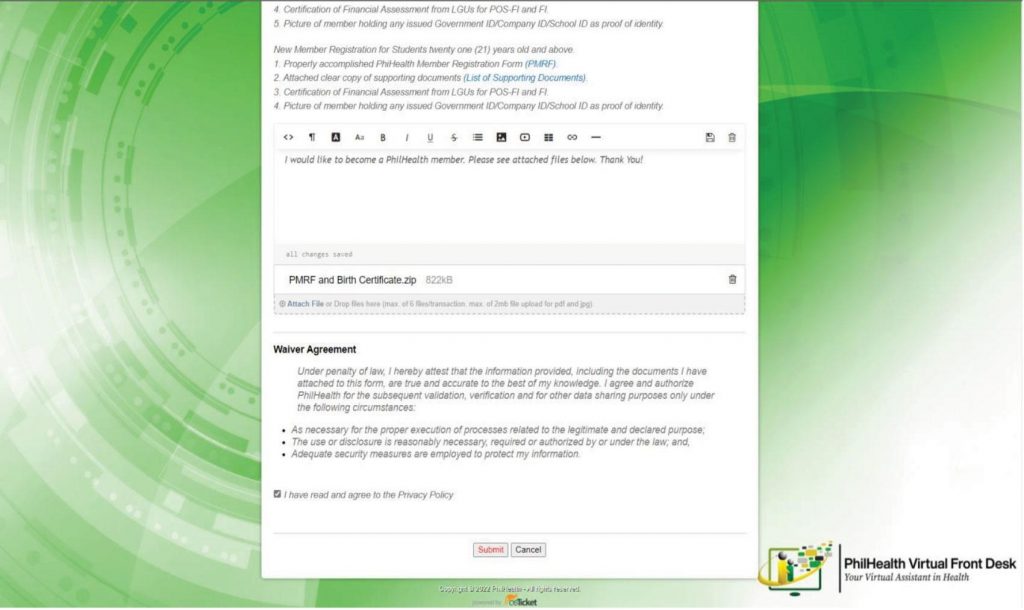
Digital platforms, chatbot services, and online portals are critical tools designed to enhance the accessibility, efficiency, and responsiveness of its customer service operations. These platforms cater to the public’s need for convenient, low-touch interactions, especially in the context of evolving digital trends and lessons learned during the COVID-19 pandemic. The chatbot service, accessible through platforms like Facebook Messenger (@MWSSgovph), provides an automated, user-friendly interface for customers to lodge complaints, make inquiries, and seek assistance. This service operates around the clock, offering immediate responses to routine queries while escalating complex issues to human agents when necessary. The online portals, including the agency’s website (mwss.gov.ph), serve as comprehensive platforms where citizens can access a wide range of services and information. These portals allow users to track service requests, submit feedback, and download necessary forms or documents. They also host critical updates, guidelines, and manuals, ensuring transparency and easy public access to MWSS-CO policies and initiatives. Collectively, these digital platforms reduce reliance on face-to-face interactions, streamline complaint resolution processes, and enhance service efficiency. By providing real-time communication and fostering a more seamless interaction experience, MWSS-CO digital tools reinforce its commitment to citizen-centered service and modern public sector productivity standards.
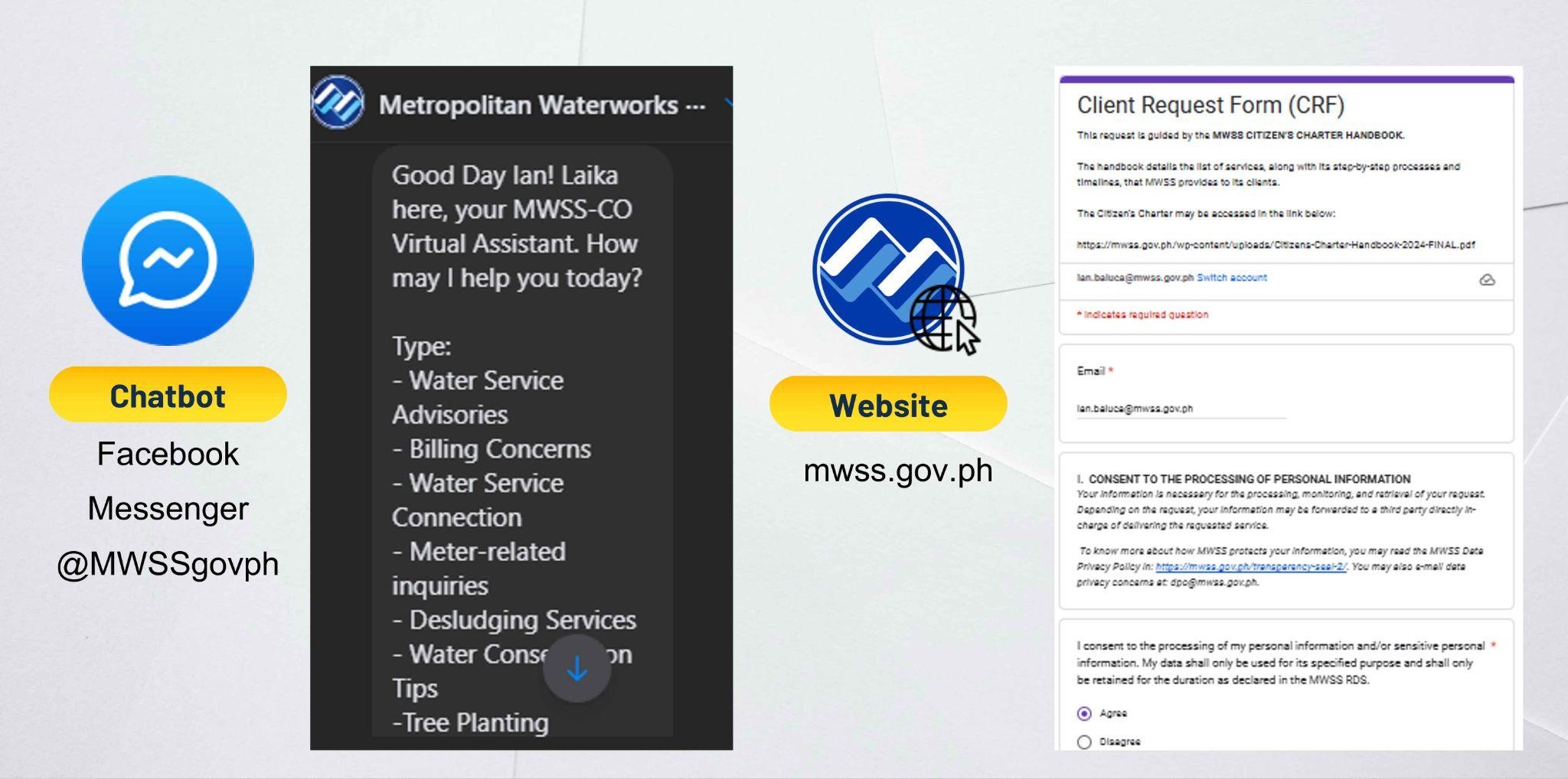
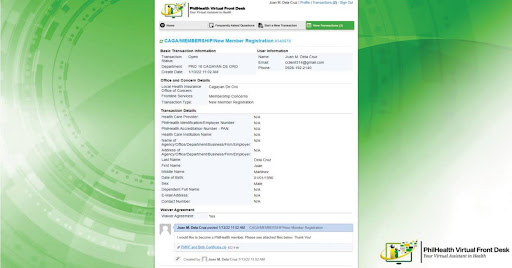
Image 2: Screenshots of the MWSS-CO Facebook Messenger Chatbot and the Client Request Form
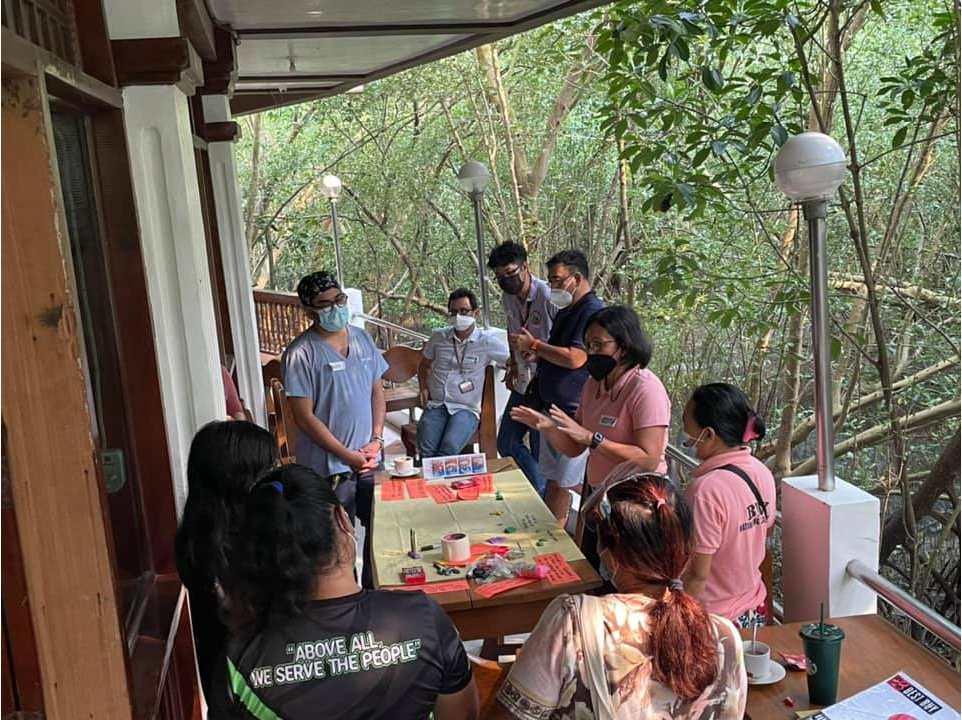
High-touch interactions and personal engagement aim to foster stronger relationships with its stakeholders and address individual concerns effectively. Recognizing that each client interaction is nuanced, MWSS-CO emphasizes empathy, responsiveness, and tailored resolutions to ensure that customer needs are met in a meaningful way. MWSS-CO also supports Concessionaires in meeting key performance indicators by offering technical assistance, permitting support, and liaising with local government units, showcasing its hands-on approach to ensuring service quality. This level of engagement allows MWSS-CO to stay informed of stakeholder needs, concerns, and satisfaction levels. Moreover, MWSS-CO incorporates the insights from these interactions into its decision-making processes, ensuring that policies and improvements reflect the lived experiences of its stakeholders. This commitment to personal engagement exemplifies MWSS-CO “Serbisyong Tunay” (Authentic Service) philosophy, which prioritizes genuine connections with its customers over impersonal transactions.
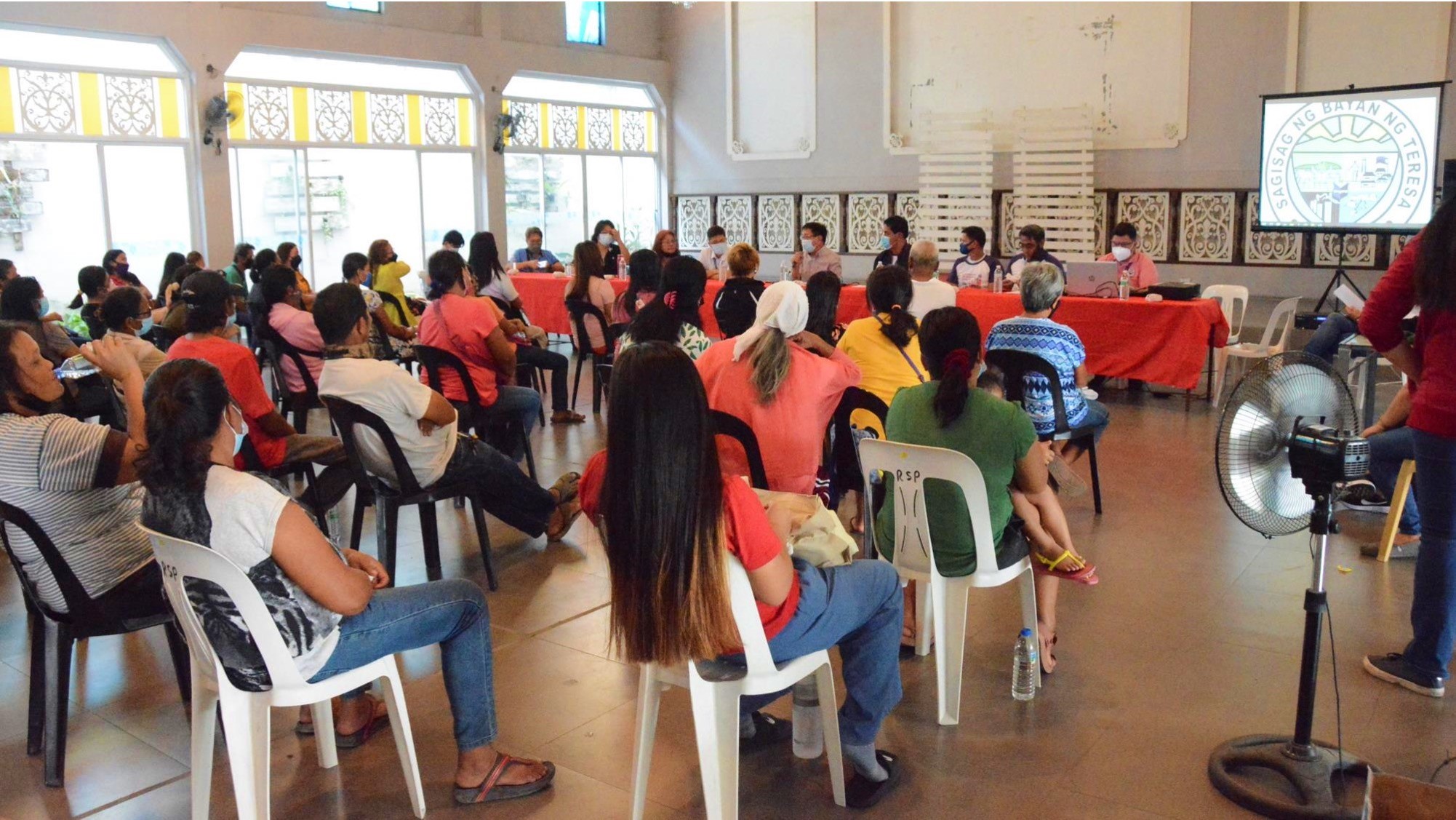

Image 3: Consultation Meeting with stakeholders from Teresa, Rizal
Client Satisfaction Survey (CSS) and Client Satisfaction Measurement (CSM) are evidence-based tools employed by the MWSS-CO to evaluate the quality of services provided to its stakeholders and identify areas for improvement. The Client Satisfaction Survey (CSS) is conducted in collaboration with the University of the Philippines-CIFAL. It gathers data on stakeholder expectations, perceptions, and satisfaction levels with MWSS-CO services. The survey helps identify the most availed services, providing insights into priority areas for operational improvements. It also supports decision-making by offering statistical data on various touchpoints between MWSS-CO and its stakeholders. The Client Satisfaction Measurement (CSM) is implemented based on the Harmonized Client Satisfaction Measurement framework mandated by the government. It evaluates customer satisfaction across eight dimensions: responsiveness, reliability, access and facilities, communication, costs, integrity, assurance, and outcome. The CSM provides standardized metrics to measure MWSS-CO performance in delivering its internal and external services, ensuring consistency and comparability across public sector entities. Both tools enable MWSS-CO to monitor the effectiveness of its service quality standards, refine its strategies, and enhance overall customer satisfaction. These initiatives emphasize transparency, accountability, and the agency’s commitment to citizen-centered service delivery.

Image 4: MWSS-CO three primary sources of customer data: Client Satisfaction Survey, Client Satisfaction Measure, and High-Touch Interactions.
Service Manuals, Citizen’s Charter, and Quality Management System (QMS) are foundational tools developed to standardize processes, ensure transparency, and enhance service delivery efficiency. The Service Manuals outline the operational guidelines and best practices for MWSS-CO employees and stakeholders. They include step-by-step instructions for processing various customer requests and complaints, ensuring consistency and adherence to established protocols. The service manuals also emphasize accountability and define key reporting and evaluation mechanisms to maintain service quality. The Citizen’s Charter is a key document mandated under Republic Act 11032 (Ease of Doing Business Act). It provides a detailed guide for citizens on how to access MWSS-CO services, outlining the step-by-step procedures, required documents, and processing times for each service. This transparency promotes accountability and helps citizens navigate MWSS-CO processes efficiently while setting clear expectations for service timelines and standards. The QMS establishes a framework to integrate stakeholder concerns into MWSS-CO plans and programs while improving organizational performance. Rooted in ISO 9001:2015 standards, the QMS ensures that MWSS-CO processes are risk-based, stakeholder-focused, and aligned with regulatory requirements. It also supports continuous improvement through regular reviews, assessments, and refinements of service delivery mechanisms.

Image 5: To concretize the SQS, the MWSS-CO has developed its Citizen’s Charter Handbook, Quality Management System Manual, and Freedom of Information Manual
These features stand out as innovative due to their citizen-focused design, integration of digital tools with human interactions, and the systematic incorporation of stakeholder feedback into service improvement strategies.
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
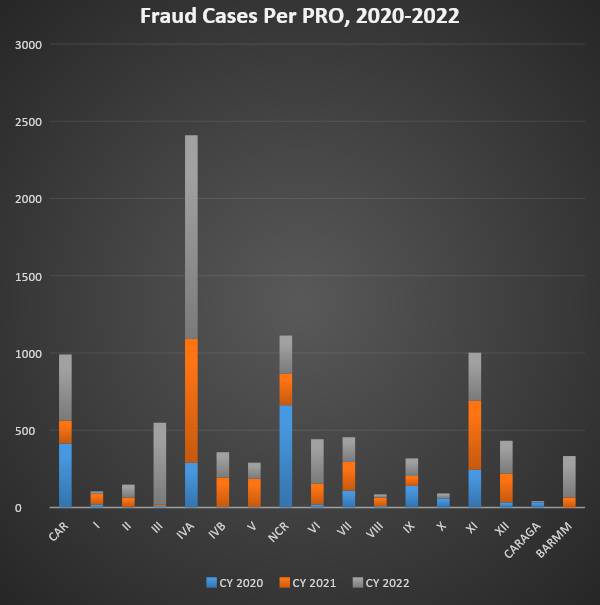
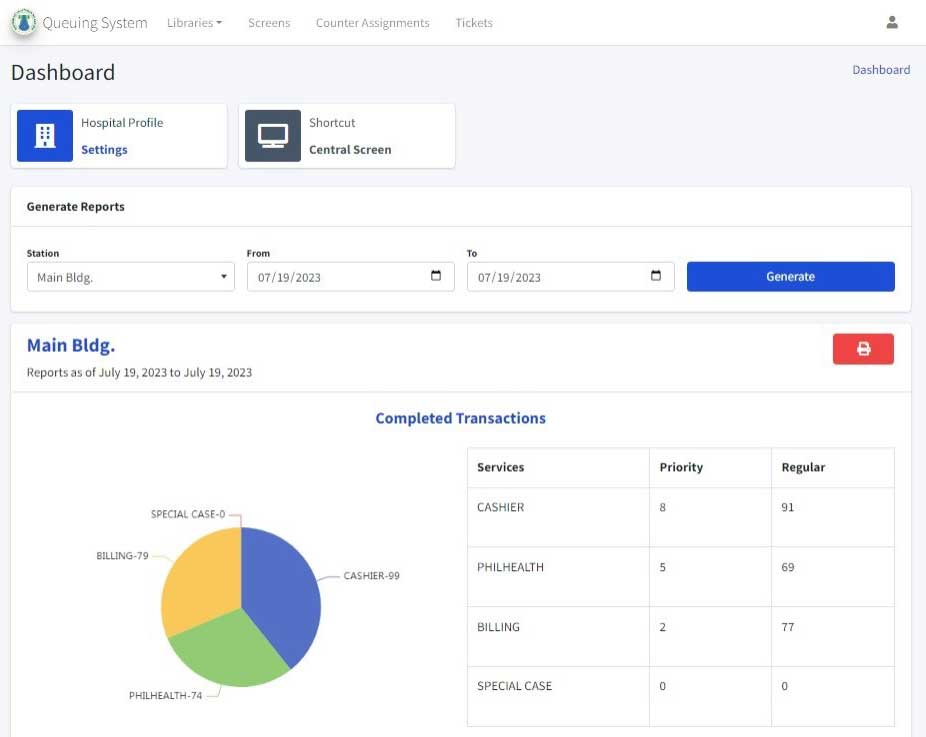
MWSS-CO has achieved an overall 2023 Client Satisfaction Measurement rate of 99.40%, reflecting excellence in stakeholder service delivery, with high scores in awareness (93.87%), visibility (95.52%), and helpfulness (96.70%). These metrics demonstrate MWSS-CO ability to align its operations with public expectations, thereby enhancing trust and efficiency. Another notable result is the remarkable 63% rise in feedback responses and 12% increase in total transactions as of 2024, indicating improved engagement and accessibility through initiatives like the Customer Contact Hub (CCH) and online platforms. The shift to digital and remote services has streamlined complaint resolution processes, with MWSS-CO resolving 100% of customer concerns submitted via the 8888 hotline, maintaining a compliance rate of 98.61% for addressing cases within 72 hours. These interventions have minimized delays, especially for concerns like billing disputes, water interruptions, and reconnections. The integration of chatbot services and online portals has facilitated low-touch transactions, with 40.12% of stakeholders expressing preference for website and app-based services, aligning with evolving user behavior post-pandemic.
These efforts have directly benefited stakeholders by ensuring quicker resolutions, transparent communication, and equitable service access across MWSS-CO jurisdiction. Moreover, enhanced collaboration with Concessionaires has bolstered accountability in service delivery. The overall outcomes signify MWSS-CO success in modernizing its operations, increasing public satisfaction, and demonstrating the value of good governance and efficient resource utilization in the public sector. These measurable gains not only validate MWSS-CO interventions but also establish a benchmark for productivity and service excellence in water governance.
Lessons Learned/Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
One of the key lessons is that transitioning to digitized, low-touch systems require careful balancing with high-touch, personalized service to maintain trust and transparency with stakeholders. The COVID-19 pandemic revealed that while digital platforms, such as chatbots and online portals, are efficient and widely accessible, some citizens still prefer face-to-face interactions, as evidenced by 47.49% of stakeholders identifying it as their most preferred mode of engagement. This highlights the importance of offering diverse service channels to accommodate varying needs and preferences.
Challenges in implementing these standards included gaps in organizational capacity, such as insufficient personnel and resources to handle the volume of customer concerns effectively. Additionally, managing coordination between MWSS-CO and its concessionaires to ensure seamless service delivery proved complex, especially in addressing issues like billing disputes and water supply interruptions. There is room for improvement in expanding staff capabilities, streamlining workflows, and using advanced data analytics to identify service bottlenecks.
Furthermore, while MWSS-CO made strides in participatory governance and accountability, integrating feedback into actionable reforms remains an ongoing area of focus. Strengthening infrastructure, enhancing stakeholder collaboration, and further innovating service delivery mechanisms will position MWSS-CO for sustained productivity and citizen-centered governance.