Themes
e-Government: Leveraging ICT through the eGovPH Superapp, eGovDX, and cloud solutions to improve public service delivery.
Innovation Leadership: Pioneering digital solutions like eGovPay and eVerify, leading to efficient, scalable, and secure public services.
Overview
The Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) is driving the Philippines’ transformation into a digitally empowered nation by introducing innovative e-Government initiatives. With robust platforms such as the eGovPH Superapp, eGovDX, and the Digital National ID, the DICT is addressing critical challenges like bureaucratic inefficiencies, redundant processes, and accessibility gaps in government services. These initiatives are designed to streamline operations, increase transparency, and enhance citizen satisfaction by integrating advanced technologies and fostering inter-agency collaboration. Through its digital transformation strategy, DICT is positioning the Philippines as a global leader in digital governance while ensuring inclusivity and accessibility for all citizens.
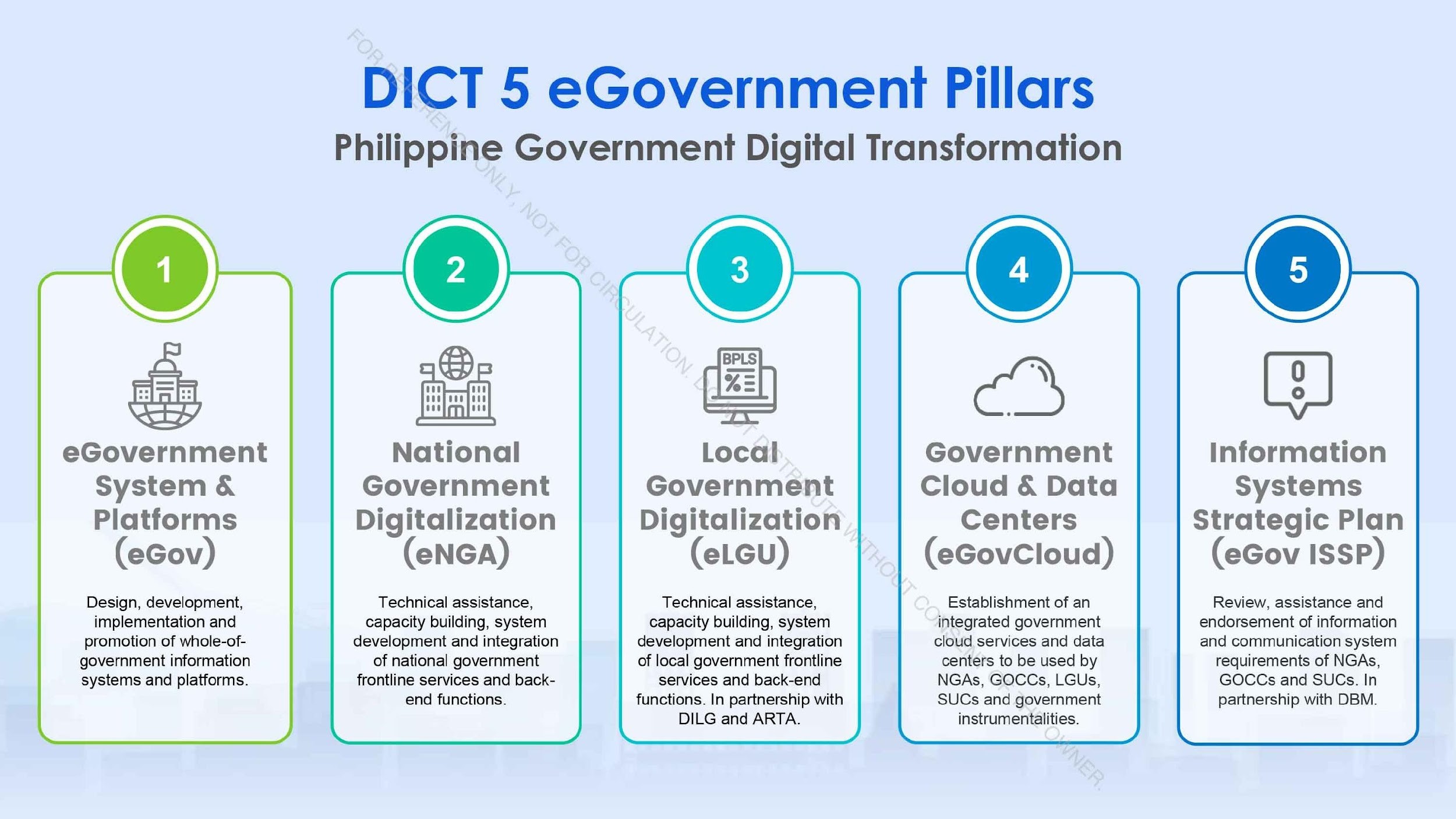
Image 1: The DICT’s eGovernment Pillars for Digital Transformation
Challenge
The Philippine Government faced longstanding productivity barriers such as legacy systems, siloed operations, and excessive bureaucracy. Inter-agency miscommunication and reliance on manual, paper-based processes resulted in delays, higher operational costs, and low public trust. Citizens and businesses experienced time-consuming transactions, with redundant submissions of documentation across multiple agencies further compounding inefficiencies. Additionally, the absence of centralized systems for identity verification and data-sharing hindered service delivery and accountability. These systemic inefficiencies were exacerbated by disparities in digital infrastructure, particularly in underserved areas, limiting access to essential government services.
Solutions
The Philippine Government’s Digital Transformation integrates an ecosystem of integrated platforms that streamline operations across national and local government agencies, ultimately fostering a whole-of-government approach. Key solutions include:
eGovPH Superapp is a centralized platform integrating over 24 eGovernment services, including eGovPay, eLGU, eReport, and eNGA, into a single, user-friendly application. It allows citizens and businesses to perform transactions such as payments, permit applications, and reporting in one seamless interface. The app features single-sign-on access, eliminating the need to manage multiple accounts. Future plans include expanding to 30 platforms, targeting 10 million users and 100 million use cases by 2024. It also aims to integrate additional services like eTourism, eHealth, and eLearning. By reducing redundancies, shortening processing times, and increasing accessibility, the eGovPH Superapp transforms citizen interactions with the government.

Image 2: The eGov Superapp used in a smartphone
Digital National ID provides a unified and secure system for citizen identity verification. The system has reduced the need for repetitive document submissions. The eVerify system, integrated with the Digital ID, allows for fast, remote, and secure authentication of individual identities without requiring physical documents. It supports over 40 types of government-issued IDs and is widely used across platforms like eGovPH, eTravel, and PhilHealth. Leveraging eGovLiveness AI, the system incorporates advanced anti-deep-fake technology and computer vision to ensure identity verification accuracy and fraud prevention. Key stakeholders using eVerify include NGAs, LGUs, banks, and educational institutions, enabling applications in eKYC processes, recruitment, academic verification, and financial transactions. This initiative not only strengthens operational efficiency and reduces fraud but also empowers citizens by simplifying access to services across sectors like health, finance, education, and social welfare.

Image 3: The Digital National ID sample in smartphone.
eGovPay is a secure government payment gateway that simplifies financial transactions for taxes, permits, and other services. It consolidates multiple payment methods such as e-wallets, online banking, and cash into a unified system. Features include automated receipt generation and integration with the Department of Finance’s general ledger for accurate tracking. With 6 million users, eGovPay reduces processing times, enhances transparency, and eliminates manual reconciliation errors. It supports compliance with Executive Order 170, mandating digital payments in government transactions. By modernizing financial workflows, eGovPay improves accountability and trust in public finance.
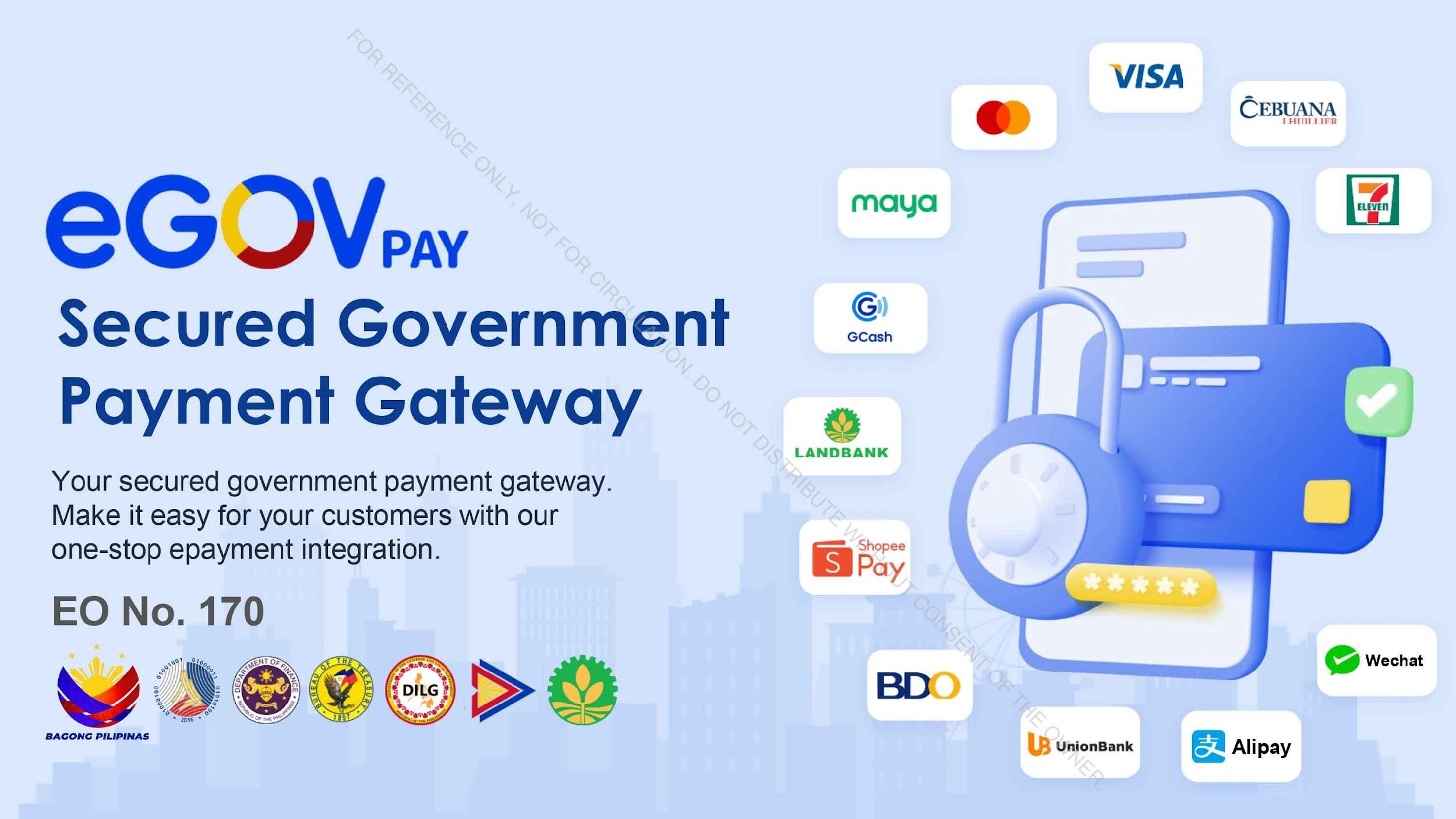
Image 4: eGovPay Partners and Digital Payment Integration
eGovDX Platform serves as the backbone for the government’s data-sharing framework, enabling secure inter-agency integration. It supports a whole-of-government approach through APIs such as the Partner’s API for data exchange and Single-Sign-On (SSO) for unified user access. The platform connects over 10 specialized APIs to simplify public service interactions and reduce redundancies. By automating data flows and ensuring interoperability, eGovDX enhances operational efficiency and decision-making. This platform streamlines services across agencies, making public services more accessible, efficient, and connected.
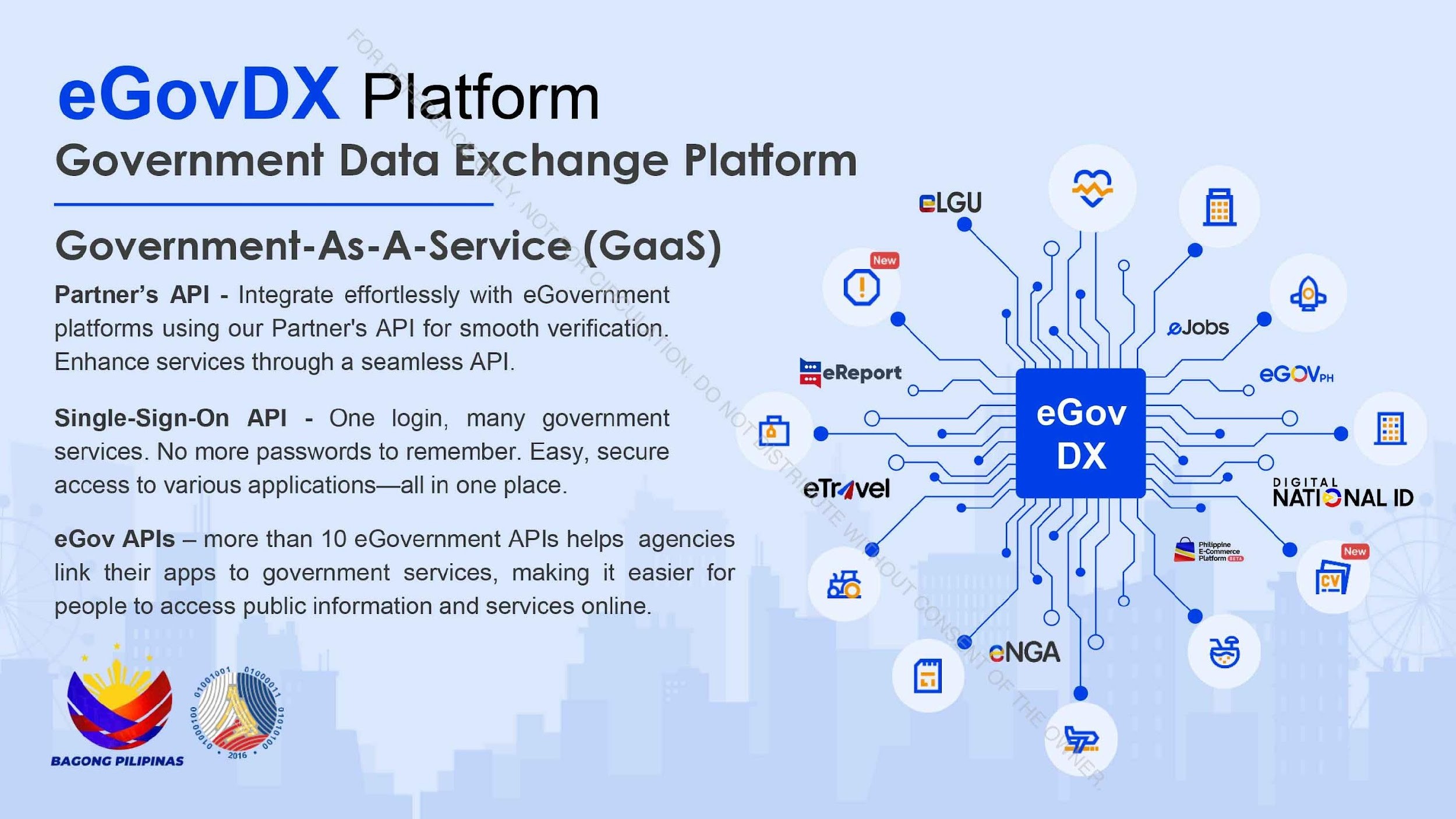
Image 5: Visualization of the eGovDX Platform, integrated with other applications.
eHealth Platform revolutionizes healthcare delivery by offering virtual consultations, electronic medical records, and streamlined PhilHealth membership management. It simplifies patient access to healthcare providers and integrates vaccination records for public health programs. The eLGU System modernizes local government services, automating processes for business permits, barangay clearances, and working permits. With 828 LGUs digitizing business permits and 318 LGUs implementing barangay clearance systems, it improves efficiency and transparency. Both platforms enhance service delivery by reducing manual processes, cutting red tape, and ensuring citizen-centric governance.

Image 6: The eHealth Platform in a smartphone and the eLGU Partner Local Government Units.
Productivity Gains, Outcomes, and Impact
The eGOVPH Superapp, which integrates 24 eGovernment platforms and currently serves over 7.2 million users, with 25 million use cases recorded. By 2024, it aims to expand to 30 platforms, supporting 10 million+ users and 100 million+ use cases, while integrating services from 80 NGAs, 990 LGUs, and 10 SUCs. This consolidation reduces redundancy and significantly improves service accessibility.
The introduction of the Digital National ID has streamlined identity verification across sectors, with 83 million Digital IDs (mobile) issued and 25.3 million eVerify use cases logged as of mid-2024. The system supports over 40 types of government IDs, enabling efficient identity authentication for services such as eGovPH, eTravel, and PhilHealth, which together account for millions of use cases. Similarly, the eLGU system has improved local government operations by automating processes for permits and clearances, with 828 LGUs implementing business permits and 318 LGUs adopting barangay business clearance systems.
The eGovPay system has revolutionized government financial transactions by introducing a secure, centralized payment gateway, reducing processing time and eliminating inefficiencies like manual reconciliation and lack of transparency. Additionally, services like eHealth, which include electronic medical records and virtual consultations, and eJobs, with over 1 million resumes built, further highlight the transformation’s citizen-centric focus.
Overall, DICT’s initiatives have significantly boosted the productivity performance of the Philippine Government by reducing bureaucratic barriers, cutting costs, and improving interagency coordination. For citizens, these programs have ensured faster, more accessible services, promoting inclusivity, transparency, and trust in government operations, thereby uplifting their quality of life.
Lessons Learned/Challenges in Implementing the Intervention
The Philippine Government’s Digital Transformation through DICT’s e-Government initiatives has provided valuable lessons and highlighted areas for improvement as it modernizes public service delivery. One key lesson learned is the importance of stakeholder collaboration and interagency coordination. The transition to digital services required breaking down silos between government agencies, which was initially challenging due to legacy systems and resistance to change. Ensuring alignment and interoperability across various systems proved critical for the success of platforms like the eGovPH Superapp and eGovPay. Resistance from some agencies and stakeholders also underscored the need for comprehensive training, capacity building, and sustained advocacy to emphasize the long-term benefits of digitalization.
Another challenge was ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity, particularly as systems like the Digital National ID and eVerify handled sensitive personal information. While robust measures were implemented, addressing vulnerabilities and maintaining public trust remains an ongoing priority. Additionally, disparities in digital infrastructure across regions created uneven access to these services, particularly in remote or underserved areas, highlighting the need for expanded internet connectivity and infrastructure investment.
Potential areas for improvement include refining user interfaces to ensure accessibility for all demographics, implementing more agile systems for real-time adjustments based on user feedback, and strengthening mechanisms for cybersecurity and data governance. These improvements will ensure the transformation remains inclusive, resilient, and adaptable to the evolving needs of citizens.
