About the Tool
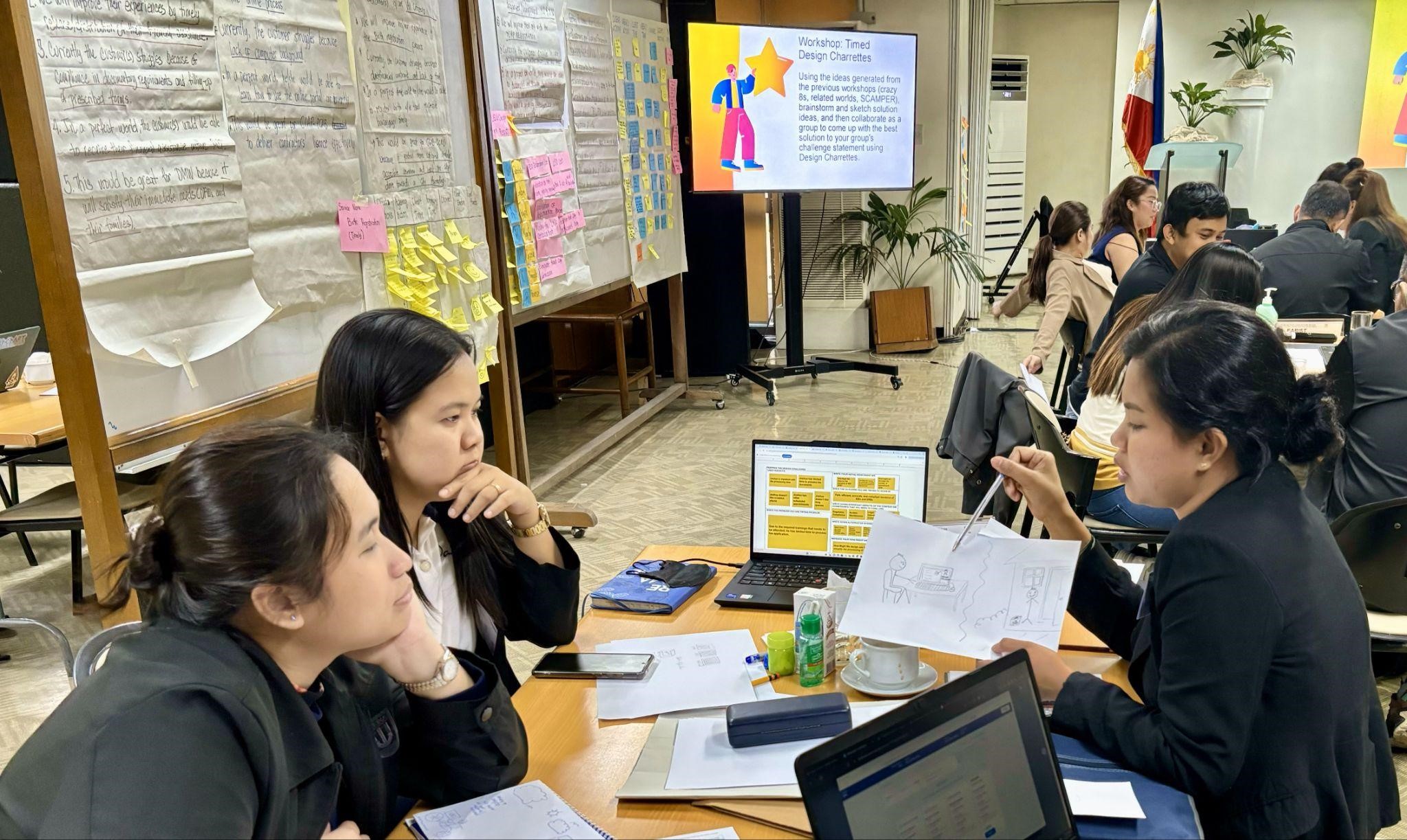
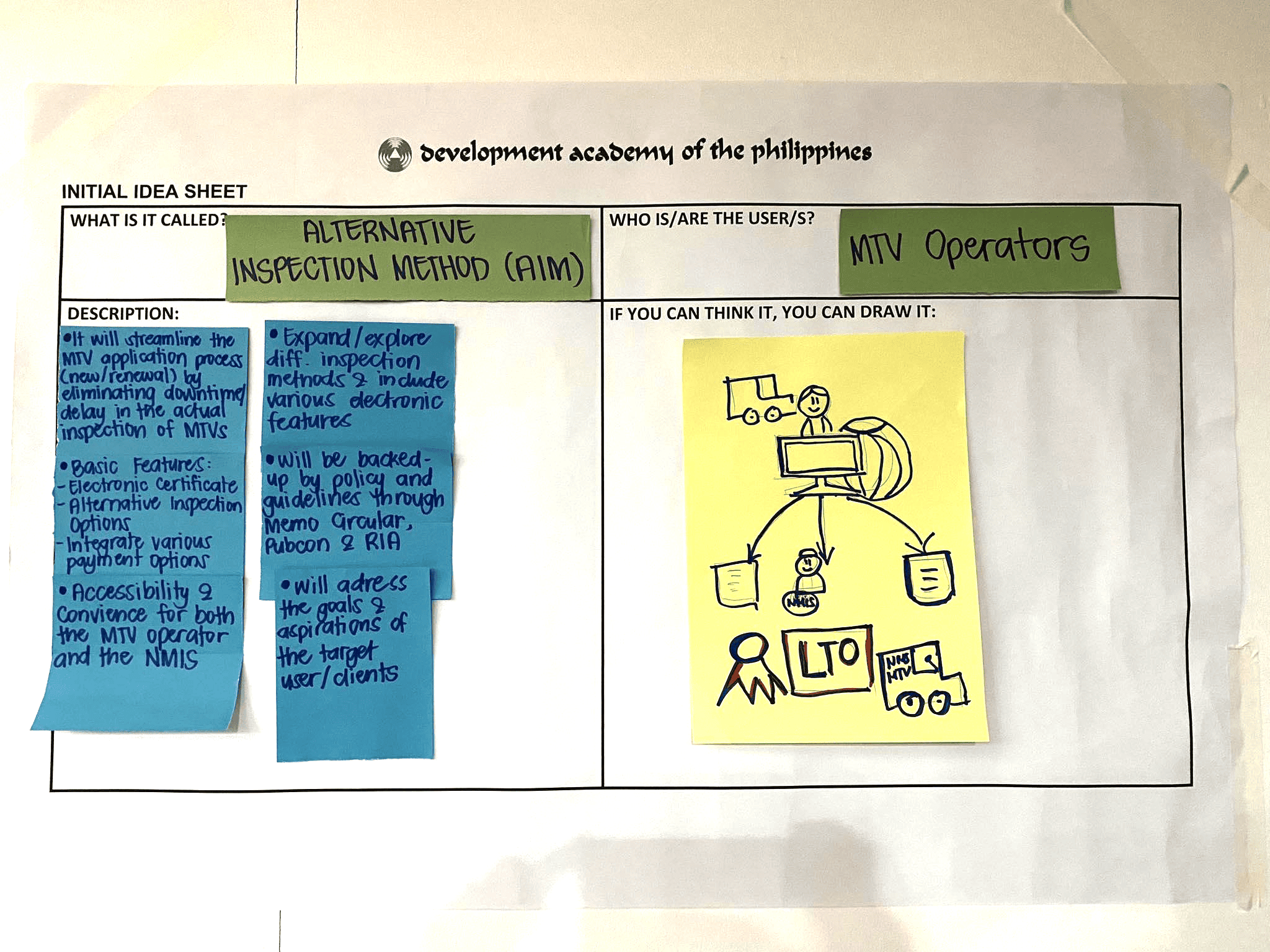
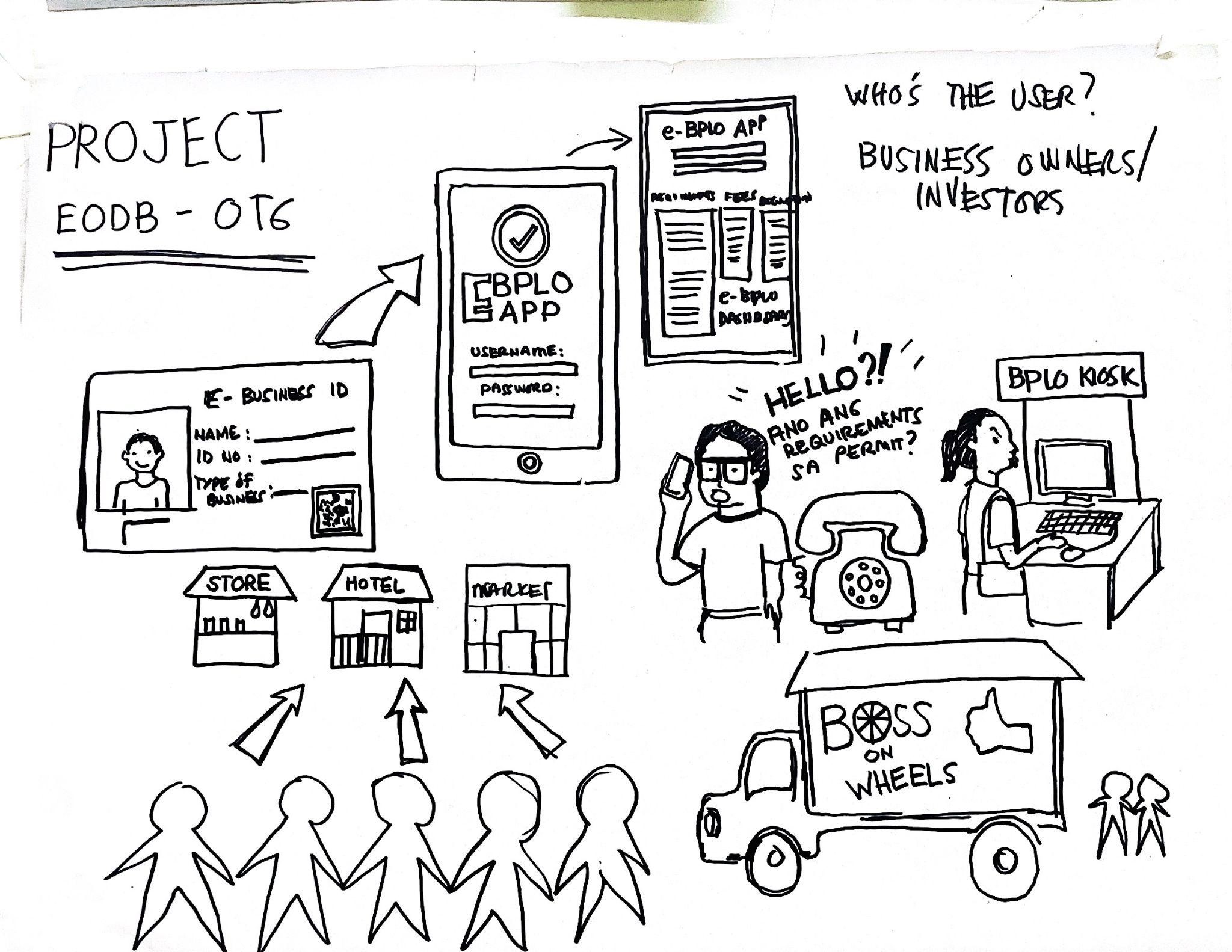
An idea sheet is an idea proposal consultation template used to organize ideas when designing a citizen-centered public service. It helps teams to document the results of ideation processes and transform them into actionable solutions. The key components include a problem statement, objectives, target audience, key features, implementation plan, and evaluation metrics. Public service designers can use an idea sheet to ensure that their solutions are well-thought-out, feasible, and aligned with the needs and expectations of the citizens they serve.
Purpose: Synthesizing of ideas
Estimated Time Needed: 30 minutes
Target Participants or Users: Change Managers, Community Engagement Teams, Operations Managers, Public Service Providers, Process Planners, Policymakers, Service Designers
How to Use the Tool
Steps:
- Select your innovation project.
- Select a stakeholder/s for your solution.
- Fill out the description using the following guide questions:
- a. What are the objectives of the idea?
- b. What are the immediate gains and long-term results for your target beneficiaries?
- c. What are the basic features of the idea?
- d. What is the most important thing to look for?
- e. How different is it from the existing one?
- f. How will this idea be executed?
- g. How does this idea align with the needs or requirements of your target users?
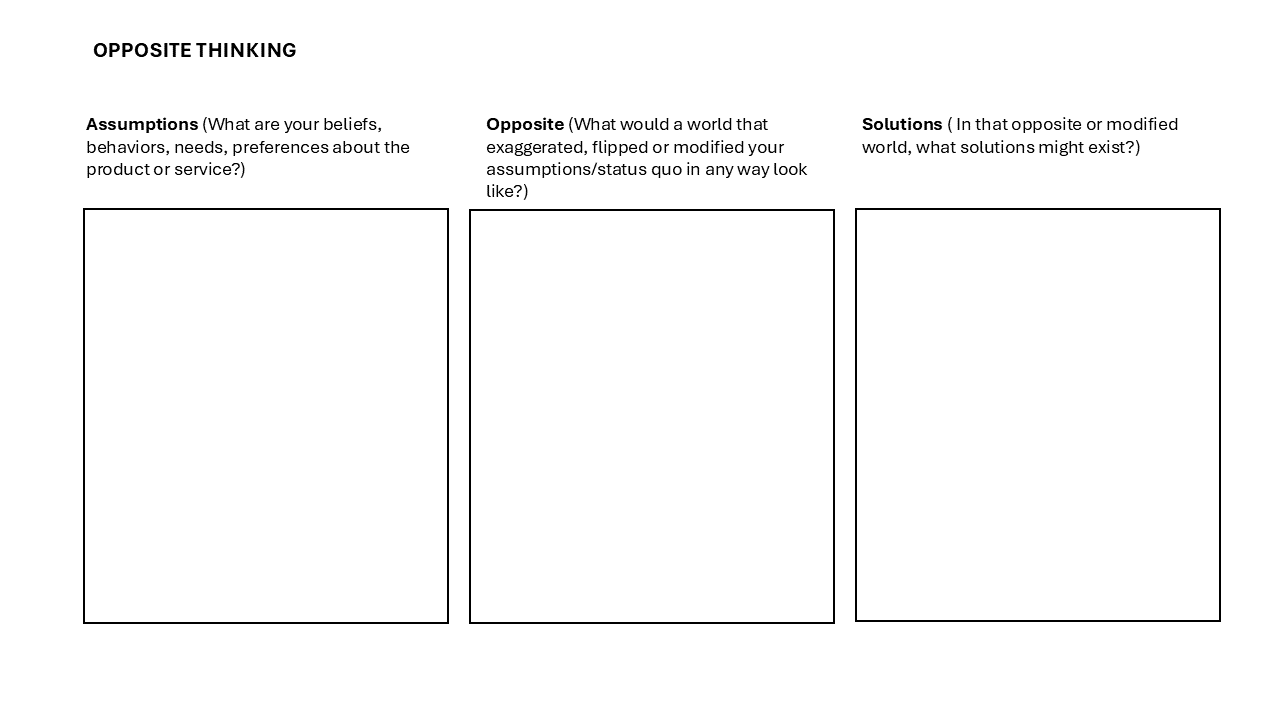
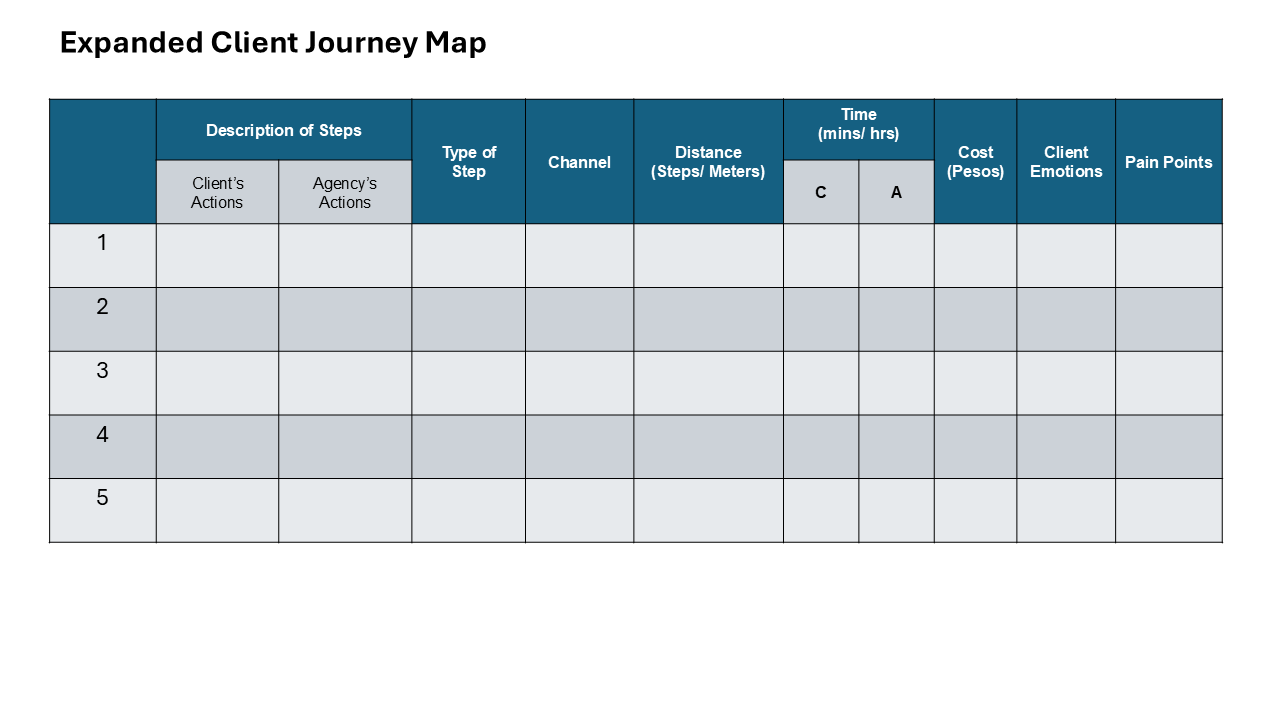
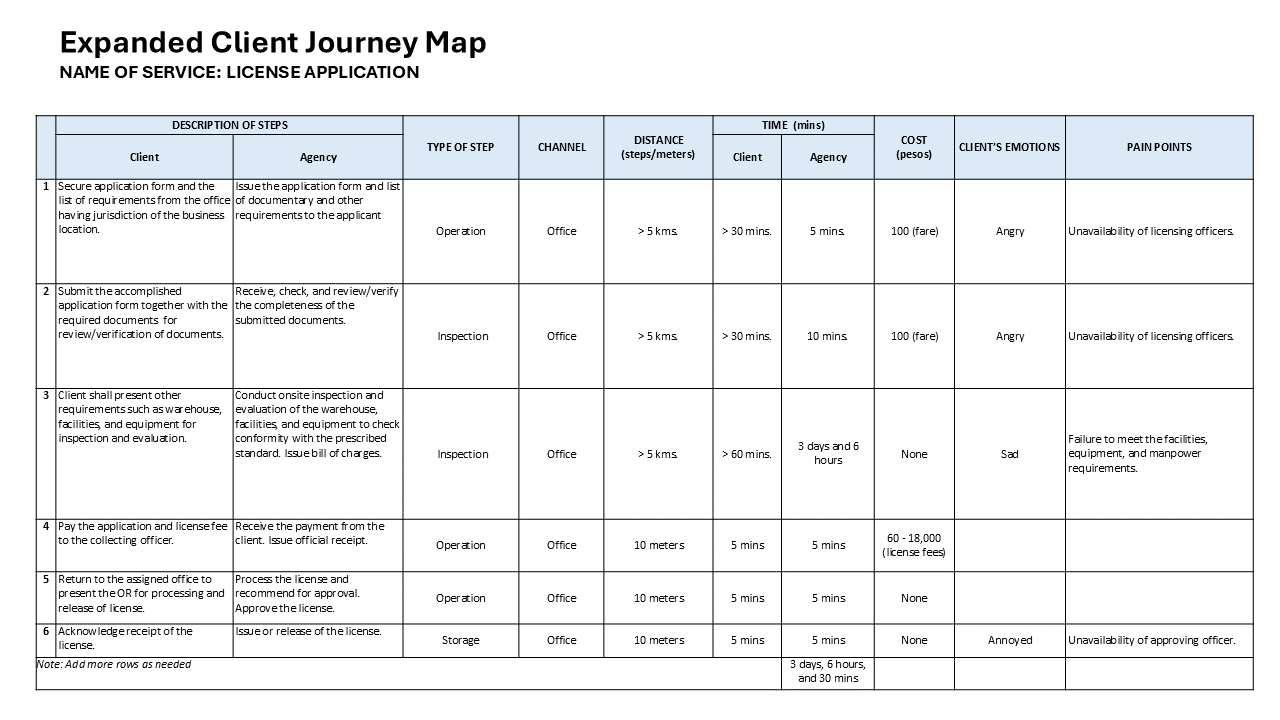
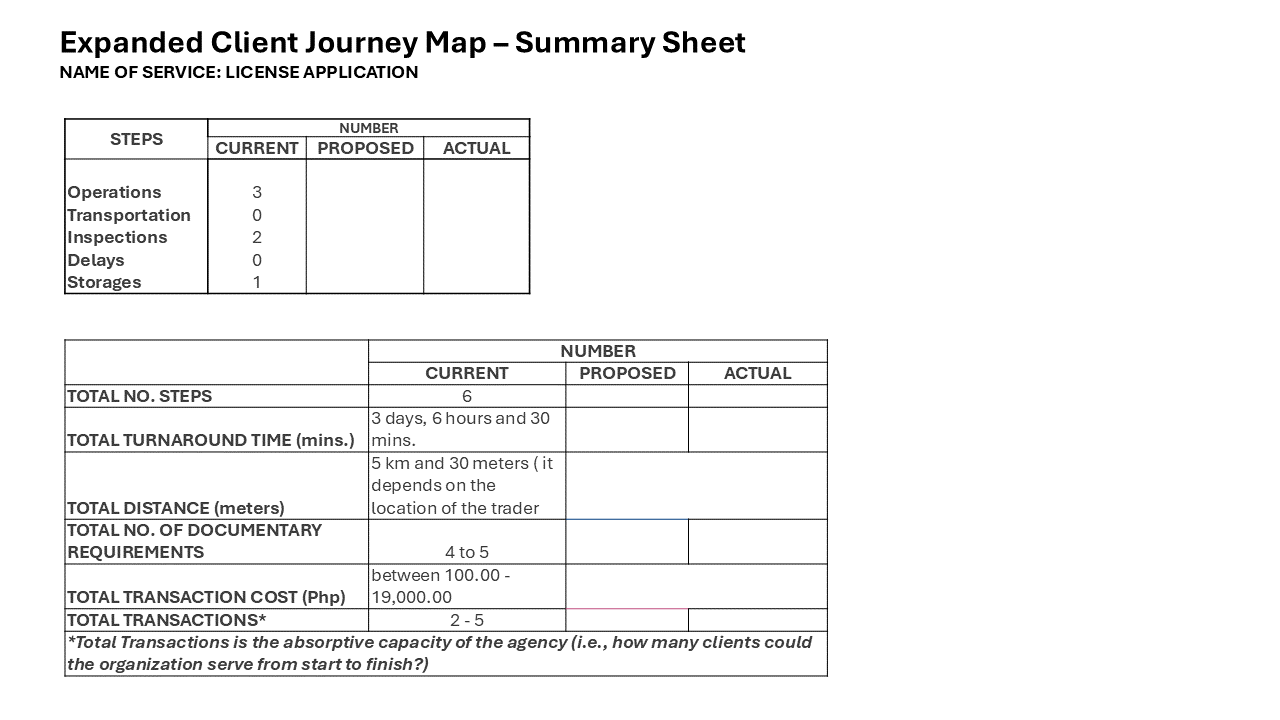
Sample Idea Sheet Template

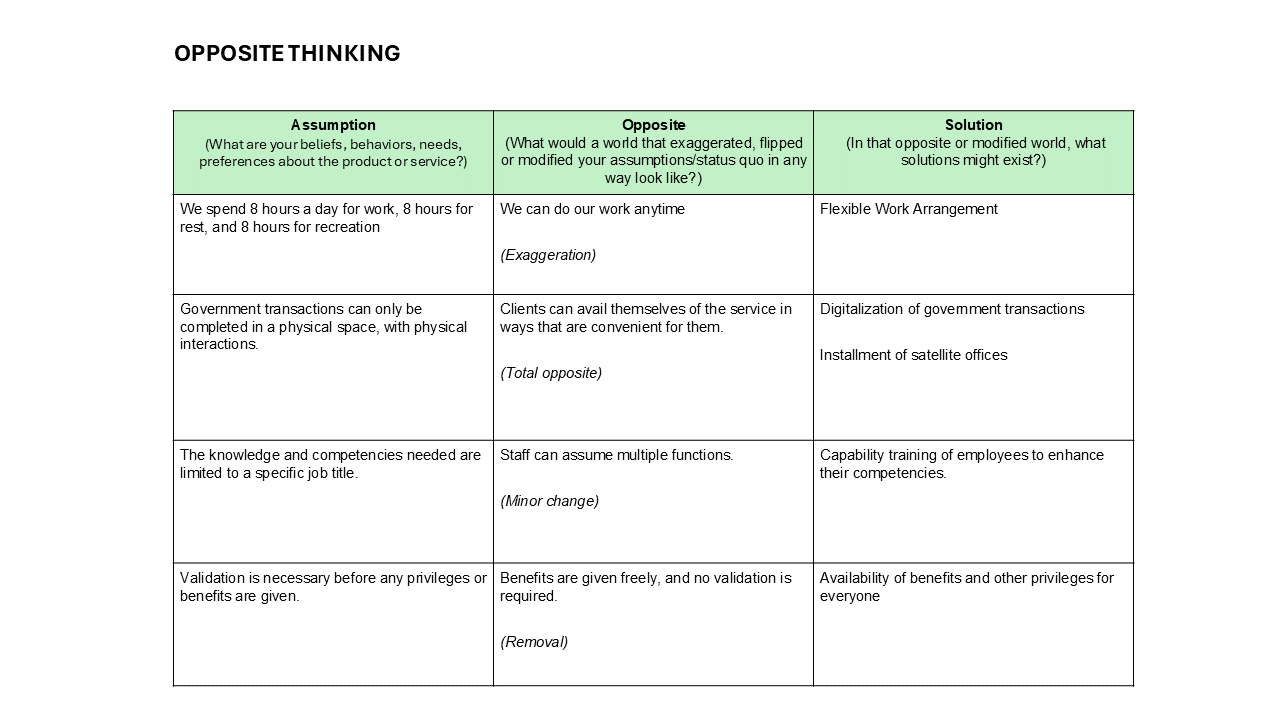
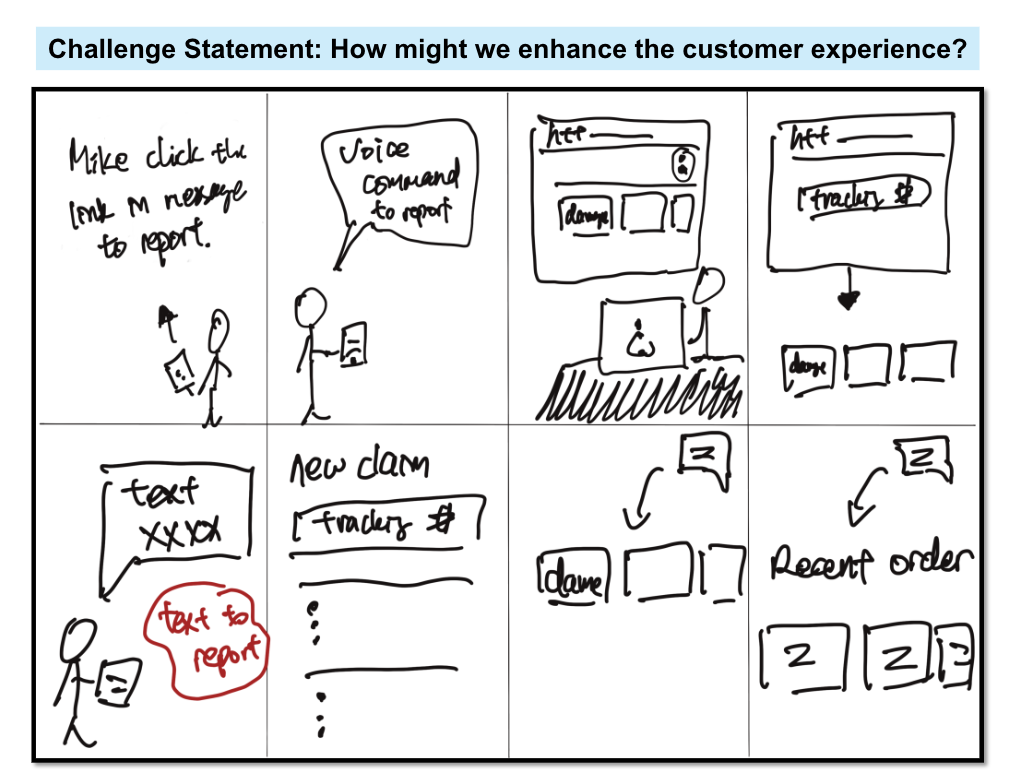
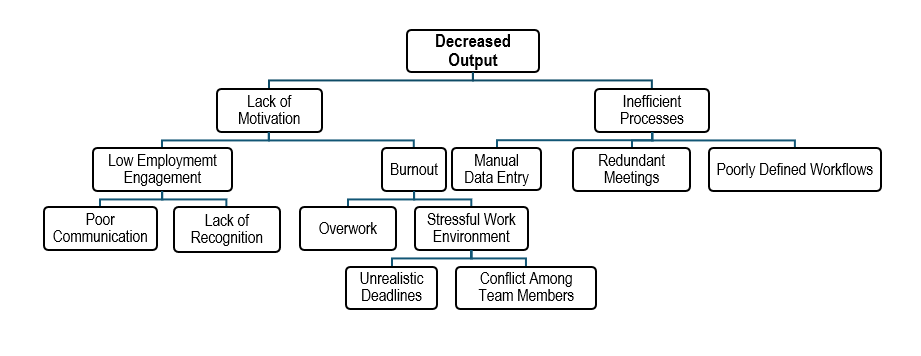
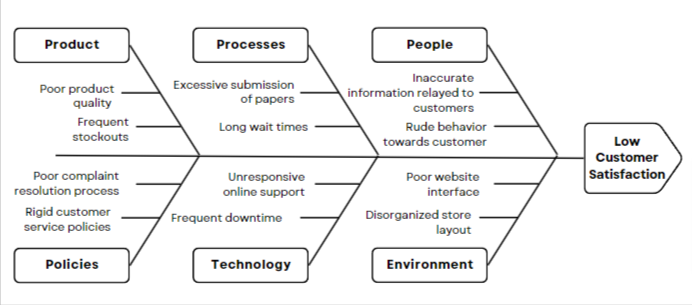
Sample Idea Sheet Activity Output