DAP Highlights Islamic Republic of Iran Public Sector: Insights from the APO COE-PSP Factsheet
The Development Academy of the Philippines (DAP), the focal organization for the APO Center of Excellence on Public-Sector Productivity, continues its feature on governance indicators across APO member economies. In this edition, we turn our focus to the Islamic Republic of Iran, providing a snapshot of its key performance indicators, relevant fiscal metrics and civil service statistics.
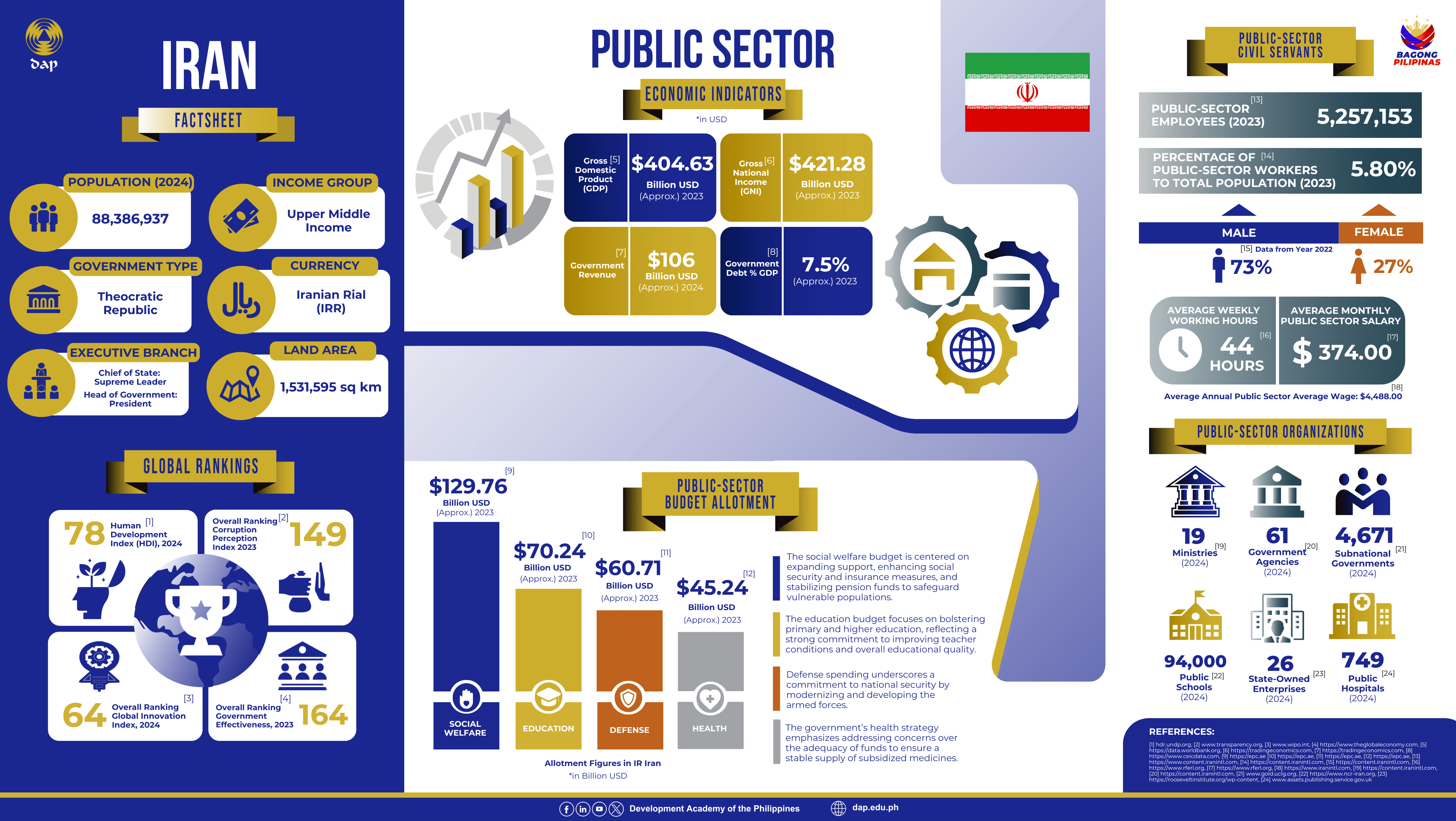
According to the World Bank’s Iran Overview, the country ranks second globally for natural gas reserves and fourth for proven crude oil reserves, yet its government remains vulnerable to external shocks such as sanctions and commodity price volatility. Iran is classified as an upper‐middle–income country with a population of approximately 88 million, and its executive authority is shared between the President and the Supreme Leader.
Despite a recent economic rebound—fueled by post-pandemic recovery in services, increased activity in the oil sector, and adaptive policy measures—Iran’s fiscal balance continues to face pressure from high inflation and the ongoing need for expansive cash transfers and subsidies. Their new five-year development plan under preparation aims to build a resilient economy, advance science and technology, and promote cultural excellence, with reforms targeting state-owned enterprises and the financial and banking sectors to optimize oil revenue management.
By examining these economic indicators, fiscal allocations, and civil service compositions, the DAP delivers actionable insights into Iran’s public sector, offering a data-driven foundation for promoting sustainable, inclusive, and effective public management.